# 1. Background
## 1.1 Vectorization
- 一次性地 对多对操作数执行一个操作。
## 1.2 SIMD
- 一类 CPU 指令,允许处理器同时对多个 data points 执行相同的操作。
- 所有主流的 ISAs 都有 microarchitecture 支持 SIMD 操作
- **x86**:MMX,SSE,SSE2,SSE3, SSE4,AVX,AVX2,AVX512
- **PowerPC**:Altivec
- **ARM**:NEON,[SVE](https://developer.arm.com/documentation/100891/0606/sve-overview/introducing-sve)
- **RISC-V**:[RVV](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-v-spec)
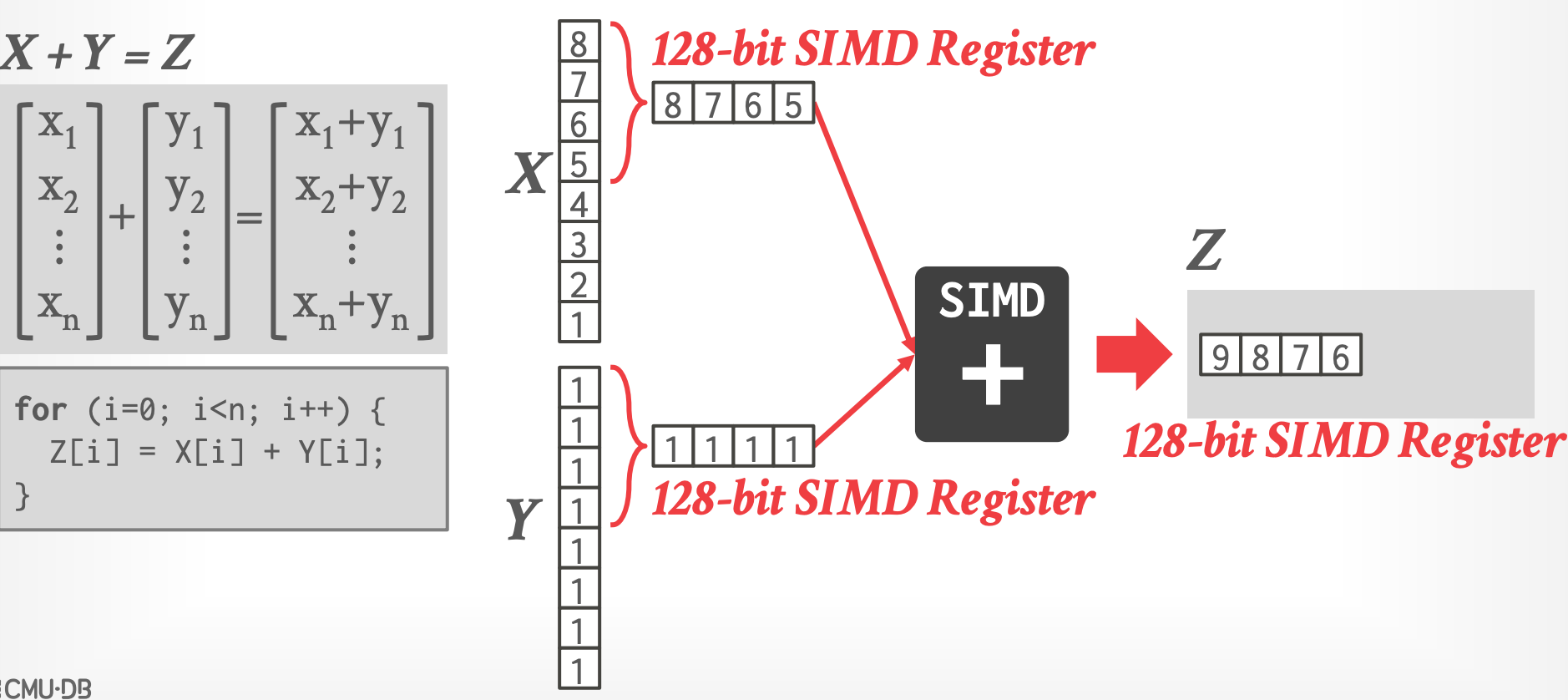
- **Example**
- 
## 1.3 Vectorization Direction
1. **Horizontal**
- 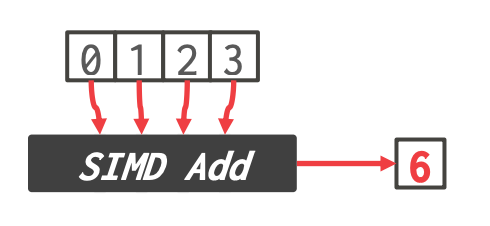
- 对一个 vector 中的所有元素执行操作
2. **Vertiacal** (更常见) ^7ab6af
- 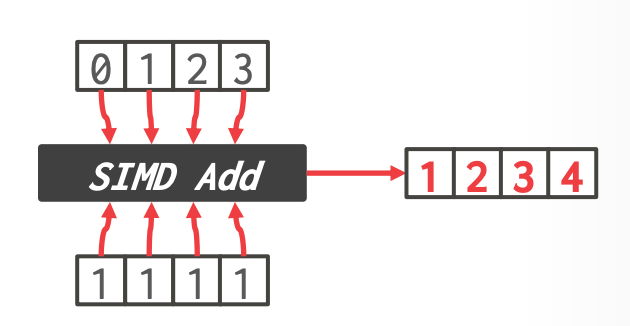
- elementwise operation,并行对每个 vector 相同位置的元素执行操作
> Source: [PRZEMYSŁAW KARPIŃSKI](https://gain-performance.com/2017/05/01/umesimd-tutorial-2-calculation/)
## 1.4 SIMD Instructions
- **Data Movement**
- 将 data move in / out 到 vector registers
- **Arithmetic Operations**
- 在多个 data items(如 2 doubles,4 floats,16 bytes)上执行操作
- 例子:ADD,SUB,MUL,DIV,SQRT,MAX,MIN
- **Logical Operations**
- AND,OR,XOR,ANDN,ANDPS,ANDNPS
- **Comparsion Instructions**
- $==, <, <=, >, >=, !=$
- **Shuffle instructions**
- Move data between SIMD registers
- **Miscellaneous**
- Conversion:在 x86 和 SIMD registers 间转换数据
- Cache control:从 SIMD registers 直接到内存(bypassing CPU cache)
### Intel SIMD Extensions
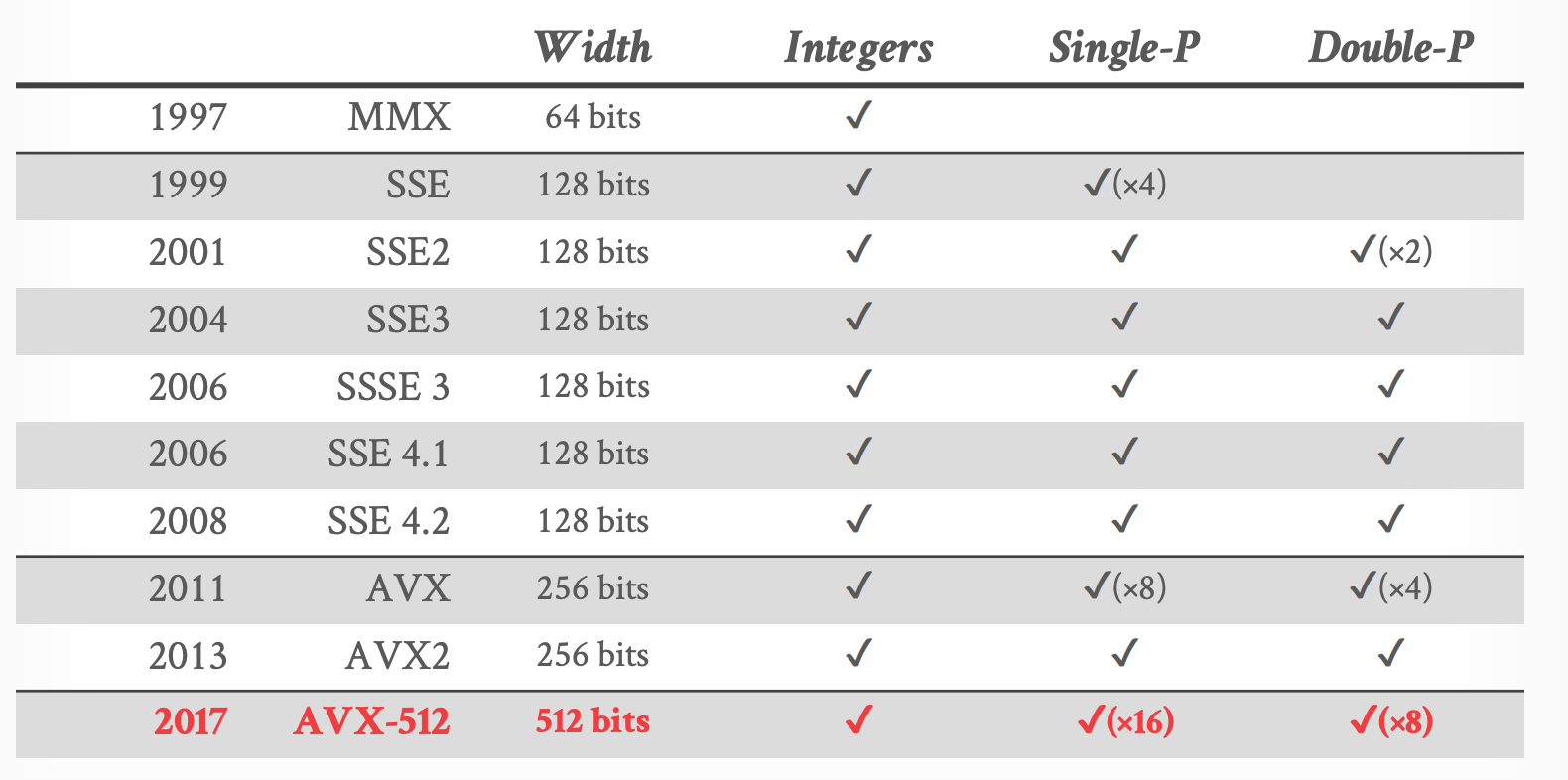
- 来源: [James Reinders](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_OJmxi4-twY)
## 1.5 SIMD Trade-Offs
- **Advantages**
- 如果算法可以向量化,可以显著提升性能和资源利用率
- **Disadvantages**
- 使用 SIMD 实现算法大多数是手动进行
- SIMD 可能对 data alignment 有限制
- Gathering data into SIMD registers,以及 scattering 到正确的位置,是棘手的,也可能是低效的。 ***(AVX-512 不再适用此条)***
## 1.6 AVX-512
- Intel 对 AVX2 指令的 512 位 扩展
- 还提供了新的操作来支持 data conversions、scatter 和 permutations
- 不同的 CPU 对 AVX-512 的支持情况不一样。
- 拆分成了不同的 groups,CPU 可以选择支持哪些组
- 基础组:AVX-512F
----------
# 2. Implementation
- 三种选择:
1. **Automatic Vectorization**
2. **Compiler Hints**
3. **Explicit Vectorization**
## 2.1 Automatic Vectorization
- Compiler 可以识别何时将循环内的指令重写为向量化操作
- 对于简单的循环可以奏效,database 的 operators 很少可以自动向量化
```cpp
void add(int *X, int *Y, int *Z) {
for (int i=0; i<MAX; i++) {
Z[i] = X[i] + Y[i];
}
}
```
- 无法自动向量化:因为 `Z`,`X`,`Y` 可能指向相同的地址。
## 2.2 Compiler Hints
- 给 compiler 提供额外的信息,告诉它可以安全地进行向量化。
- 两种方式:
- 提供关于 memory locations 的额外信息
- 告诉 compiler 忽略 vector 依赖
- C++ 中的 **restrict** 关键字告诉 compiler : arrays 的内存位置不同
```cpp
void add(int *restrict X, int *restrict Y, int *restrict Z) {
for (int i=0; i<MAX; i++) {
Z[i] = X[i] + Y[i];
}
}
```
- 使用 **pragma** 告诉 compiler 忽略 vectors 的循环依赖。
```cpp
void add(int *X, int *Y, int *Z) {
#pragma ivdep
for (int i=0; i<MAX; i++) {
Z[i] = X[i] + Y[i];
}
}
```
## 2.3 Explicit Vectorization
- 不能跨 CPU(ISAs / verisions)移植
- SIMD 指令的封装库:
- [Google Highway](https://github.com/google/highway)
- [Simd](https://ermig1979.github.io/Simd/)
- [Expressive Vector Engine](https://jfalcou.github.io/eve/)
- [std::simd](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/simd/index.html) (Experimental)
-----------------
# 3. SIMD Fundamentals
- 一些基础的 SIMD 操作,DBMS 可以使用它们来构建更复杂的功能:
- Masking
- Permute
- Selective Load / Store
- Compress / Expand
- Selective Gather / Scatter
- [Make the most out of your SIMD investments: counter control flow divergence in compiled query pipelines](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3211922.3211928)
## 3.1 SIMD Masking
- 大多数的 AVX-512 操作都支持 **predication** 变种
- 只对 input bitmask 指定的 lanes 上执行操作。
- 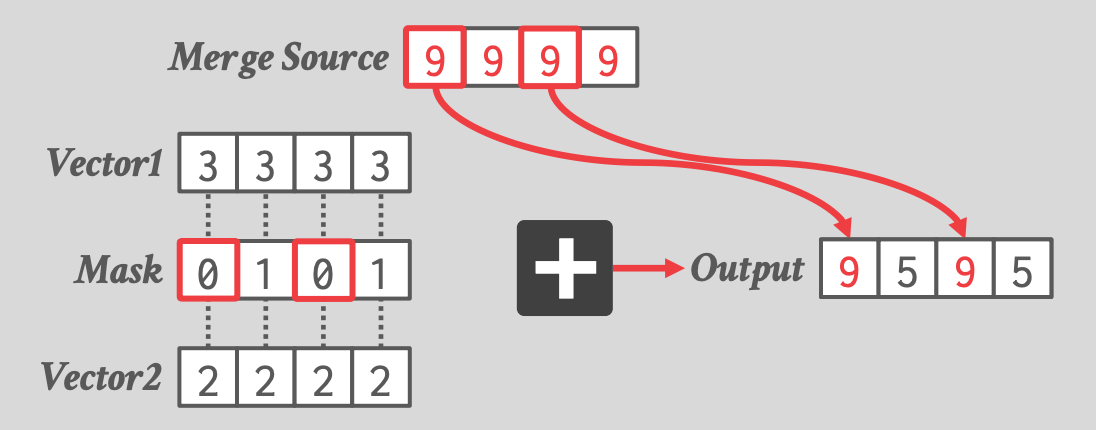
- 1 对应的位置执行操作(Add)
- 0 对应的位置从 Merge Source 拷贝
- 原子地完成上述操作
- 本例是一个 Merge Version,还有一个 Zero Version
## 3.2 Permute
- 根据一个 offset / index vector,将 input vector 中的 values 拷贝到 output vector。
- 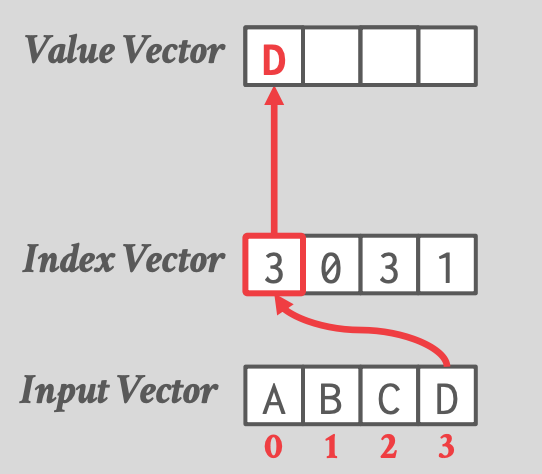
- AVX-512 以前,DBMS 必须将 SIMD register 的数据写入内存,再写回 SIMD register。
## 3.3 Selective Load / Store
- Selective Load
- 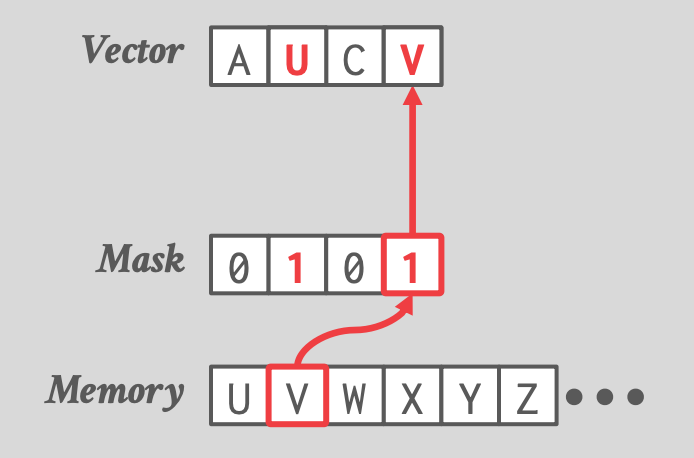
- Mask 位置对应 Vector 的位置,两个 1 表示从内存加载前两个字节
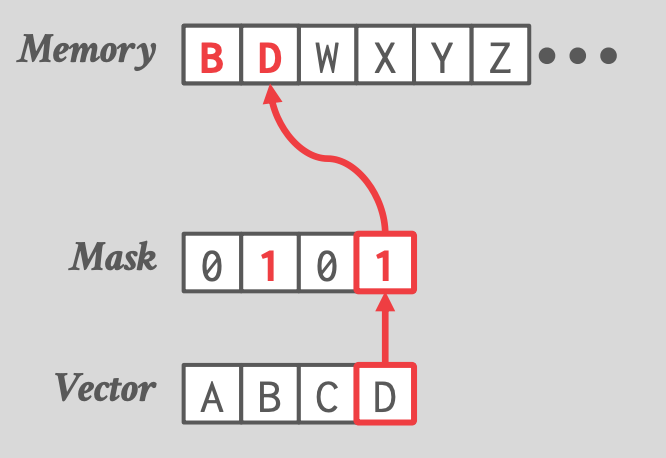
- Selective Store
- 
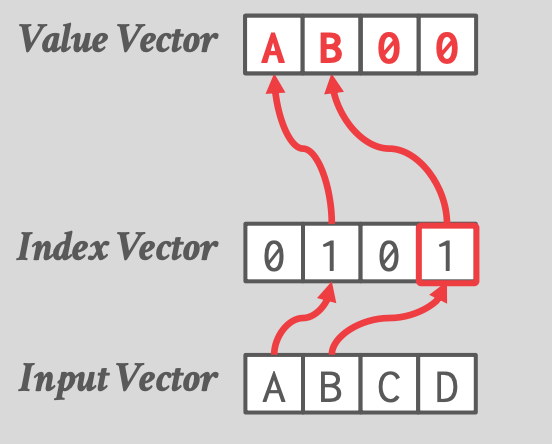
## 3.4 Compress / Expand
- Compress
- 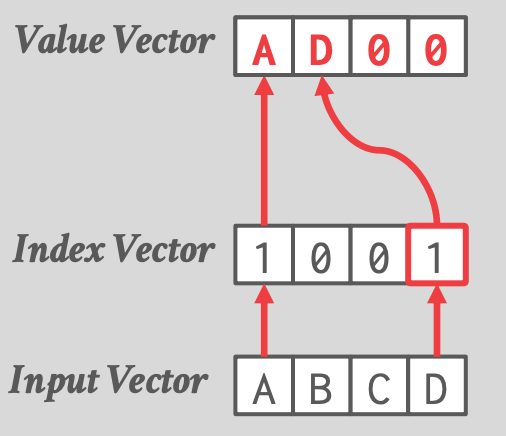
- 使用场景:selective scan,1 表示 predicate 为 true
- Expand
- 
## 3.5 Selective Scatter / Gather
- Selective Scatter
- 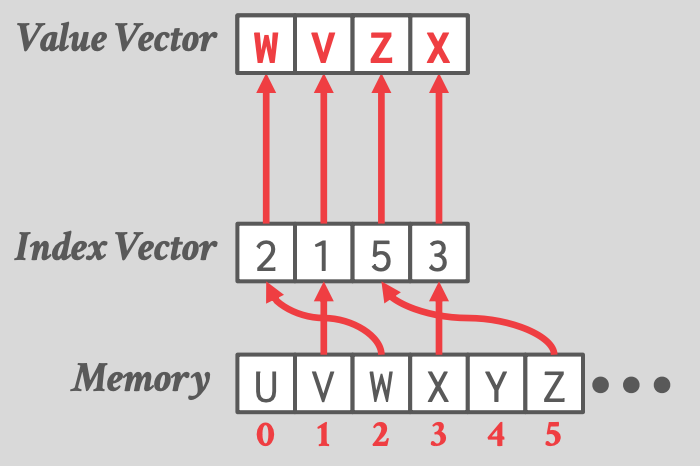
- Index Vector:读取内存中的哪些位置
- Selective Gather
- 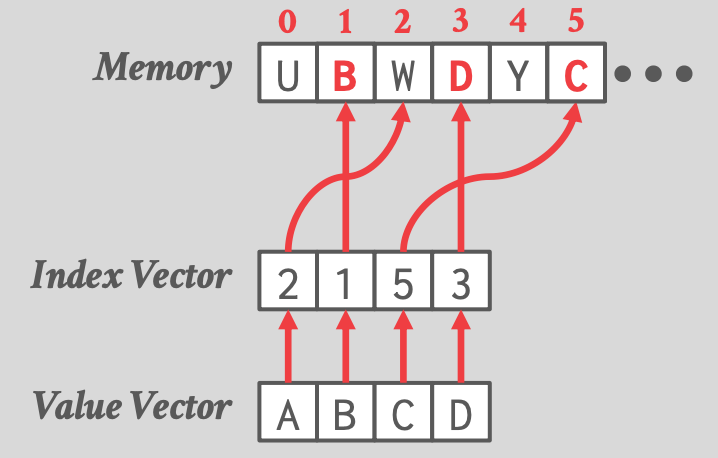
- 写入到内存中的哪些位置
----------
# 4. Vectorized DBMS Alogrithms
- 使用 fundamental vector operations 来构建更高级功能时的原则:
- 倾向使用 [[08-vectorized-execution#^7ab6af|vecrtial vectorization]],每个 lane 的输入数据不同
- Vectorized Operators:
- Selection Scans
- Hash Tables
- Partitioning / Histograms
- Paper: [Rethinking SIMD Vectorization for In-Memory Databases](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/2723372.2747645)
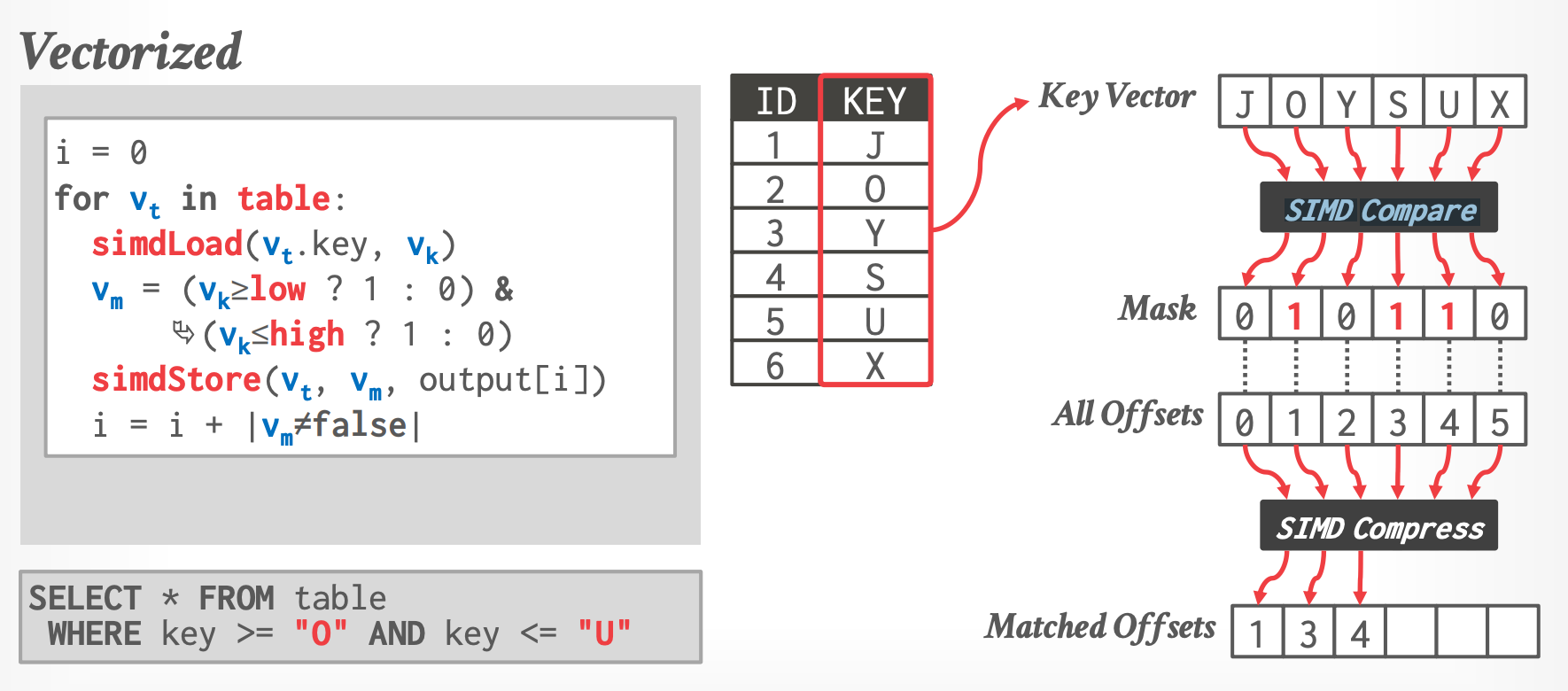
## 4.1 Selection Scans
- 
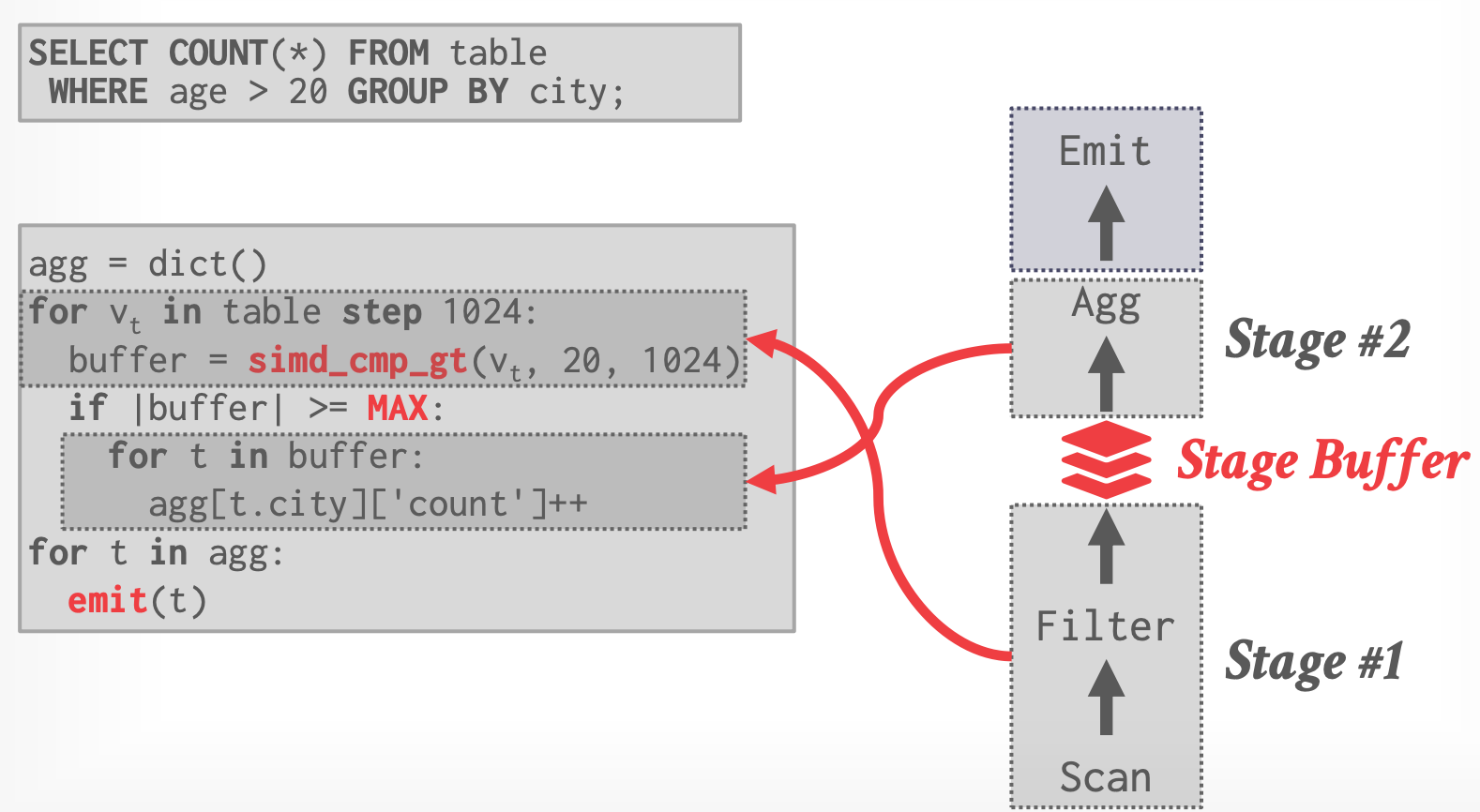
## 4.2 Relaxed Operator Fusion
- 对于每个 batch,SIMD vectors 里可能包含了不再有效的 tuples。
- Relaxed Operator Fusion
- 在 pipeline 之间增加 stage buffer,buffer 满了再传递给下一个 stage
- 
- ROF Software Prefetching
- DBMS 告诉 CPU 来 prefetch next vector
## 4.3 Hash Tables
- build side 很难加速,因为都是 random lookups
### Vectorized(Horizontal)Probing
- 一个 input key 同时跟多个 key 比较
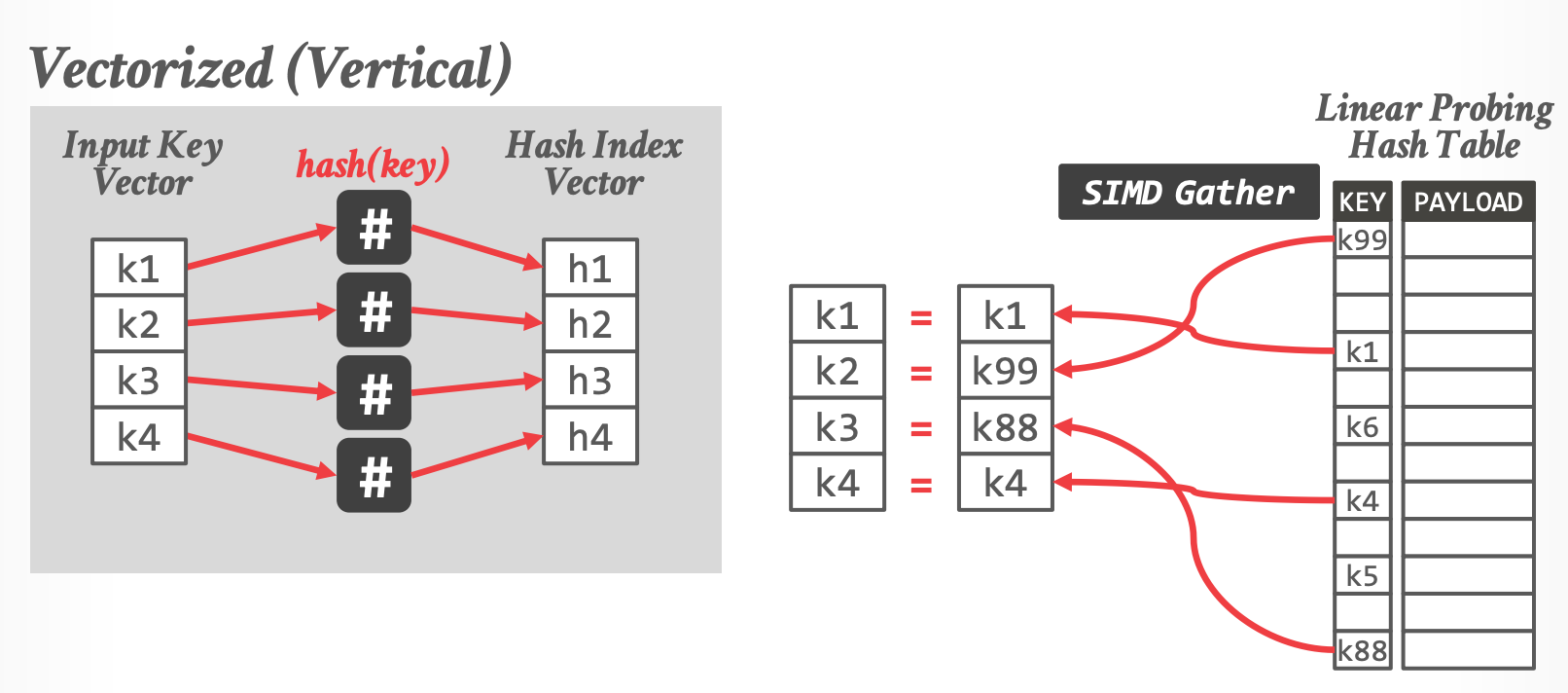
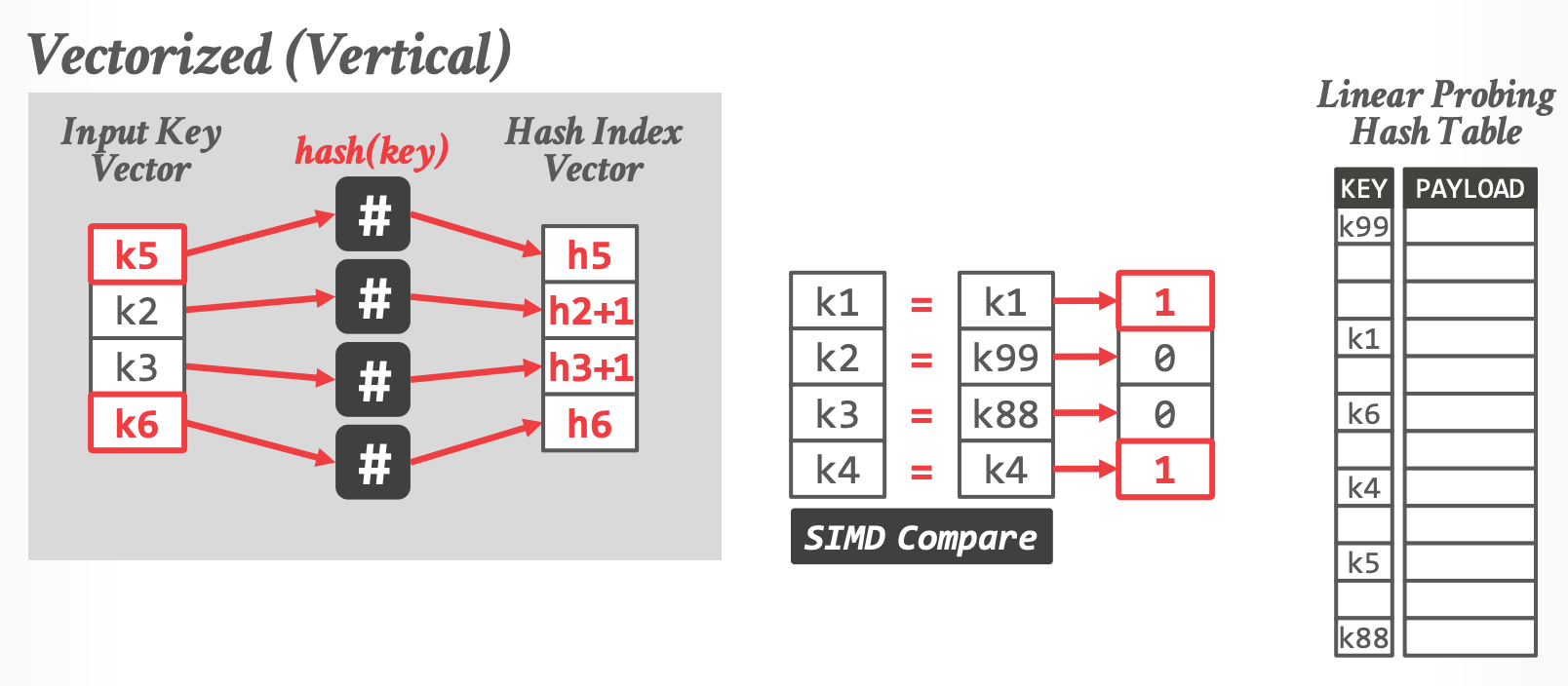
### Vectorized(Vertical)Probing
- 同时比较多个 input key
- 
- 
- 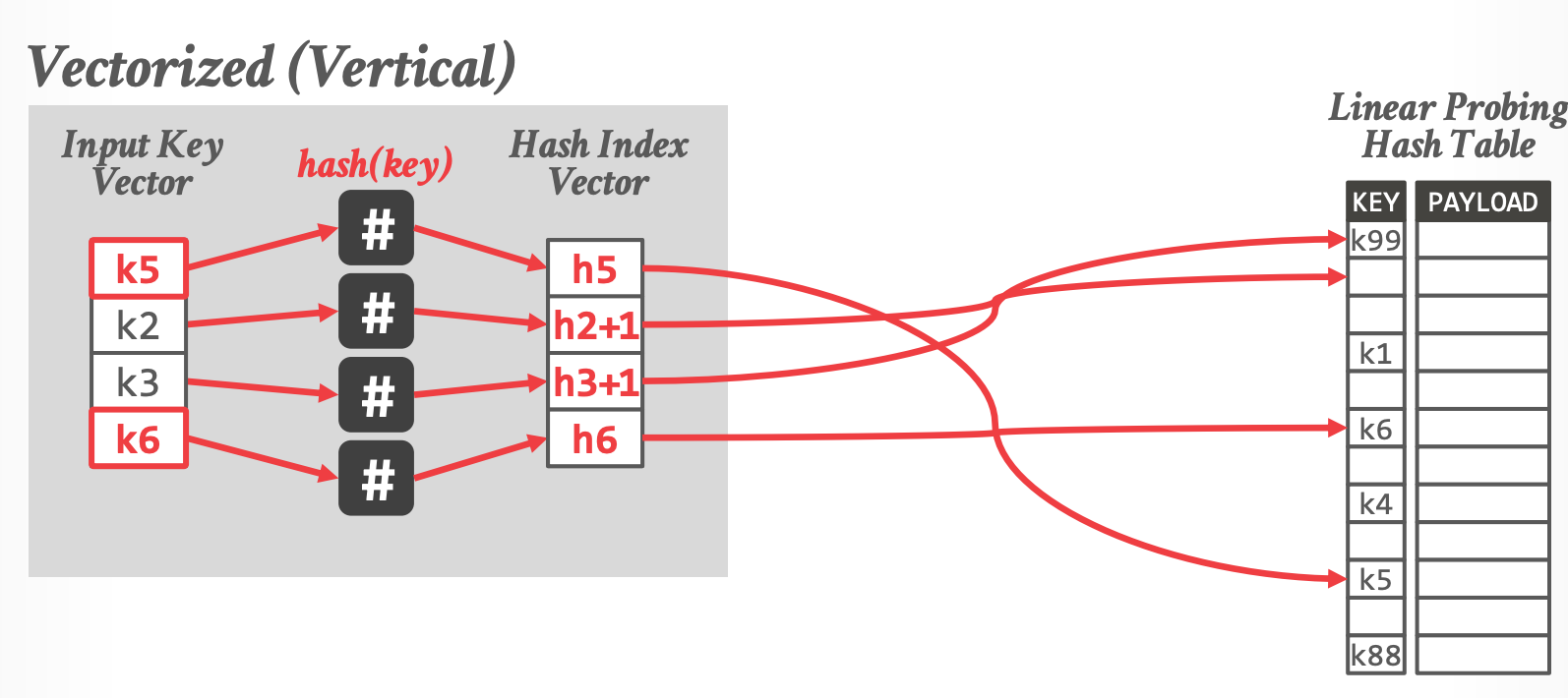
- k1, k4 已经匹配,k2, k3 需要继续liner probing(直到遇到空位置才算失败)
- 读入新 input,填充 k1,k4
- **问题**:gather 是随机读取,CPU cache 利用率低
- 如果 Hashtable 很大(大于 L3 Cache),SIMD 无法起到加速作用
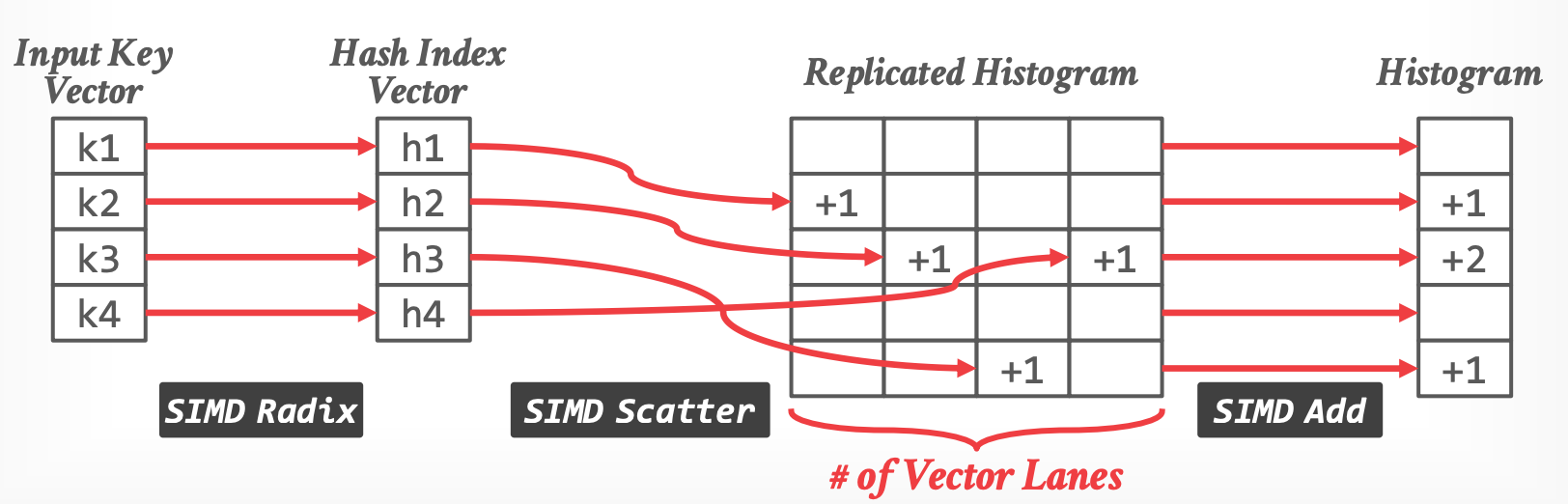
## 4.4 Partitioning - Histogram
- 使用 scatter 和 gather 来增加 counts(key 的出现次数)
- 处理冲突:Replicate the histogram
- 
-------
# Caveat Emptor
- AVX-512 并不总是快于 AVX2。
- 一些 CPU 当切换到 AVX-512 模式时会对 clockspeed 进行降级
- 因此 compilers 倾向于使用 256 位 SIMD 操作
- stack overflow: [SIMD instructions lowering CPU frequency](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/56852812/simd-instructions-lowering-cpu-frequency)
------------
# Parting Thoughts
- 向量化对于 OLAP 查询很有必要。
- 我们可以结合所有的 intra-query parallelism 一起使用
- 多个线程处理同一个 query
- 每个线程可以执行一个 compiled plan
- compiled plan 可以调用 vectorized operations