# 1. Background
- sort merge join 基本上都要比 hash join 差
- sort merge join 典型使用场景:
- join 后需要按 join key 排序(order by)
## 1.1 Sort-Merge Join (R⨝S)
- **Phase 1:Sort**
- 按照 join key(s) 排序 R 和 S 中的 tuples
- **Phase 2:Merge**
- 维护两个 iterators,比较两者指向的 tuples
## 1.2 Parallel Sort-Merge Joins
- Sorting 是最昂贵的部分。
- 尽可能正确利用硬件来加速
- 使用尽可能多的 CPU cores
- NUMA-aware
- SIMD
- [Multi-Core, Main-Memory Joins: Sort vs. Hash Revisited](https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol7/p85-balkesen.pdf)
- **Phase 1:Partitioning**(可选地)
- Partition R,分配到不同的 workers / cores
- 可以使用 radix partitioning
- **Phase 2:Sort**
- 按 join key 排序两个 relation
- **Phase 3:Merge**
-----------------
# 2. Sorting Algorithms
- Quicksort 可能是大多数 DBMSs 在使用的算法。
- Mergesort 很好,但是需要 O(N) 额外的空间存储中间结果。
## 2.1 Cache-Conscious Sorting
- [Sort vs. Hash Revisited: Fast Join Implementation on Modern Multi-Core CPUs](https://15721.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2020/papers/18-sortmergejoins/kim-vldb2009.pdf)
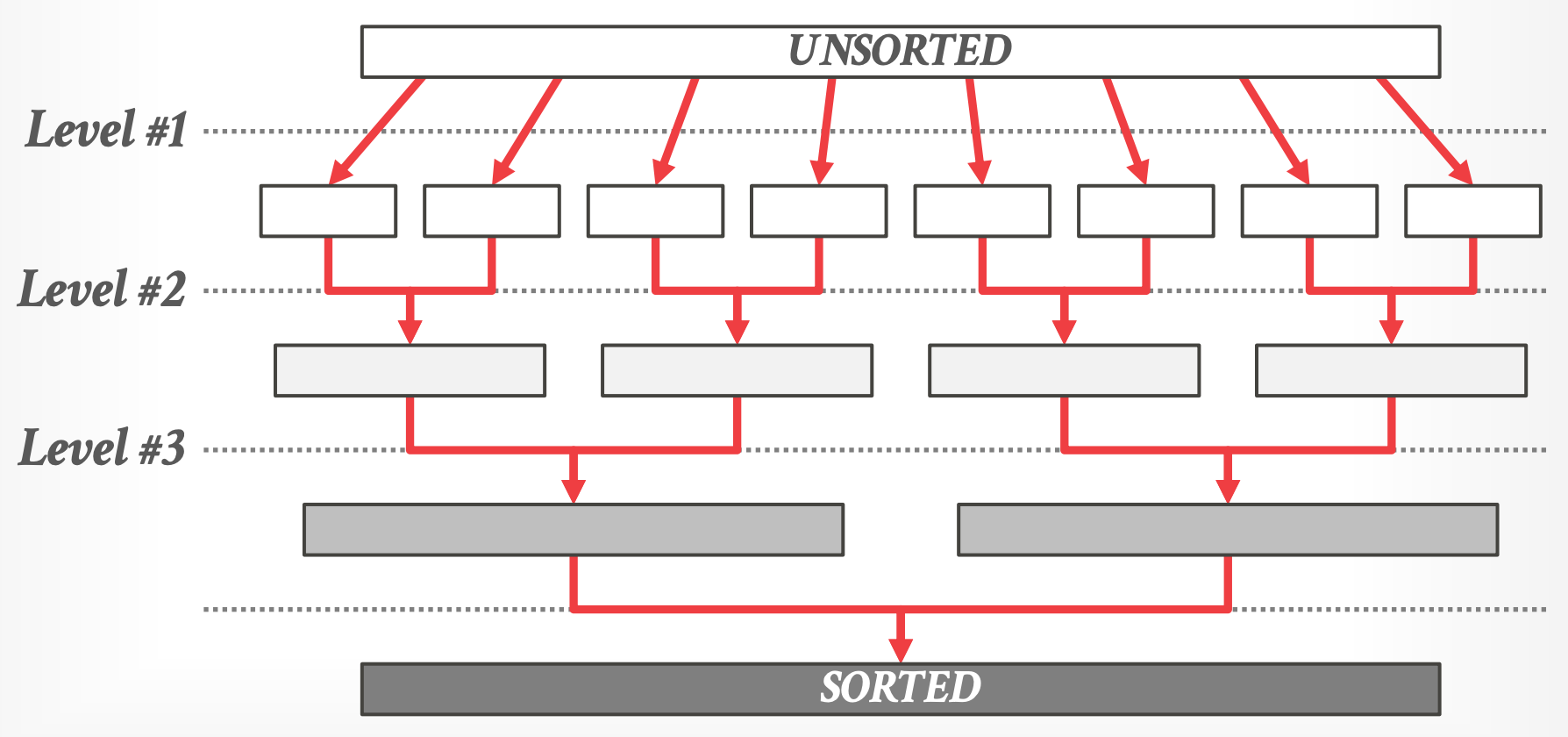
- 将所有数据拆分成不相交的 runs,对 run 进行排序,相同大小的 sorted runs 再合并成更大的 runs。
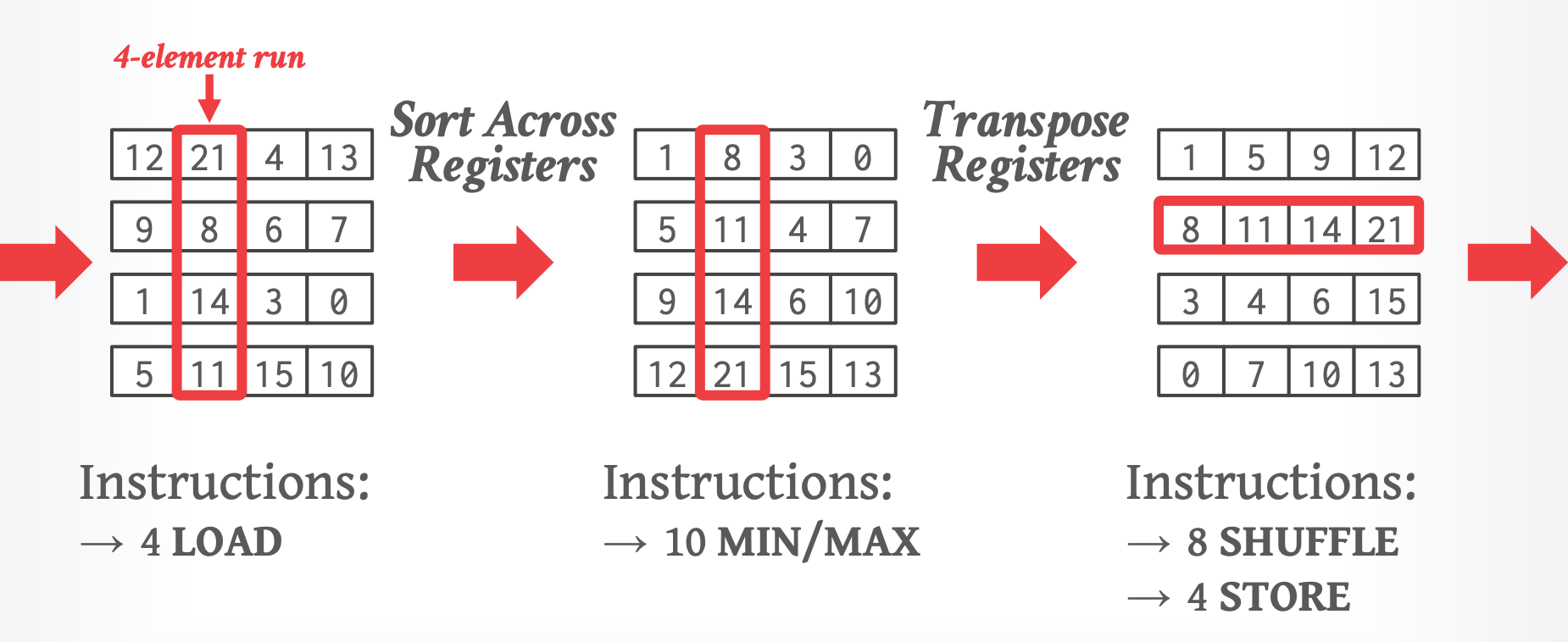
- **Level 1: In-Register Sorting**
- sort runs 可以放进去 CPU 寄存器
- **Level 2: In-Cache Sorting**
- 将 Level 1 的输出合并到可以放到 CPU caches 的 runs 中
- 重复进行直到 sorted runs 达到 cache size 的 1/2
- **Level 3: Out-of-Cache Sorting**
- 当 Level 2 runs 超出 cache 大小时使用
- 
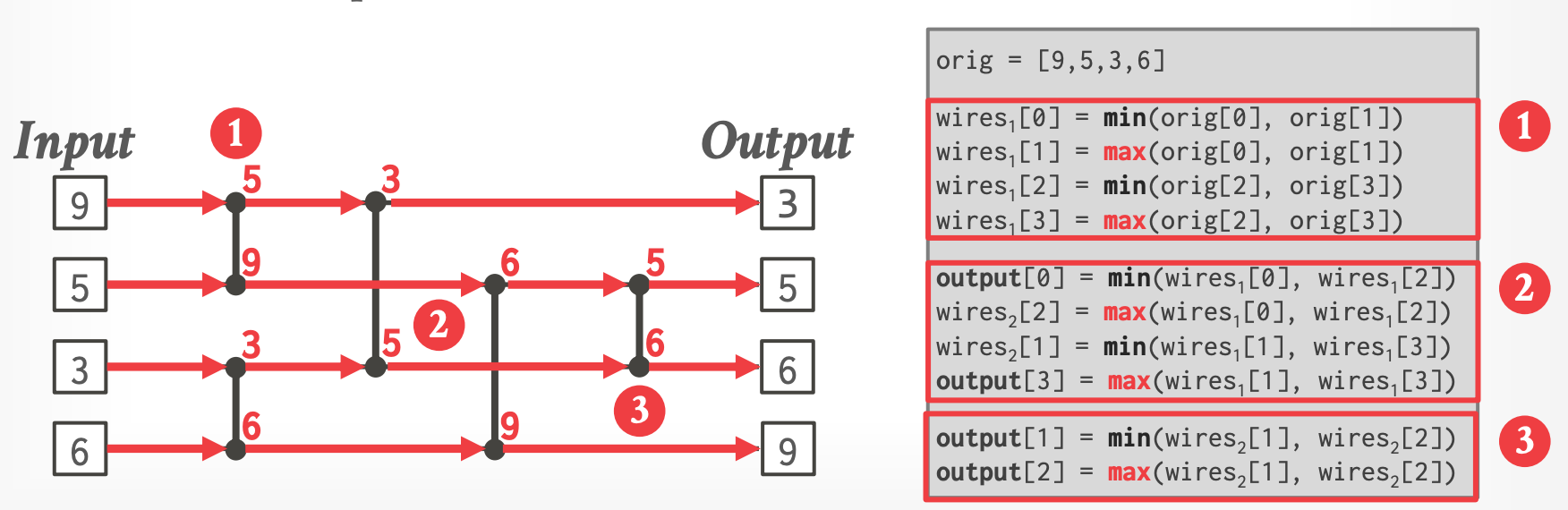
### Level #1 - Sorting Networks
- 用于排序 keys 的抽象模型
- Fixed wiring “paths” for lists with the same # of elements
- 在现代 CPU 上执行很高效:因为没有数据依赖、没有分支、SIMD
- 
- 
- 每个元素:<64-bit Join Key, 64-bit Tuple Pointer>
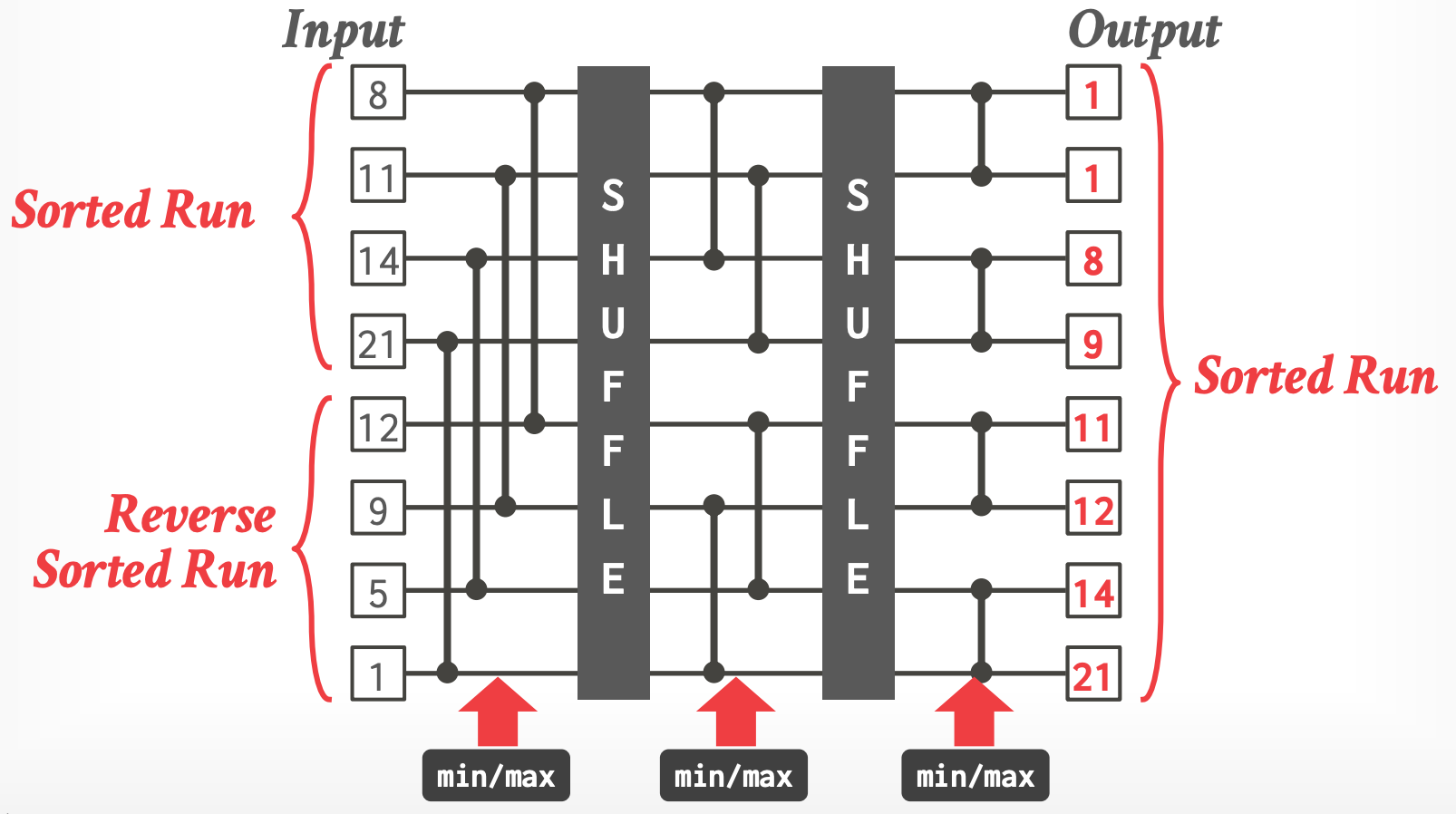
### Level #2 - Bitonic Merge Network
- [Efficient implementation of sorting on multi-core SIMD CPU architecture](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.14778/1454159.1454171)
- 类似 Sorting Network,但是 merge 两个 locally-sorted list 成一个 globally-sorted list
- 可以扩展 Network 以逐步合并更大的 lists,最多可达到 1/2 LLC 大小。
- Intel 的测试数据
- 比 SISD 实现快 2.25-3.5 倍
- 
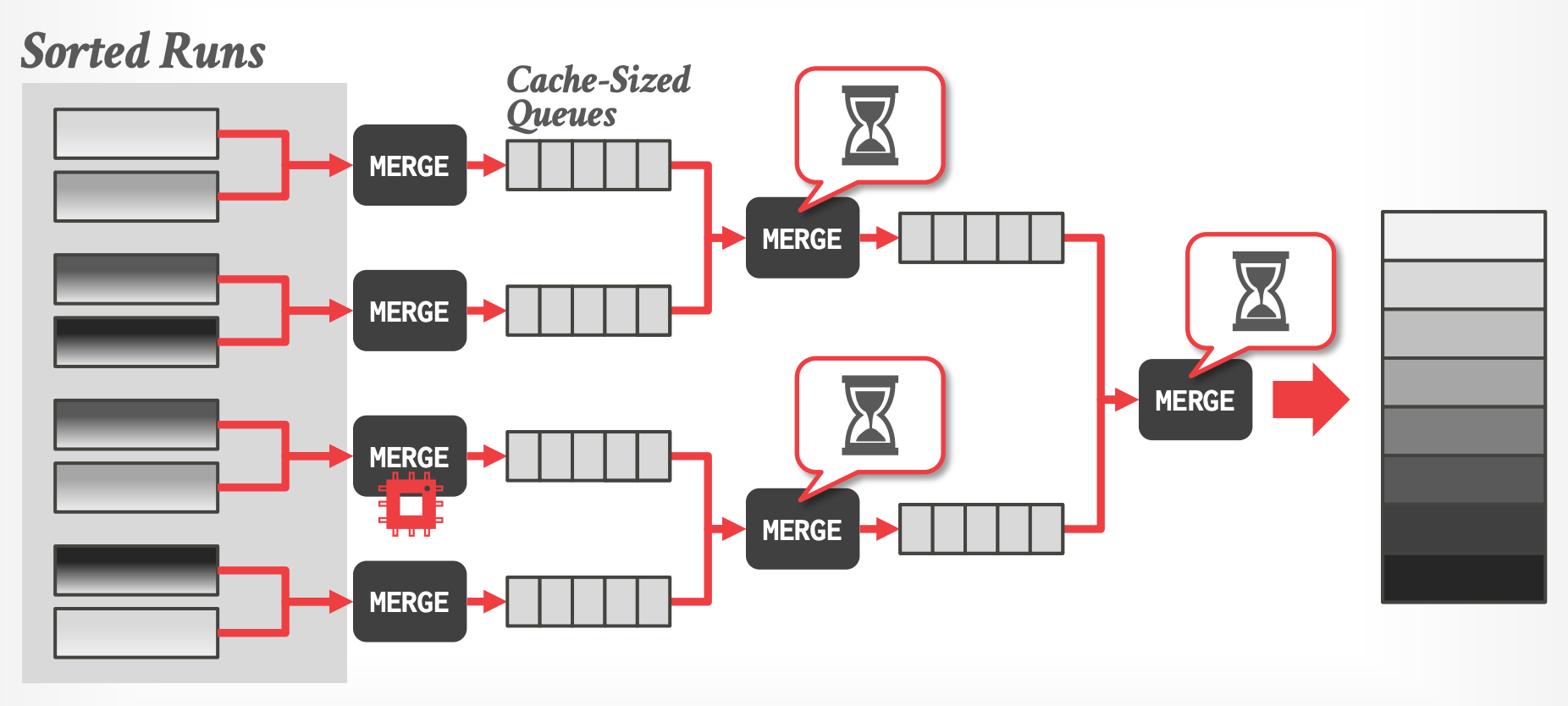
### Level #3 - Multi-Way Merging
- 继续使用 Bitonic Merge Networks,但是将过程拆分成 tasks。
- 继续每个 core 一个 worker thread
- 使用一个 cache-sized FIFO queue 将 tasks 链接到一起
> 暂时还没有系统实现它。
- 当 input queue 为空或者 output queue 满了时,task 会阻塞。
- 需要更多的CPU指令,但可以将带宽和计算平衡起来。
- 
## 2.2 In-place SuperScalar SampleSort
- [In-place Parallel Super Scalar Samplesort (IPS4o)](https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.02257)(2017)
- generalization of quick sort
- recursively partition relation by sampling keys to determine partition boundaries
- paritionning阶段将 data 拷贝到 output buffers
- 当 buffer 满了后,DBMS 将它写回现有 input buffers 的部分中,而不是分配新 buffer
- branchless
- [NoisePage 的实现](https://github.com/cmu-db/noisepage/blob/master/src/execution/sql/sorter.cpp)
## 2.3 Vectorized QuickSort
- [Google vqsort](https://opensource.googleblog.com/2022/06/Vectorized%20and%20performance%20portable%20Quicksort.html)(2022)
- 小于 256 keys 时使用 sorting networks,更大时使用 vectorized quicksort
- 基于 [Google Highway](https://github.com/google/highway)库来提供对不同 ISA 和 SIMD register sizes 的支持
- 声称比 IPS4o 快 1.59倍
- [Intel x86-simd-sort](https://github.com/intel/x86-simd-sort)(2022)
- 积极使用 AVX512 指令
-----------
# 3. Merge Phase
- 同时迭代 outer 和 inner table,比较 join keys
- 如果有重复,可能需要 backtrack
- DBMS 可以使用多个 workers 并行进行,如果使用独立的 output buffers 则不需要同步
-----------
# 4. Sort-Merge Join Variants
- **Muti-Way Sort-Merge(M-WAY)**
- [Multi-Core, Main-Memory Joins: Sort vs. Hash Revisited](https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol7/p85-balkesen.pdf)
- **Multi-Pass Sort-Merge (M-PASS)**
- [Multi-Core, Main-Memory Joins: Sort vs. Hash Revisited](https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol7/p85-balkesen.pdf)
- **Massively Parallel Sort-Merge (MPSM)**
- [Massively Parallel Sort-Merge Joins in Main Memory Multi-Core Database Systems](https://15721.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2020/papers/18-sortmergejoins/p1064-albutiu.pdf)
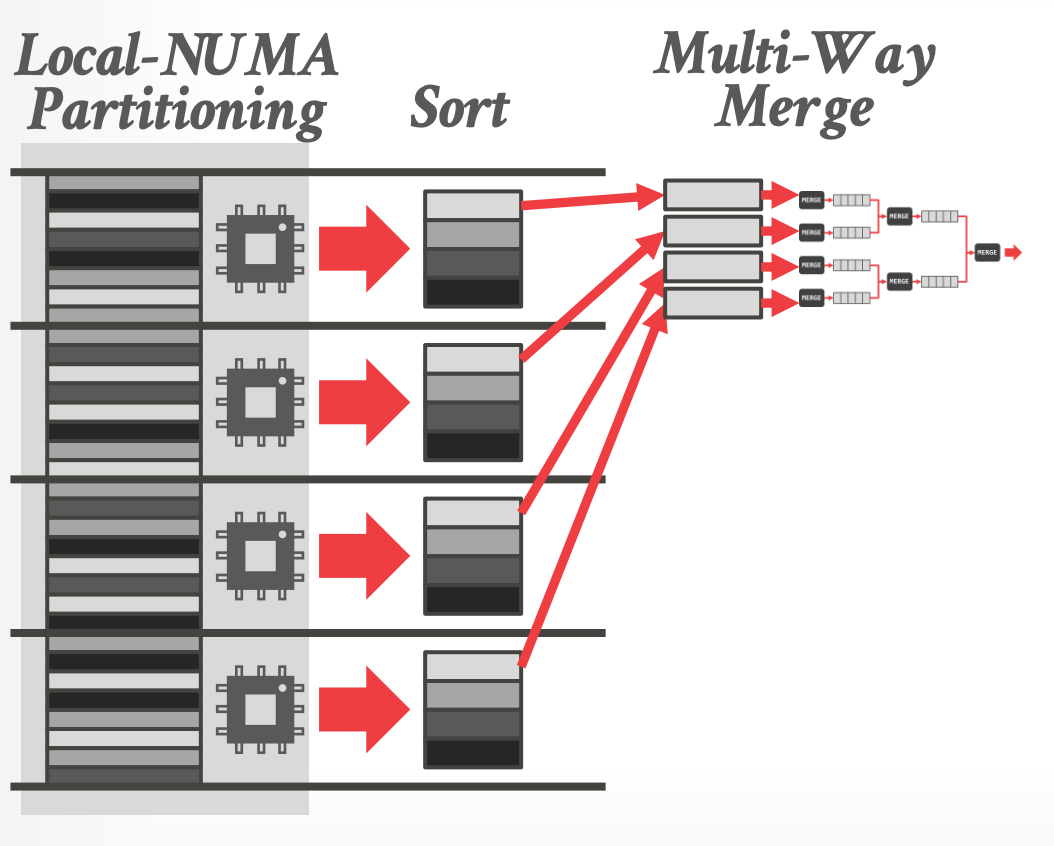
## 4.1 Muti-Way Sort-Merge
- 三者中最佳
- **Outer Table**
- 每个 core 并行排序 local data(levels #1 / #2)
- 使用 range partitioning 将 sorted runs 重写分布到多个 cores,然后执行 muti-way merge(level #3 )
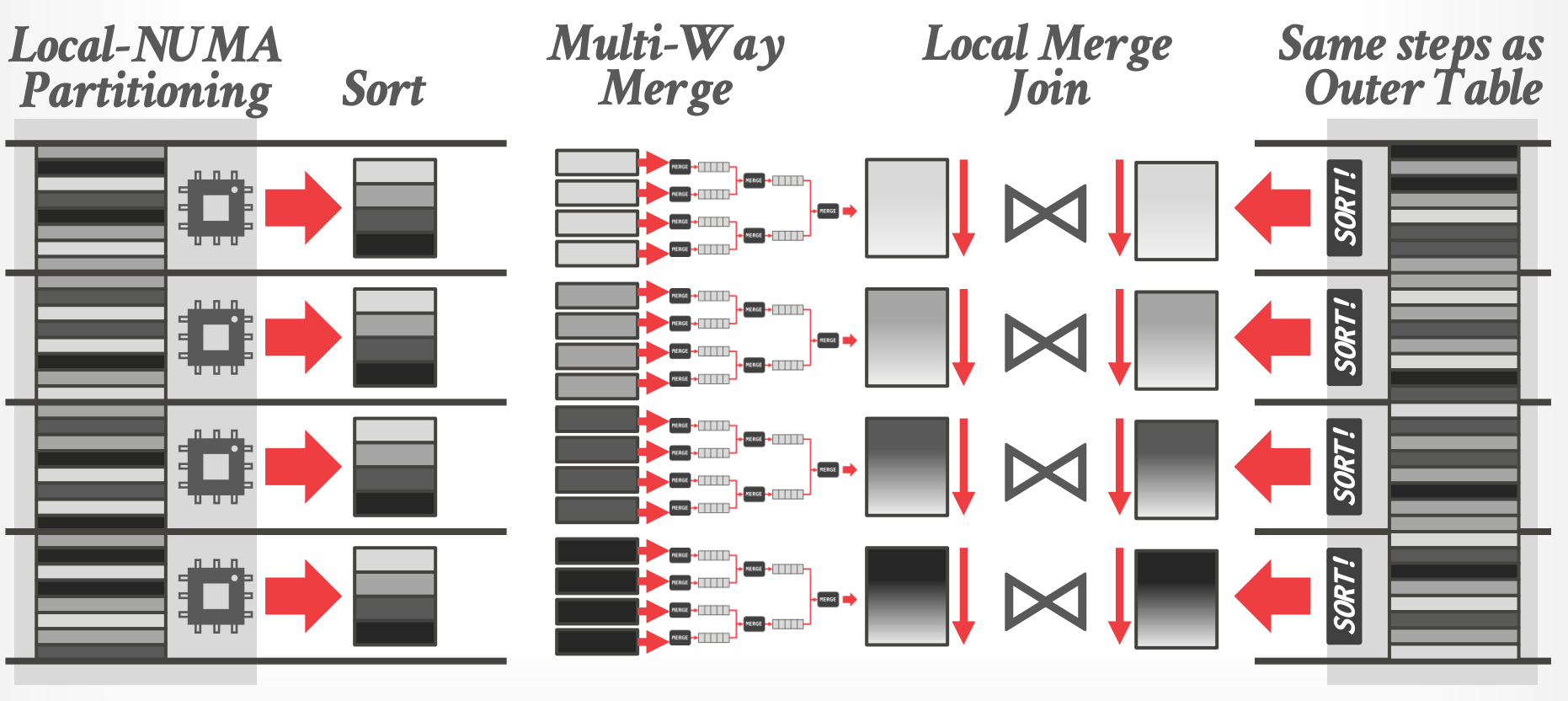
- **Inner Talbe**
- 同 outer table 一样
- Merge phase is between matching pairs of chunks of outer table and inner table **at each core**
- 
- 
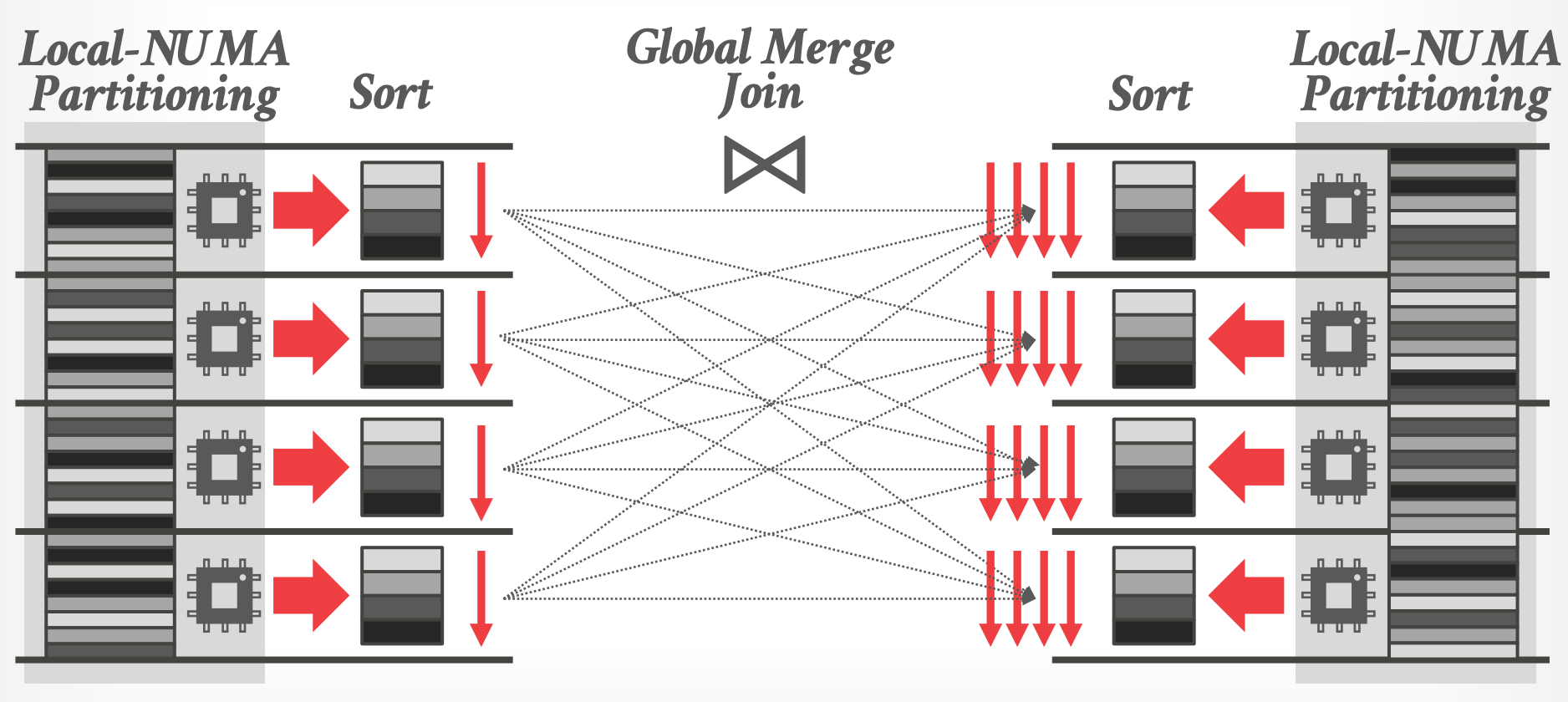
## 4.2 Muti-Pass Sort-Merge
- level #1 / #2 跟 Multi-Way Merge 一样
- 对 sorted runs 执行 multi-pass naive merge
- 
- prefetch
## 4.3 Massively Parallel Sort-Merge
- Hyper 的方式
- **Outer Table**
- 按 range 分区,分布到多个 cores 上
- 每个 core 并行 sorts 自己 local partition
- **Inner Table**
- Not redistributed like outer table. (不进行 redistributed)
- Each core sorts its local data.
- 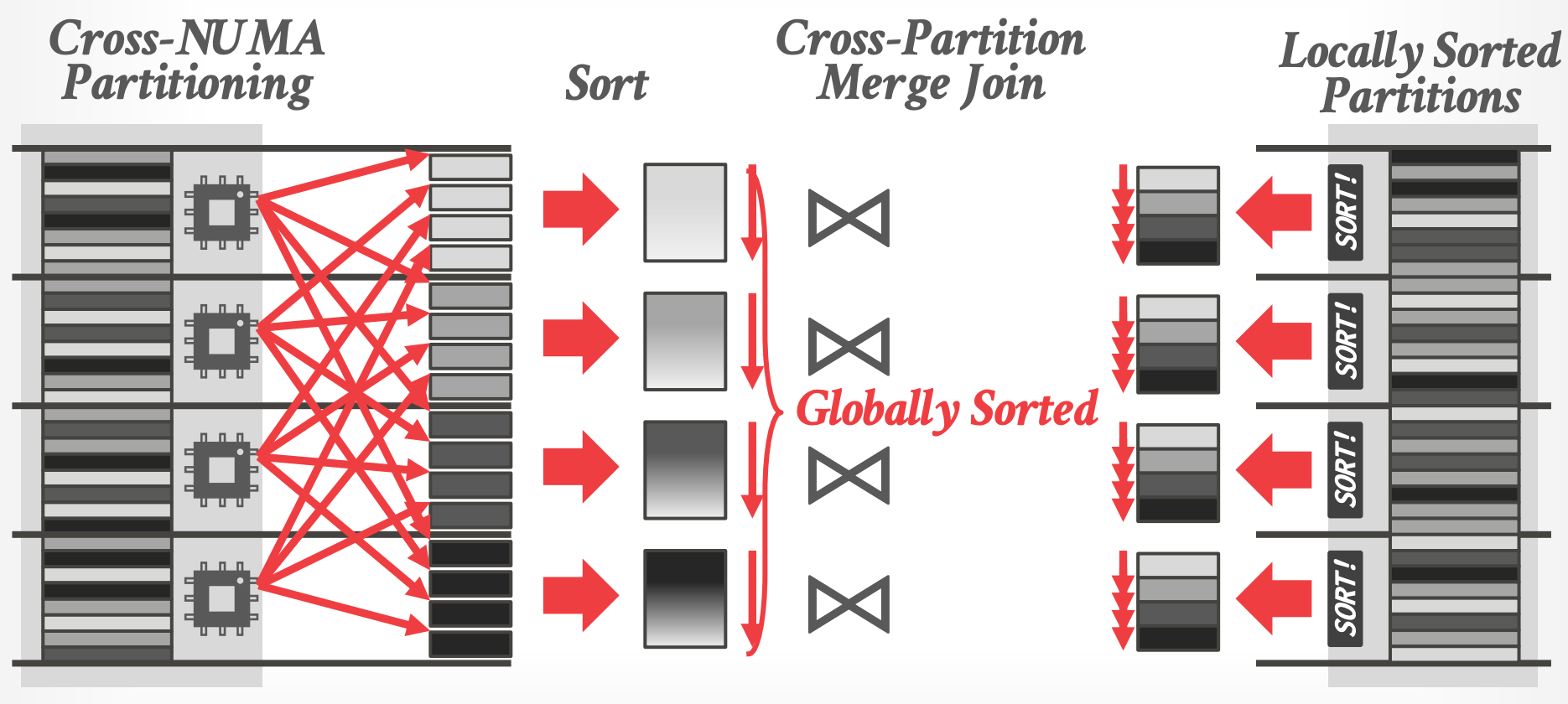
- merge 时每个 parition 可能只与 inner table parition 的部分进行 join(根据 outer table parition 的 范围)
- 顺序读
## 4.4 Hyper Rules For Parallelization
- 不要对 non-local memory 进行随机写
- 对 non-local memory 只进行顺序读取
- 利用 hardware prefetcher 来隐藏 remote access latency
- 每个 core 都不要等待其他 core
- 避免 fine-grained latching 或者 sync barriers
--------
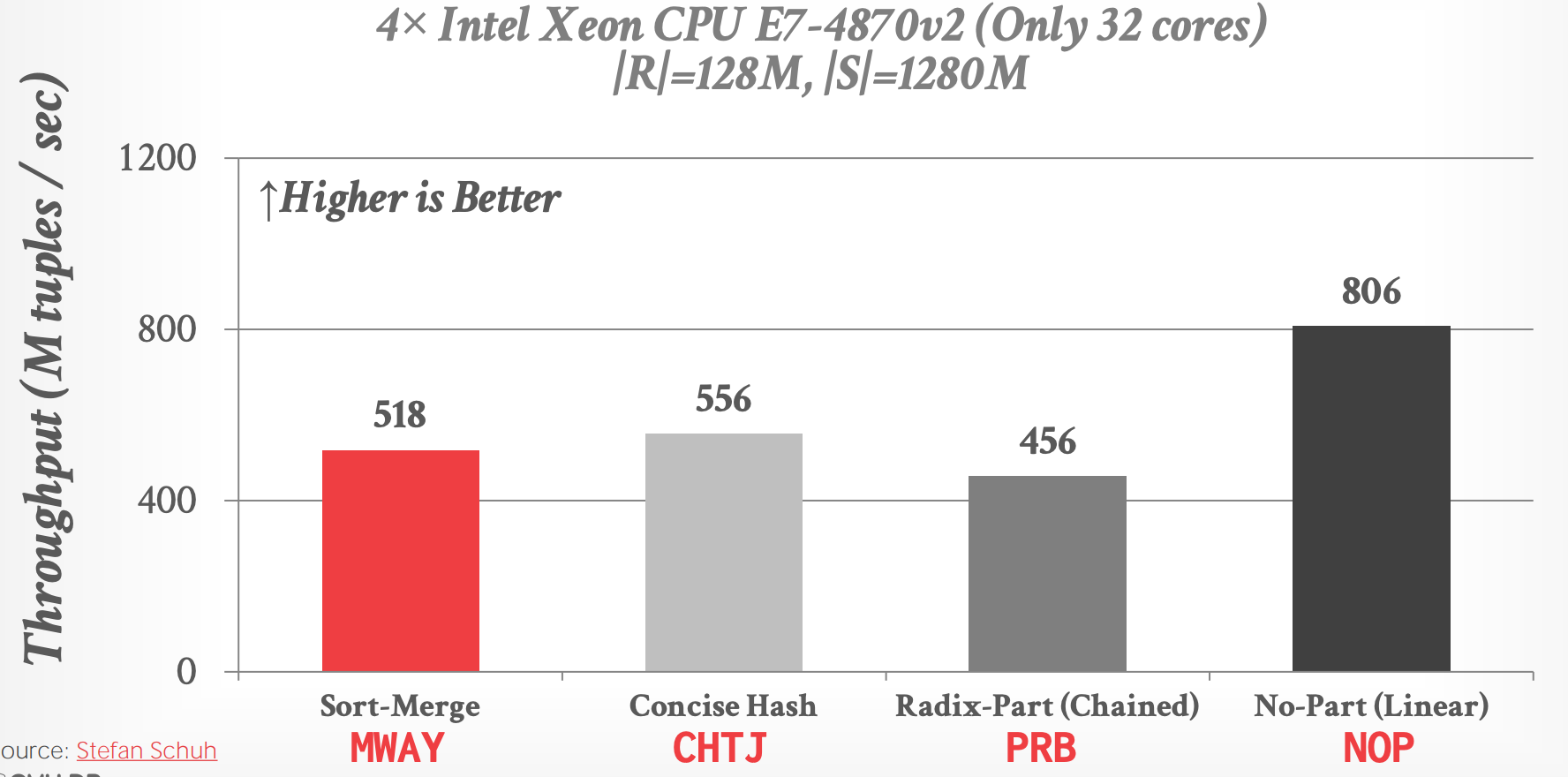
# 5. Join Comparsion
- 
-----
# Parting Thoughts
- Hash join 在当前硬件下几乎总是 join 算法的最优方式
- 大多数企业级的 OLAP DBMS 两种都支持
- 不考虑查询的 output 需要排序(order-by)