# 1. Background
## 1.1 Parallel Join Algorithms
- 只考虑两表 Join
- 两种主要方式:
- Hash Join
- Sort-Merge Join
- 不考虑 nested-loop joins,因此 OLAP DBMS 很少使用
### Observation
- 许多 OLTP DBMS 没有实现 hash join。
- 但是 index nested-loop join 在概念上等同于 hash join
- index nested-loop join 使用一个已经存在的 B+ Tree
- Hash join 将会在操作过程中动态地构建一个哈希表(索引),并在操作完成后立即丢弃。
## 1.2 Hashing VS. Sorting Joins
- **1970s**:倾向于 Sorting(内存小,使用 external merge sort)
- **1980s**:倾向于 Hashing
- 出现 spillable 的 hash 算法
- 可以实现 hash join 的 database machines
- **1990s**:Equivalent
- **2000s**:Hashing
- **2010s**:Hashing(Partitioned vs. Non-Partitioned)
- **2020s**:Non-Partitioned Hashing
## 1.3 Parallel Join Algorithm Papers
- [Sort vs. Hash revisited: fast join implementation on modern multi-core CPUs](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.14778/1687553.1687564)
- VLDB 2009, By ORACLE 和 Intel
- Hashing 比 Sort-Merge 快
- 认为 wider SIMD(AVX512)出现,Sort-Merge 更快
- [Design and evaluation of main memory hash join algorithms for multi-core CPUs](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1989323.1989328)
- SIGMOD 2011
- Partitioning 与 Non-Partitioning Hash-Join 之间的权衡
- [Massively parallel sort-merge joins in main memory multi-core database systems](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.14778/2336664.2336678)
- VLDB 2012, Hyper
- Sort-Merge 已经比 Hashing 快,即使不使用 SIMD
- [Massively Parallel NUMA-aware Hash Joins](https://imdm.ws/2013/papers/Lang.pdf)
- IMDM 2013,Hyper
> Ignore what we said last year. You really want to use Hashing!
- [Main-memory hash joins on multi-core CPUs: Tuning to the underlying hardware](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1109/ICDE.2013.6544839)
- ICDE 2013
- 对 Radix Hash Join 的新的优化
- [An Experimental Comparison of Thirteen Relational Equi-Joins in Main Memory](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/2882903.2882917)
- SIGMOD 2016
- Non-Partitioning Hashing 更优
- [To Partition, or Not to Partition, That is the Join Question in a Real System]()
- SIGMOD 2021,UMBRA
- Benefits of Radix Hash Join aren't worth engineering costs
## 1.4 Join Algorithm Design Goals
- **目标一:Minimize Synchronization**
- 执行时避免获取 latches
- **目标二:Minimize Memory Access Cost**
- 确保数据对于 worker thread 是 local 的
- 重用存在于CPU缓存中的数据
- 不管 Join 算法是 hardware-conscious 还是 hardware-oblivious 的,这些目标都很重要
### Improving Cache Behavior
- DBMS 中影响 cache misses 的因素
- Cache 和 TLB 的容量
- Locality(时间和空间)
- **Non-Random Access(Scan)**
- Clustering data to a cache line.
- Execute more operations per cache line.
- Cache by-pass
- **Random Access(Lookups)**
- Partition data to fit in cache + TLB
---------
# 2. Parallel Hash Join
- 利用多个核心加速 DBMS Join 算法非常重要
- 期望保持所有核心繁忙,而不要变为 memory bound。
## 2.1 Hash Join (R⨝S)
1. **Partition(可选)**
- 将 R 和 S 的 tuples 拆分成不相交的子集(使用对 join key 的 hash 函数)
2. **Build**
- Scan 表 R,按 join key 创建 hash table
3. **Probe**
- 对于 S 中的每个 tuple,在 hash table 中查询它的 join key
- 如果找到匹配的,输出 combined tuple
## 2.2 Partitioning Phase
- **Implict & Expilcit Partitioning**
- **方式一: Implicit Partitioning**
- 数据加载到 Database 中时,已经按照 join key 做好了分区
- **方式二:Explicit Partitioning**
- 只拆分 outer relation,重新分配到不同的 CPU cores 上
- 通过对 tuple 的 join key 进行 hash 将 input relations 拆分到不同的 partitioned buffers 中
- 理想下,partitioning 的开销小于 build 阶段 cache misses 的开销
- 有时称为 **Grace Hahs Join** / **Radix Hashing Join**
- buffers 中的内容取决于 storage model:
- **NSM**:通常是整个 tuple
- **DSM**:只有 join 需要的列和 offset
- **Non-Blocking & Blocking Partitioning**
- **方式一:Non-Blocking Partitioning**
- 只扫描 input relation 一次
- 增量地产生输出,同时让其他线程构建 hash table
- **方式二:Blocking Partitioning(Radix)**
- 扫描 input relation 多次
- Only materialize results all at once.
- 有时称为 **radix hash join**
### 2.2.1 Non-Blocking Partitioning
- 只scan input relation 一次,并即时生成输出(generate the output on-the-fly)
- **方式一:Shared Partitions**
- 所有线程都更新一个 global partitions set
- 多线程之间必须使用 latch 来同步
- **方式二:Private Partitions**
- 每个线程有自己的 partitions set
- 所有线程完成后必须进行 consolide(合并)操作。
#### Shared Partitions

- 优势:容易实现
- 劣势:更新相同 partition 时存在冲突竞争
#### Private Partitions
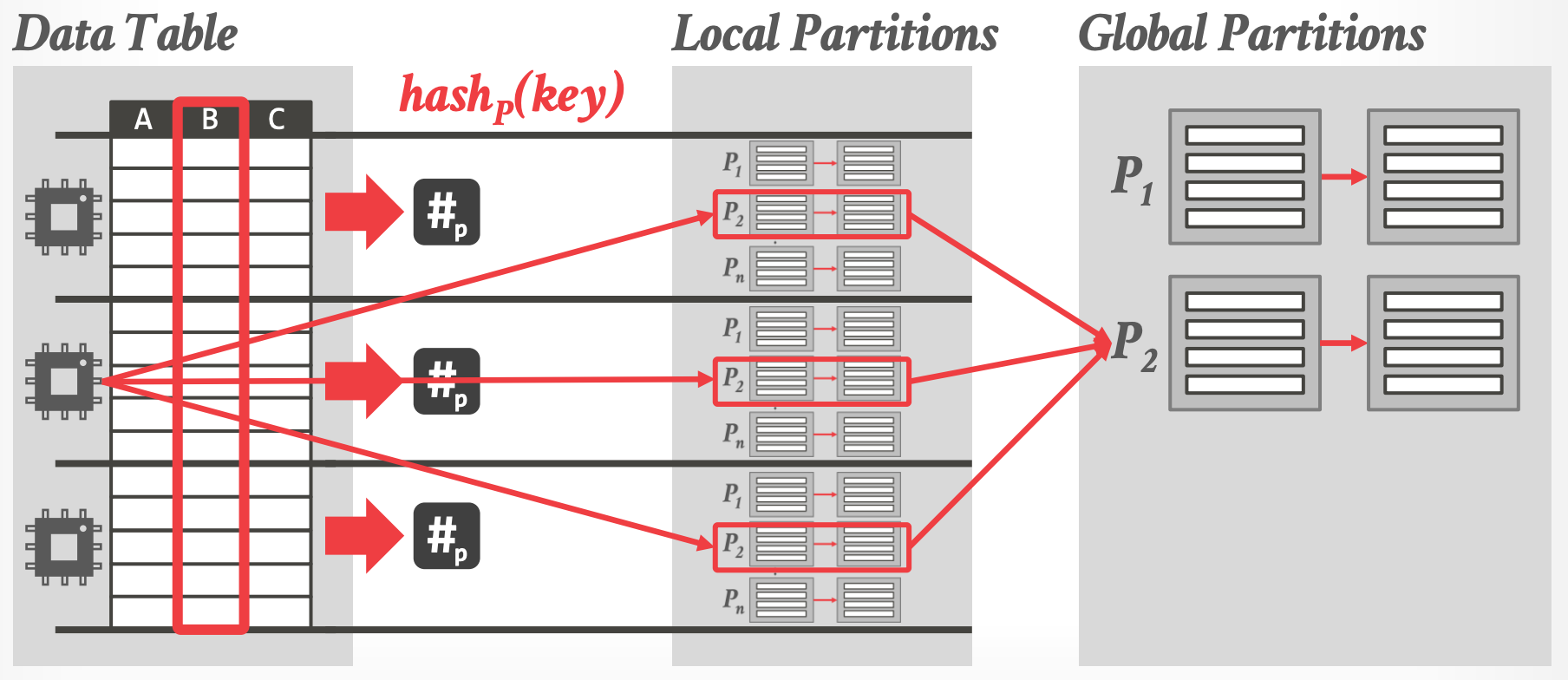
### 2.2.2 Radix Partitioning
- 多次 Scan input relation 来生成 partitions
- [Main-Memory Hash Joins on Multi-Core CPUs: Tuning to the Underlying Hardware](https://15721.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2016/papers/balkesen-icde2013.pdf)
- Two-pass 算法:
1. Scan R and compute a histogram of the # of tuples per hash key for the radix at some offset.
2. Use this histogram to determine per-thread output offsets by computing the prefix sum. (每个线程写入到哪里)
3. Scan R again and partition them according to the hash key.
#### Radix
- 一个 key 的 radix 是在某个位数上的整数值(使用它的进制)
- 使用位移和乘法可以很高效地计算
- 计算每个 key 的 radix,然后为每个 radix 生成关于 count 的直方图
- 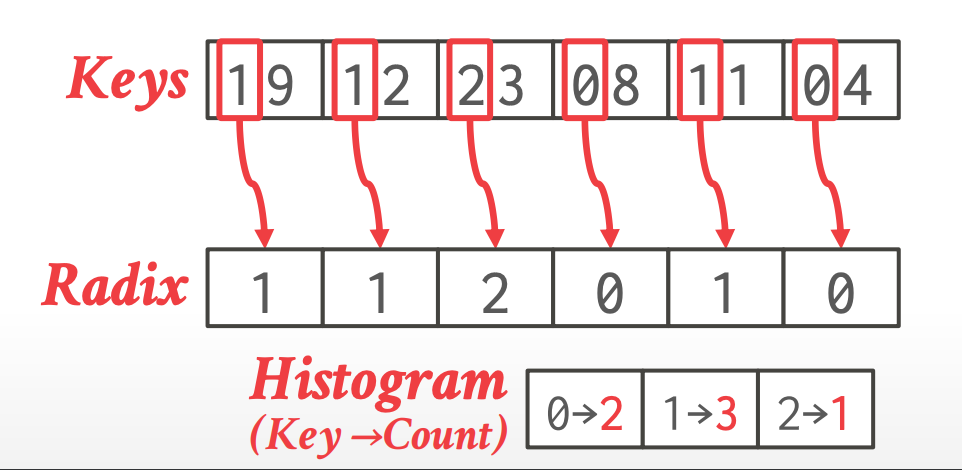
- Keys:原始 key 的 hash 值
#### Prefix Sum
- 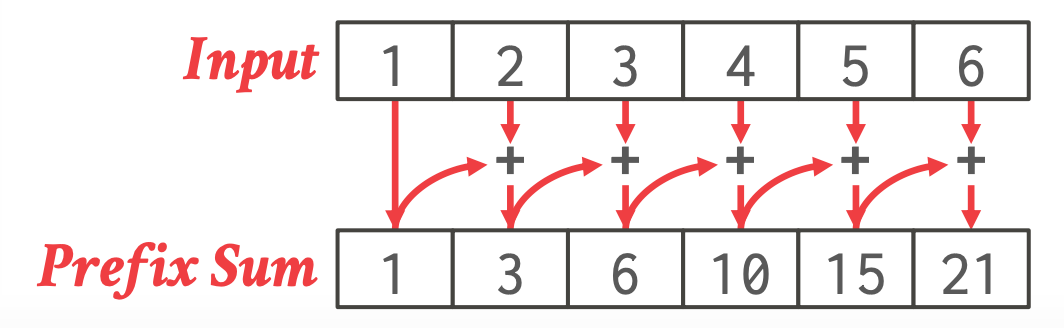
- 该 offset 和之前所有 input 的累加
- 根据直方图的 prefix sum 来确定写入的位置
#### Radix Partitions
1. 检查输入,创建直方图
2. 计算 output offsets

3. 读取输入,进行分区
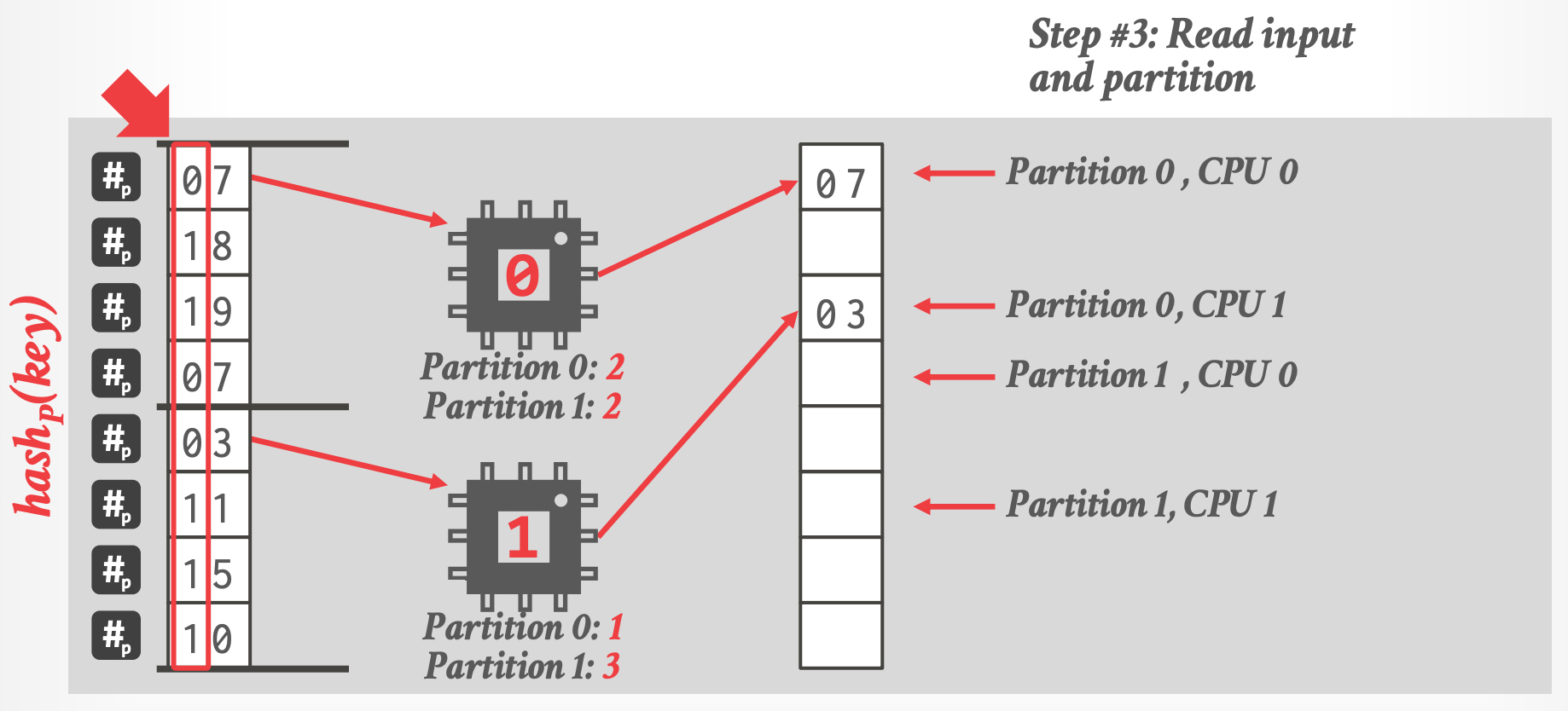
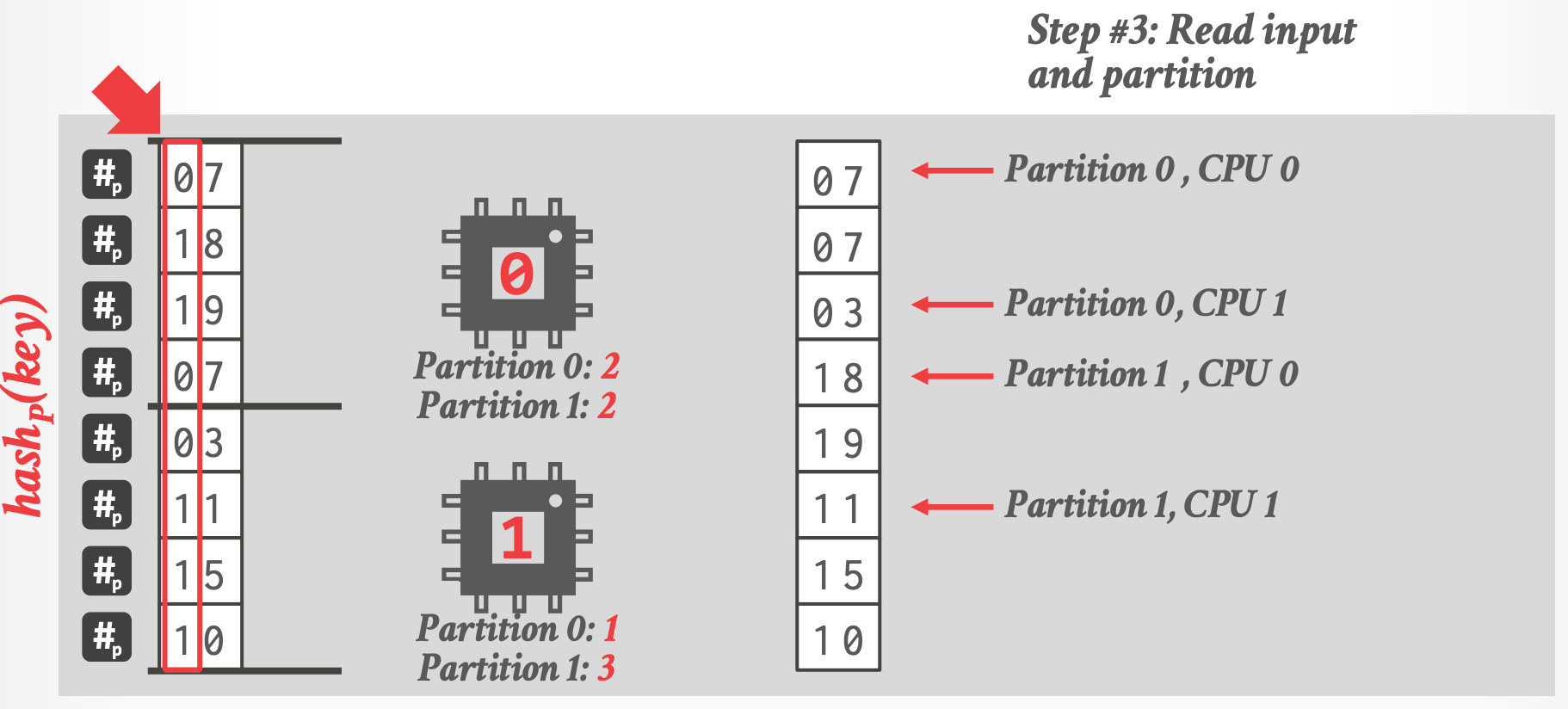
- 最后的分区结果:
- 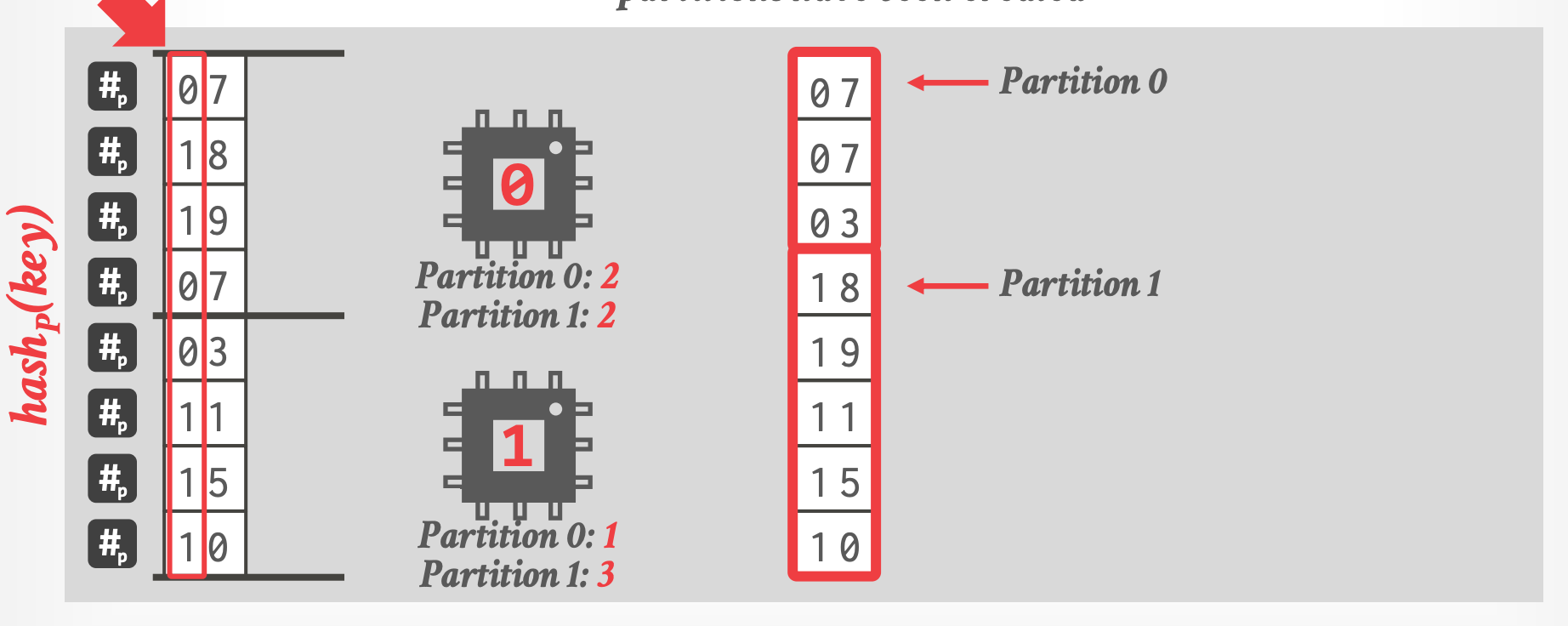
- CPU 0 负责 Partition 0, CPU 1 负责 Partition 1
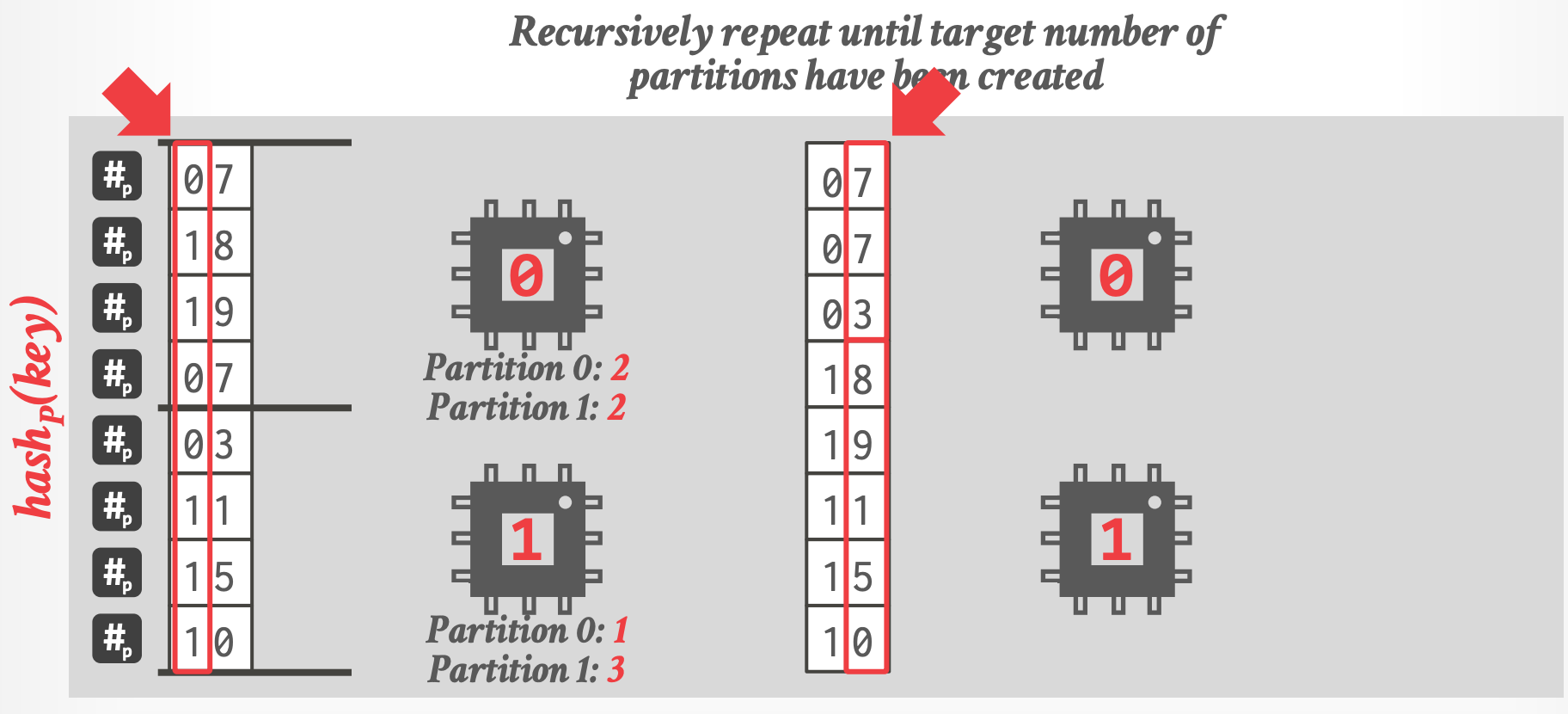
- Recursively repeat until target number of partitions have been created
- 
#### Optimizations
- [On the surprising difficulty of simple things: the case of radix partitioning](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.14778/2777598.2777602)
- **Software Write Combine Buffers**
- 每个 worker 维护 local output buffer 来暂存写入
- 当 buffer 满了后,写入到 global parititon
- 类似 private paritions,但是没有单独的结尾合并阶段
- **Non-temporal Streaming Writes**
- 写入 global paritition memory 时,采取 bypass CPU caches
## 2.3 Build Phase
- Threads 扫描 R 的 tuples 或者 partitions
- 对于每个 tuple,按 join key 计算 hash,添加到 hash table 对应的 bucket 中
- buckets 的大小应该只有几个 cache lines
-------------
# 3. Hash Functions
- hash table 有两个组件:
- **Hash Function**
- 将一个巨大的 key space 映射到一个小的值域
- 速度和冲突概率之间的权衡(fast vs. collision rate)
- **Hashing Scheme**
- 如何处理 key 冲突
- 权衡:allocating a large hash table vs. additional instructions to find/insert keys.
- hash 函数的目标:快速且冲突率低
- **速度最快**:永远返回 1
- **冲突率最低**:Perfect hashing
- hash 函数 benchmark:[SMHasher](https://github.com/aappleby/smhasher)
## 3.1 Hash Functions
- [**CRC-64**](https://create.stephan-brumme.com/crc32/)(1975)
- 使用网络纠错
- **MurmurHash**(2008)
- 设计目标是快,通用的 hash 函数
- [**Google CityHash**](https://github.com/google/cityhash)(2011)
- 对于短 keys(小于 64 字节)的场景更快
- [**Facebook XXHash**](http://cyan4973.github.io/xxHash/)(2012)
- 来自 zstd 压缩的作者
- [**Google FarmHash**](https://github.com/google/farmhash)(2014)
- CityHash 的新版本,better collision rates
## 3.2 Benchmark
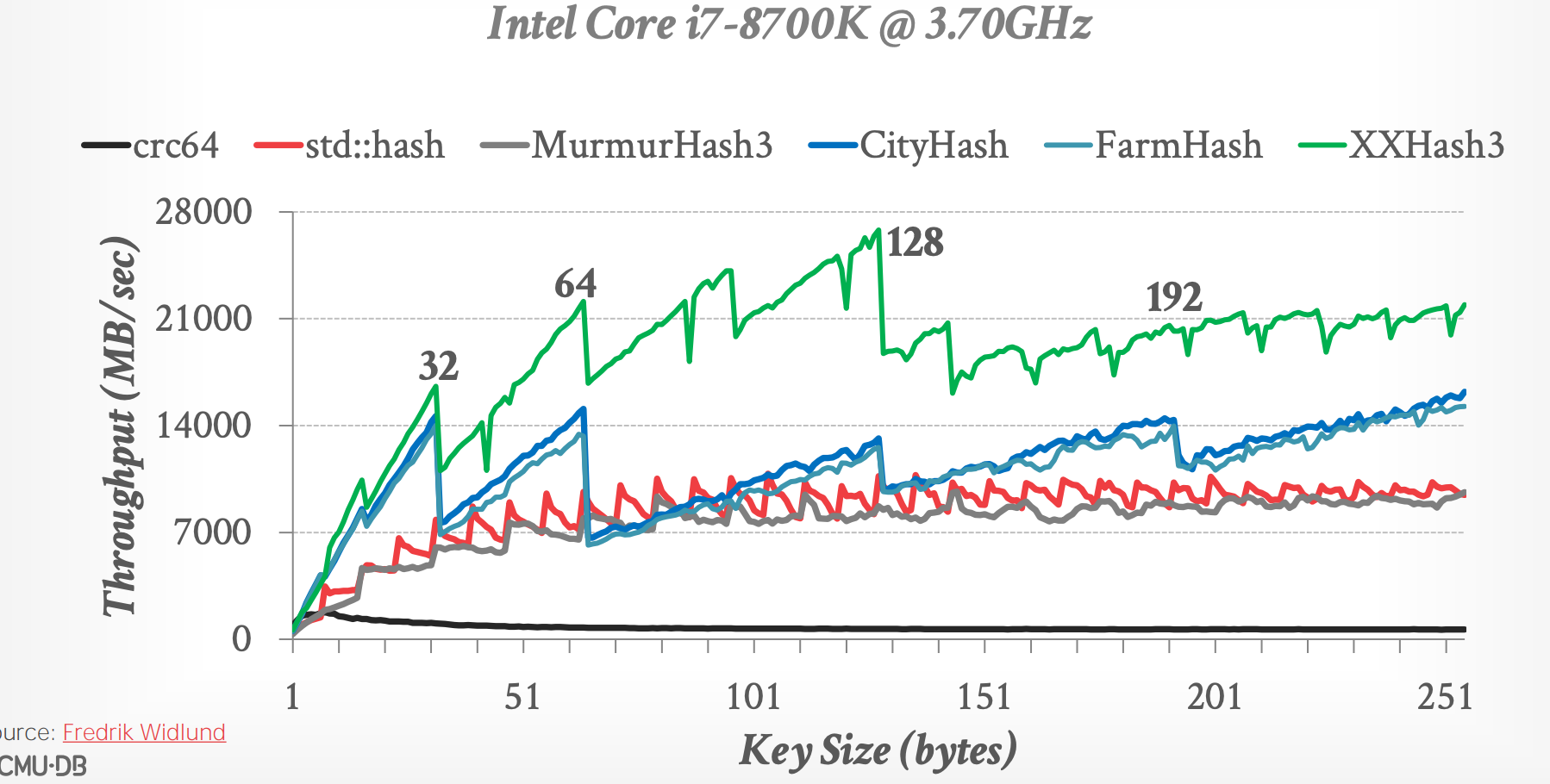
- [hash-function-benchmark](https://github.com/apavlo/hash-function-benchmark)
------------
# 4. Hashing Schemes
- 不同的方式:
- **Chained Hashing**
- **Linear Probe Hashing**
- **Robin Hood Hashing**
- **Hopscotch Hashing**
- **Cockoo Hashing**
## 4.1 Chained Hashing
- hash table 的每个 slot 维护一个 buckets 的链表
- 
## 4.2 Linear Probe Hashing
- single giant table of slots
- 遇到冲突后在 table 中搜索下一个 free slot
- 为了减少 build / probse 时多余的比较次数,避免冲突很重要,这需要 slots 足够多(2倍元素的数量)
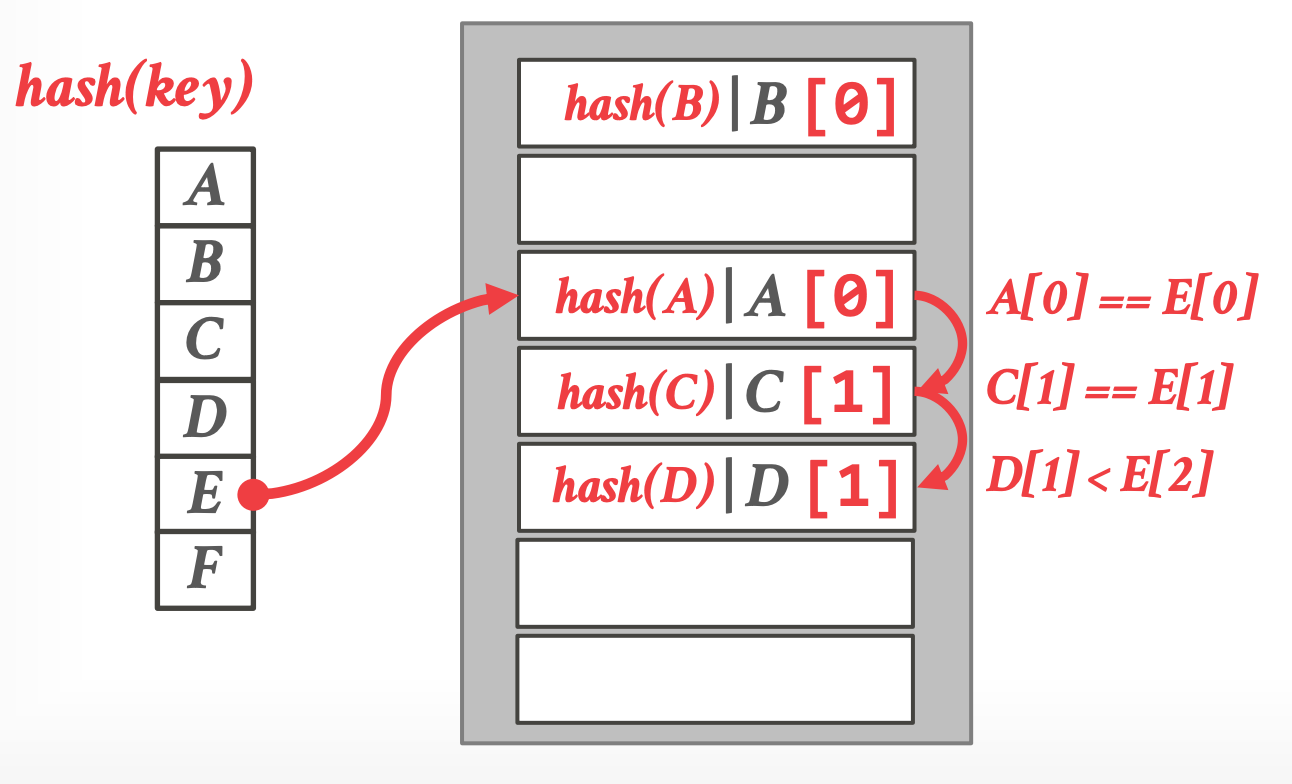
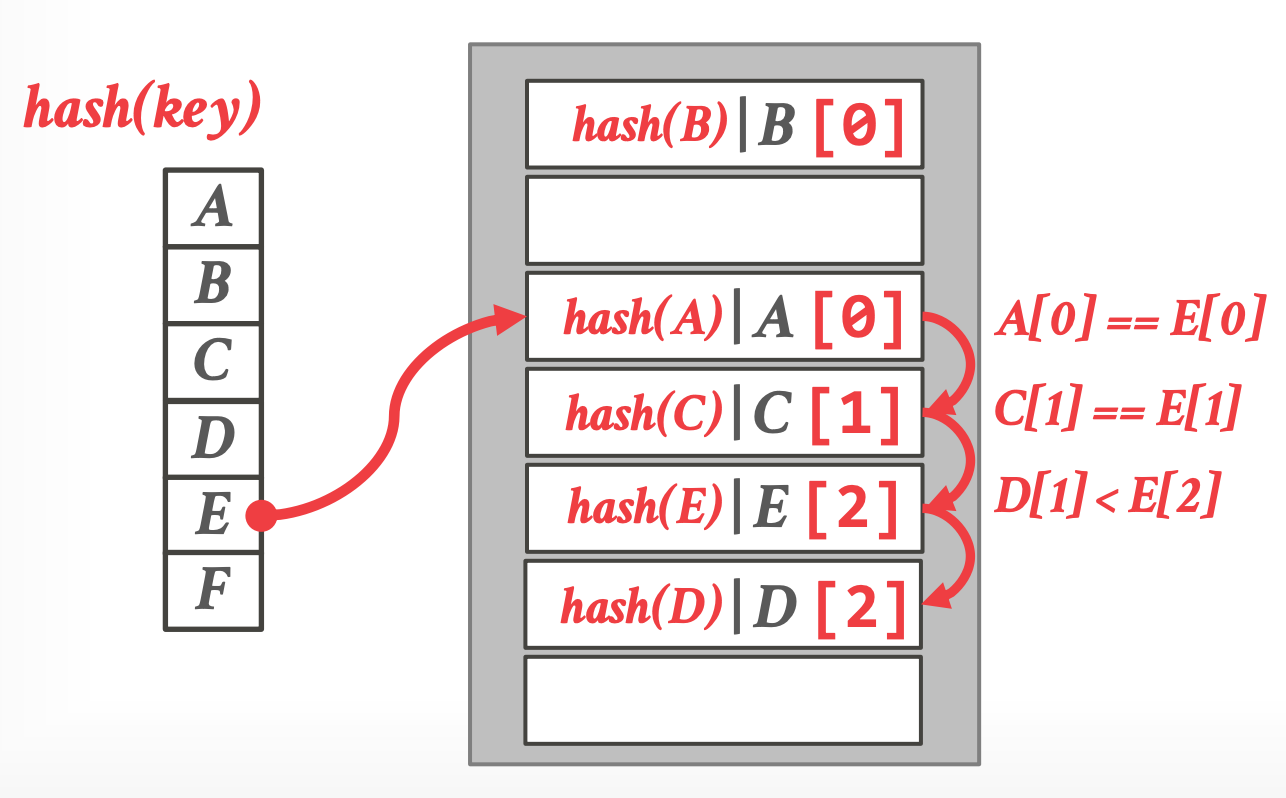
## 4.3 Robin Hood Hashing
- [Robin hood hashing](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4568152)
- linear probe hashing 的变种,从 rich keys 中窃取 slots 给 poor keys
- 每个 key 跟踪距离理想位置的距离
- 插入时,占据另外一个 key 的 slot,如果 insert key 距离理想位置更远
- 
- 
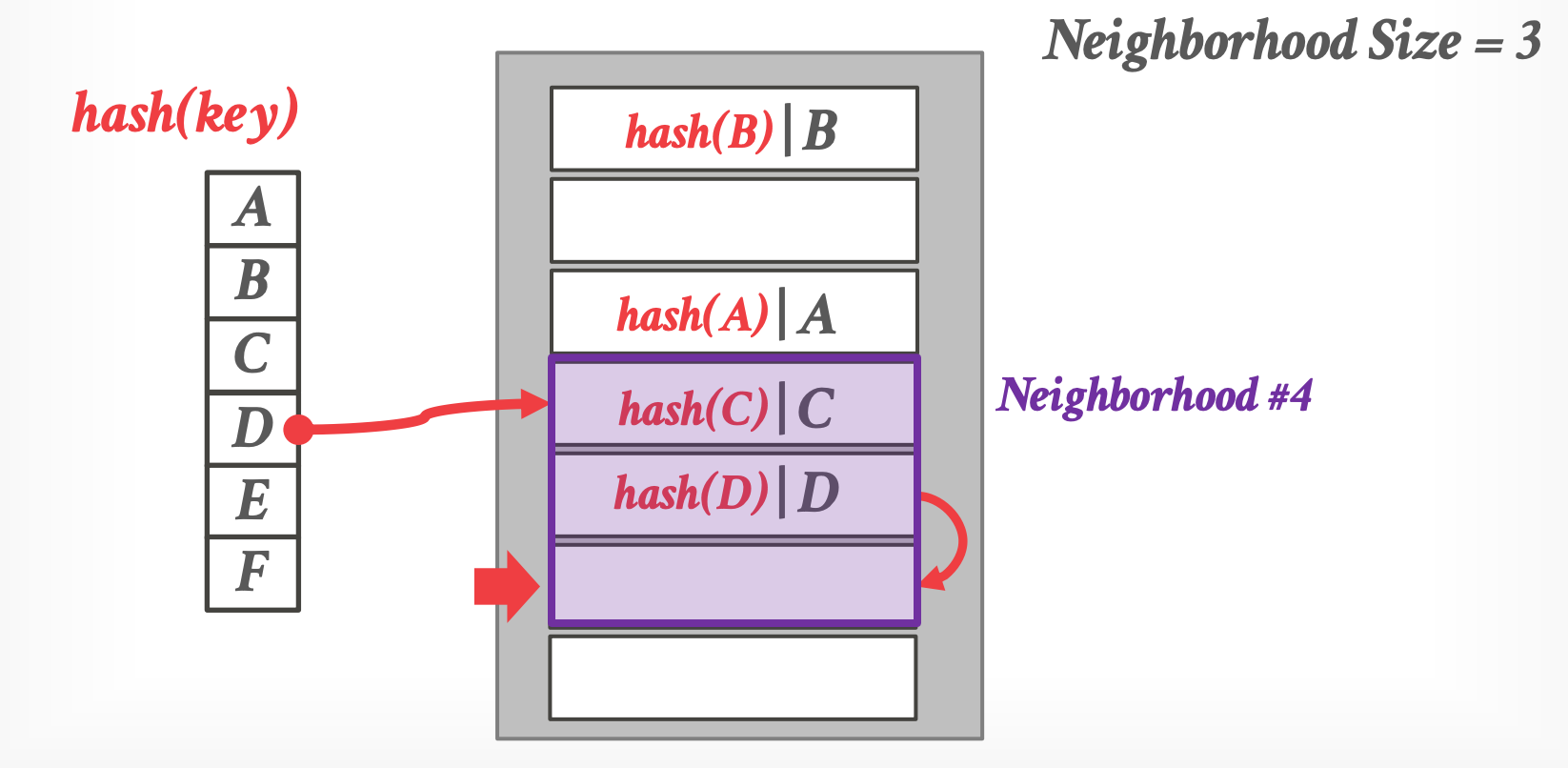
## 4.4 Hopscotch Hashing
- [Hopscotch Hashing](https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-540-87779-0_24)
- Linear probe 的变种,keys 可以 neighborhood 之间移动
- neighborhood:table 内的一段连续 slots 区间
- neighborhood 的长度是个可配置的常量(理想下是一个 cache-line)
- key 保证在它的 neighborhood 内,或则不存在
- 限定了查找一个 key 时最多就搜索 neighborhood 区间
- 
## 4.5 Cockoo Hashing
- 多个 tables(每个使用不同的 hash 函数)
- 插入时,检查每个 table,挑选空闲的 slot
- 如果 table 都没有 slot,从一个 table 中淘汰一个元素,rehash 到新的位置 (淘汰可能会重复进行多轮)
- 查询永远是 O(1) 的,因此每个 table 只搜索一个位置
-------------------
# 5. Probe Phase
## 5.1 Bloom Filter
- build 阶段同时构建一个 bloom filter
- probe hash table 前先检查 bloom filter
- 也称为 sideways information passing
----------
# 6. Benchmark
- [An Experimental Comparison of Thirteen Relational Equi-Joins in Main Memory]()
--------
# Parting Thoughts
- Partitioned-based joins 在大多数情况下优于 non-partitioning 算法,但是正确地 tune 它并不容易。
- 基本上,每个。DBMS 都会挑选一种 hash join 实现,不尝试做到 adaptive。