# 1. Motivation
- 两表 join(binary joins) 在关系型数据库中非常普遍
- 几十年的研究使这些算法效率很高。
- 当 join 的 output 比两个 inputs 小时,只是最优的方式。
- **问题**:当 join 的 output 比两个 inputs 大时
- intermediate output 很大(需要物化)
- 
------
# 2. Worst-Case Optimal Joins
- Perform join by **examining a variable at a time** instead of a relation at a time.
- [Size bounds and query plans for relational joins](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.03860.pdf)(2008)
- The runtime of a WCOJ algorithm is **bounded by the output size** of the result and depends on the **variable evaluation ordering.**
- If more tuples match in the intermediate results, then the DBMS must check the other tables.
- The more tables a WCOJ algorithm joins, the better its performance relative to the input.
> Alternative Definition #1: The worst-case runtime of the algorithm meets a known lower bound for the worst-case runtime of any join algorithm.
> Alternative Definition #2: The runtime of the join algorithm is better than all other join algorithms when the query and data represent the worst possible scenario.
- 到 2023 年为止,只有很少的 DBMS 支持了 WCOJ 算法
- 首批实现:LogicBlox、EmptyHeaded(Stanford)
- 其他实现:RelationalAI、Umbra、DuckDB、[KuzuDB](https://kuzudb.com/blog/wcoj.html#a-thank-you--an-anecdote-about-knuths-reaction-to-the-term-worst-case-optimal)
- 这些 joins 以后会变得常见,因为 SQL 2023 标准包含了图查询扩展(SQL / PGQ)
------------
# 3. Leap-Frog Trie Join
- [Leapfrog Triejoin: A Simple, Worst-Case Optimal Join Algorithm](https://openproceedings.org/ICDT/2014/paper_13.pdf)
- 执行 join 前,relations 必须按照 join keys 排序 或者实时构建 trie index
- 将具有多个 attributes 的 relation 表示为 tries
- 一个 relation 一个 trie
- trie 的每一个 level 代表了 join keys 中的一个 attriubte
- Developed by LogicBlox in the early 2010s
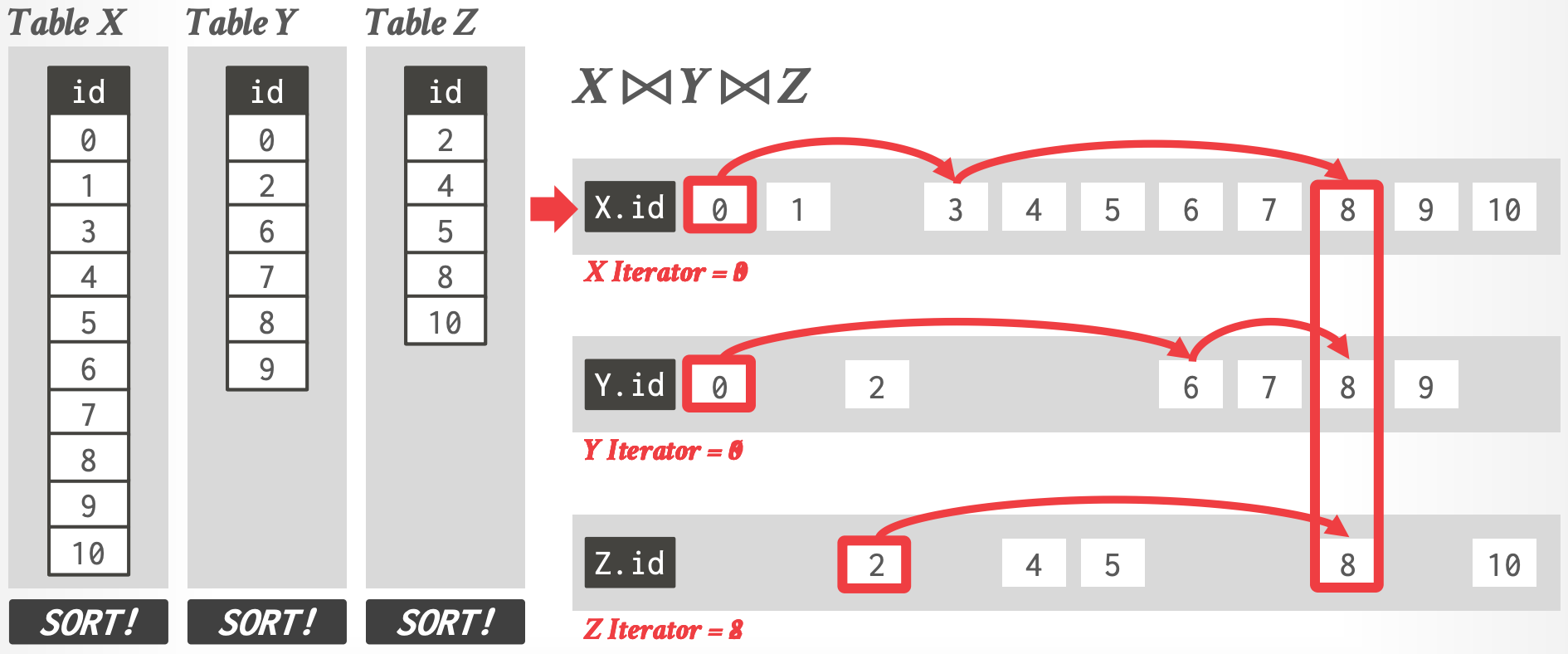
- **排序的方式:**
- 
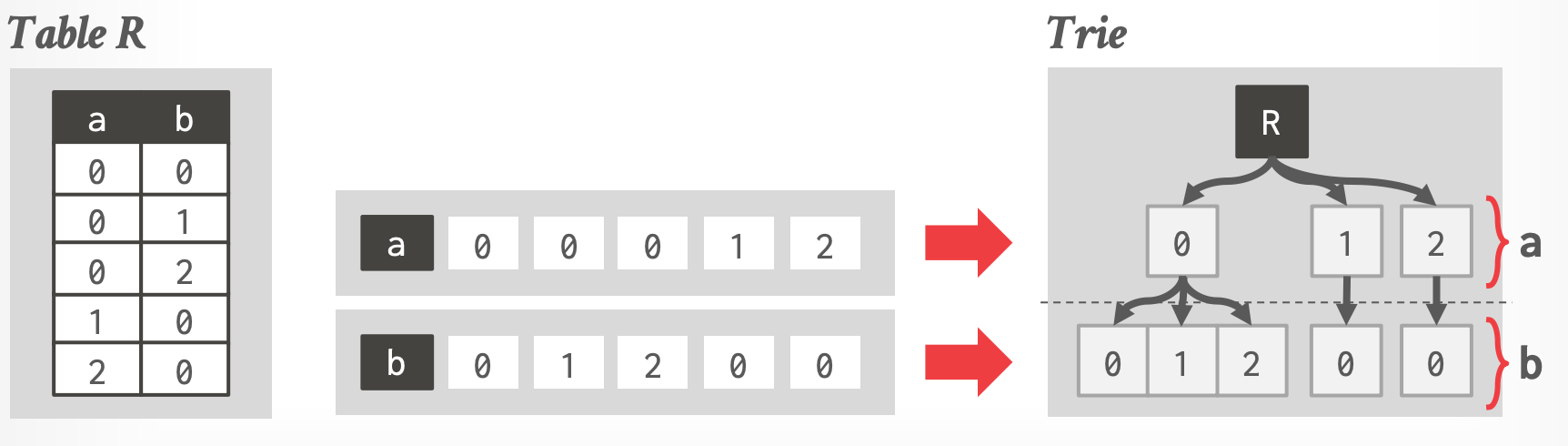
- **Trie 的形式:**
- 
- 
- 如果文件是 read-only 时,可以预先生成 trie
## Observation
- 实时为每个 relation 构建一棵 Trie 树是昂贵的
- 即使 database 是 read-only 的,为每个可能的 join ordering 预先构建 tries 也不现实
- 另一种方案是使用 nested hash tables,但是也比较昂贵
- 检查 hash 冲突至少需要一次 key 比较
- 需要存储实际的 keys 或者指向 tuples 的指针,来处理冲突。(带来许多 cache misses)
- 需要使用 dictionary encoding 来处理变长 keys
---------
# 4. Hash Trie Join
## Multi-Way Hash Trie Joins
- [Adopting worst-case optimal joins in relational database systems](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.14778/3407790.3407797)
- 不在 nested hash tables 中存储 join keys,而是存储 hash values。
- 没有 type-sepcific 逻辑来计算 set intersections 和 lookup 操作
- DBMS 只需要使用整数比较(很快)
- 当 hash 冲突时需要 remove false positive matches
## 4.1 Hash Trie
- 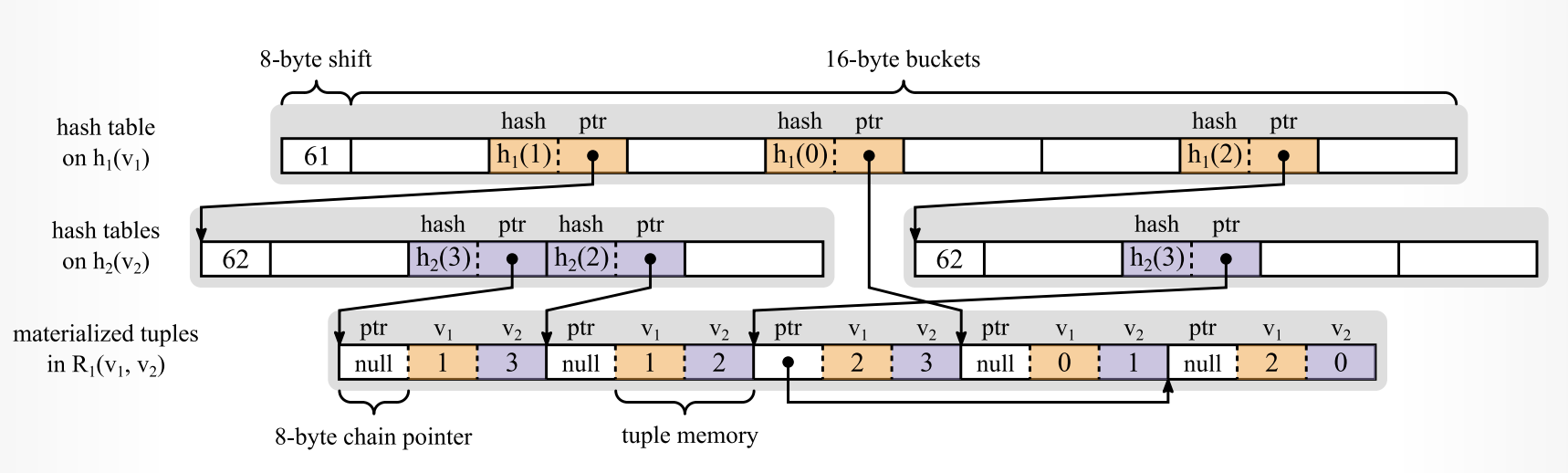
- 来自:[Michael Freitag](https://db.in.tum.de/~freitag/)
### 4.1.1 Tagged Pointers
- 利用指向 trie node 的64位指针的未使用部分 来存储额外的元数据
- x86-64 内存地址只使用 48 bits
- 元数据:所指向 trie node 的信息
- 
- **1-bit**:Singleton Flag
- **1-bit**:Expansion Flag 是否指向了一个已经 expanded 的 node
- **14-bits**:Chain Length
- **48-bits**:Memory Address
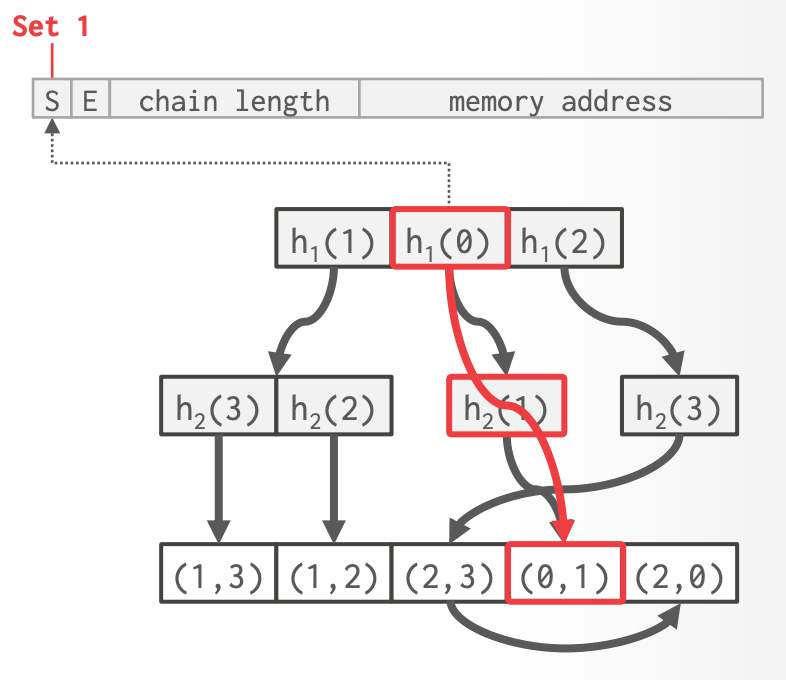
### 4.1.2 Singleton Pruning
- trie lower levels 的 hash tables 会变小
- inner nodes 经常只指向一个 tuple
- 优化:不再存储到 leaf node 的每层 trie level,而是存储直接指向 singleton tuple 的指针
- 
### 4.1.3 Lazy Child Expansion
- 根据 intersection 操作的 selectivity, DBMS 不会访问太多 inner nodes
- 优化:只有在 probe 阶段被访问时,才物化 inner nodes
- root node 是特殊的,始终物化
- 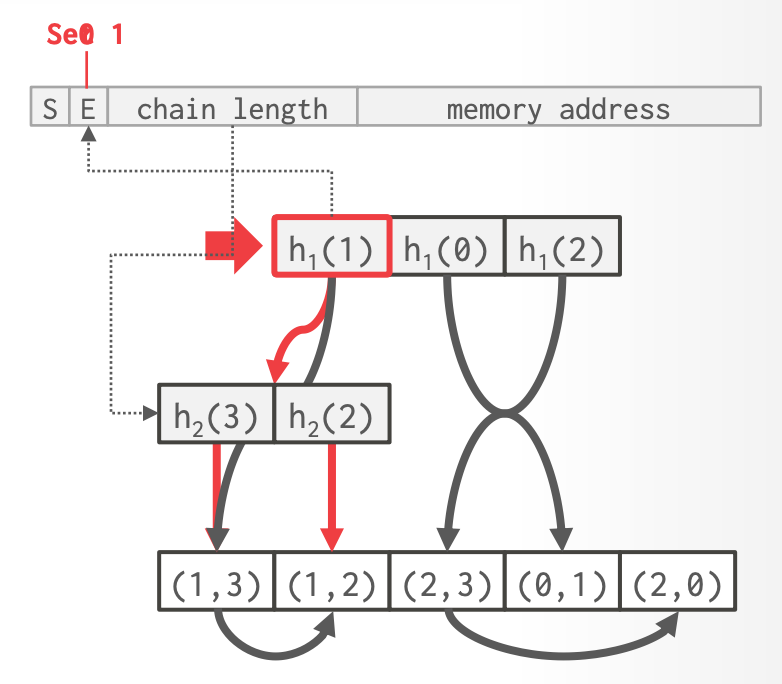
- 访问时,发现 link list,再创建中间节点
-------------
# Observation
- 如果中间结果不大于它的 inputs,则 Multi-way joins 慢于 binary joins
- Umbra 扩展了它们的优化器,使用启发式方法来决策使用 binary join 还是 WCOJ。
---------
# Parting Thoughts
- Multi-way joins 是一个活跃的研究领域
- 接下来的十年中,**它们可能会成为关系数据库中 join 的默认选择**
- **这会是图数据库的致命一击**