# 1. Background
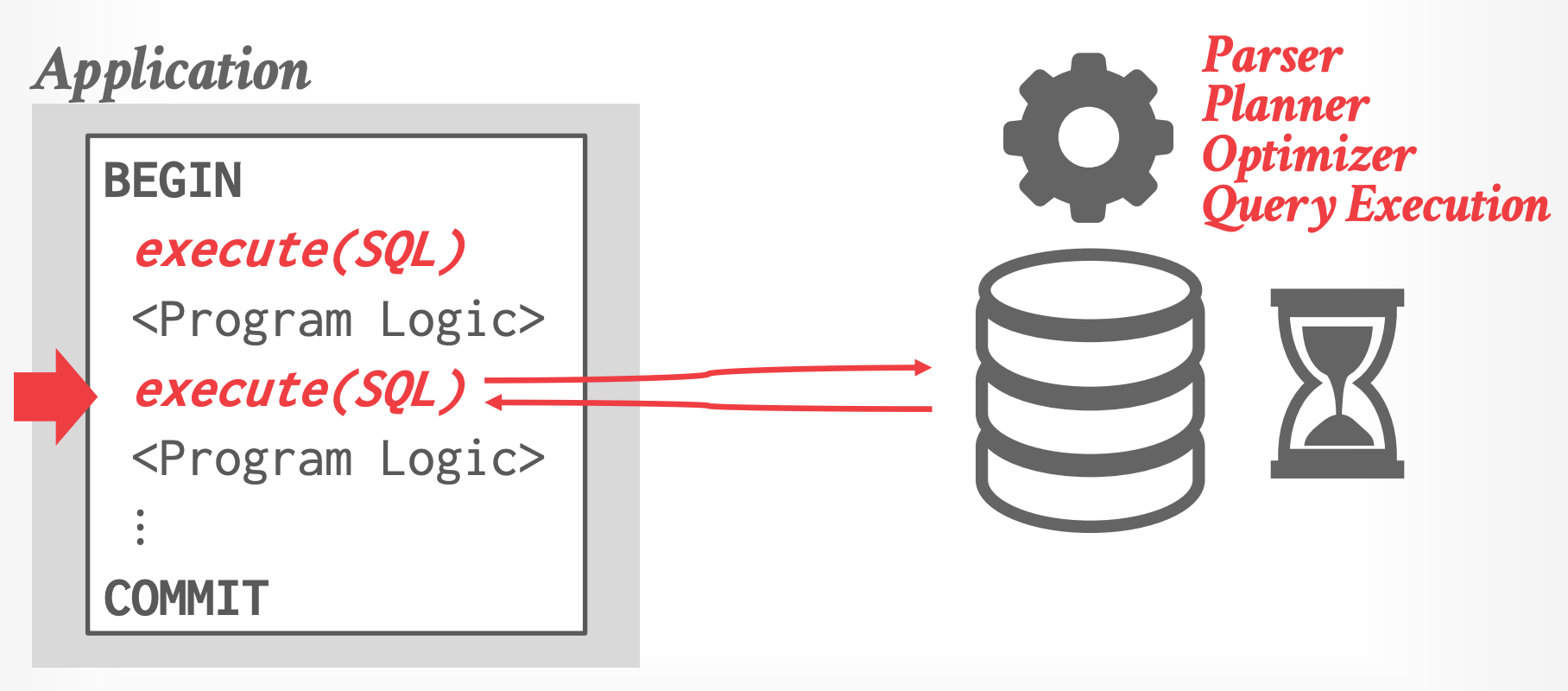
## 1.1 Conversational Database API
- 应用程序的所有逻辑都在应用侧实现
- 应用程序使用 "conversation" 的形式与 DBMS 交互(存取数据)
- 应用程序从 DBMS 获取一批数据,对数据执行计算,然后再向 DBMS 获取下一批数据
- 
## 1.2 Embedded Database Logic
- 将应用程序的逻辑移动到 DBMS,可能带来的好处:
- 减少网络交互
- 有变更后及时通知(如 Triggers)
- 事务执行过程中,减少了 DBMS 等待 COMMIT 的时间(网络交互少了)
- 开发者不用重复实现相似的功能
- 扩展 DBMS 的功能性
- 五种不同的类型:
- UDF
- Stored Procedures
- Tiggers
- User-Defined Types(UDTs)
- User-Defined Aggregates(UDAs)
- [Procedural Extensions of SQL: Understanding their usage in the wild](https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol14/p1378-ramachandra.pdf)
-------
# 2. UDF
- UDF:user-defined function,由应用程序开发者编写,可以扩展系统的功能,超出其内置操作。
- 可以有输入参数(scalars)
- 执行一些计算
- 返回结果(scalars,tables)
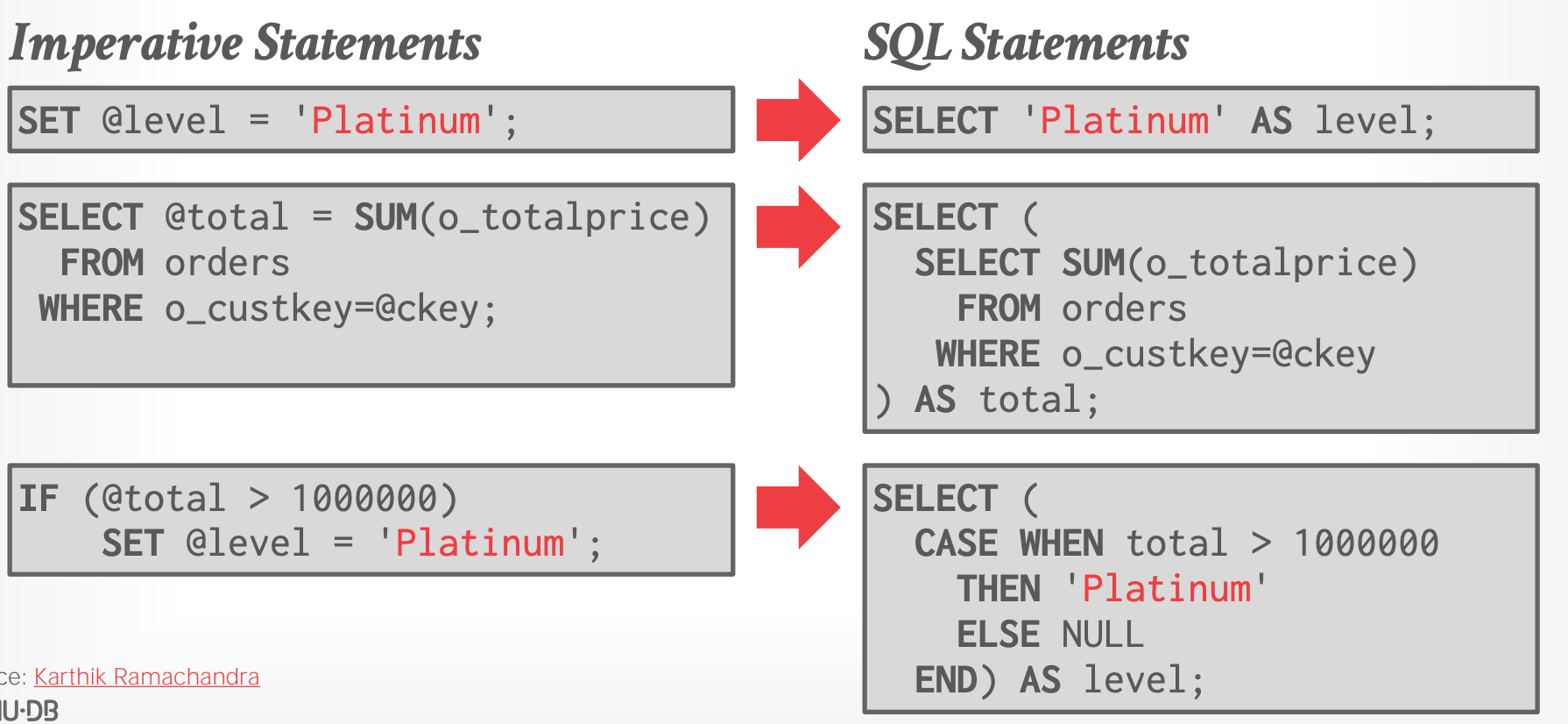
### 2.1 UDF: SQL Functions
- SQL-based UDF:包含一系列 queries,但 UDF 执行时顺序执行这些 queries
- 函数返回值是最后一条 query 的执行结果
```sql
-- 定义
CREATE FUNCTION get_foo(int)
RETURNS foo -- Return Args
LANGUAGE SQL AS $
SELECT * FROM foo WHERE foo.id = $1; -- Function Body
$;
-- 使用
SELECT get_foo(1);
SELECT * FROM get_foo(1);
```
- SQL 标准提供了 `ATOMIC` 关键字来告诉 DBMS 它应该跟踪 SQL UDFs 之间的依赖。
```SQL
CREATE FUNCTION get_foo(int)
RETURNS foo
LANGUAGE SQL
BEGIN ATOMIC;
SELECT * FROM foo WHERE foo.id = $1;
END;
```
### 2.2 UDF: External Programming Language
- 一些 DBMS 支持使用 SQL 之外的语言来编写 UDFs
- **SQL 标准**:[SQL/PSM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SQL/PSM)
- **Oracle/DB2**: [PL/SQL](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PL/SQL)
- **Postgres**: [PL/pgSQL](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PL/pgSQL)
- **DB2**: [SQL PL](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SQL_PL)
- **MSSQL/Sybase**: [Transact-SQL](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transact-SQL)
- 其他系统支持更多常见的编程语言
- Sandbox vs. non-Sandbox
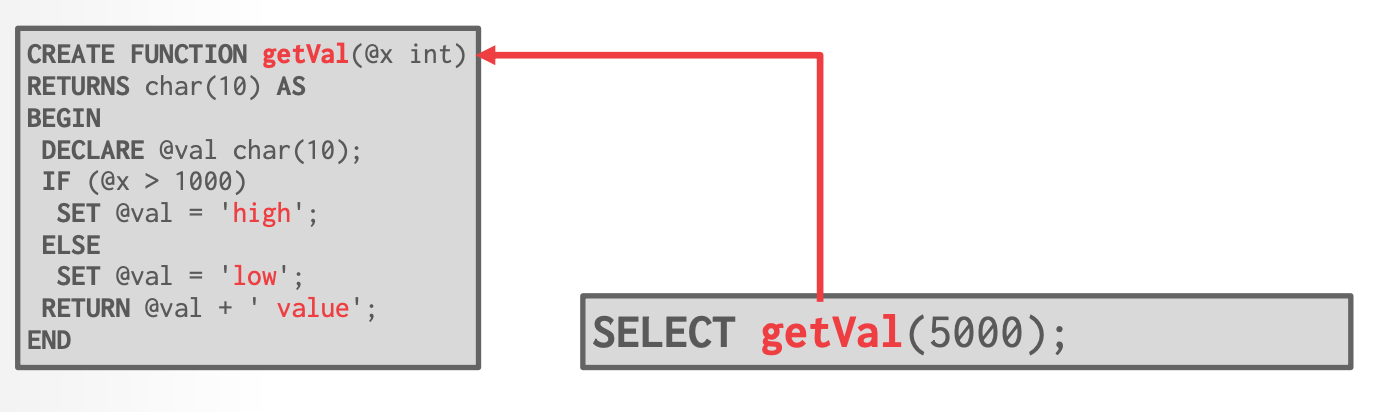
```SQL
-- Transact-SQL:
CREATE FUNCTION cust_level(@ckey int)
RETURNS char(10) AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @total float;
DECLARE @level char(10);
SELECT @total = SUM(o_totalprice)
FROM orders WHERE o_custkey=@ckey;
IF (@total > 1000000)
SET @level = 'Platinum';
ELSE SET @level = 'Regular';
RETURN @level;
END
```
## 2.3 UDF Advantages
- 有助于模块化和代码重用
- 不同的查询可以复用相同的应用程序逻辑,不需要每次重复实现
- 应用程序与DBMS之间的网络交互次数变少
- 某些类型的应用程序逻辑使用 UDFs 比 使用SQL 更容易表达和可读。
## 2.4 UDF Disadvantages
- 查询优化器将 external programming language UDFs 看作黑盒
- DBMS **无法估算函数的 cost / selectivity**,无法理解函数内部的逻辑
- 例如:`WHERE val = my_udf(123)`
- **UDFs 难以并行执行**,因为它们之间的 queries 可能有关联性
- 一些 DBMS 当查询包含 UDF 时只使用一个线程来执行查询
- 特殊:UDF 是 read-only 的,没有 side effects
- Some UDFs incrementally construct queries。
- SELECT / WHERE 中包含复杂的 UDFs 时,**无法批量执行(vectorized)**,只能是 iterative
- RBAR = “Row by Agonizing Row” // 一次针对一行调用 UDF
- DBMS 以 one-by-one 的形式执行 UDF,**无法执行 cross-statement 的优化**
## 2.5 UDF Preformance
- TPC-H Q12 using a UDF (SF=1).
- Original Query: 0.8 sec
- Query + UDF: 13 hr 30 min
## 2.6 UDF Acceleration
- **Compilation**
- 将 interpreted UDF code 编译成 native machine code
- 如果 DBMS 支持整体查询编译(如 Hyper),可以将 UDF **inline** 到 compiled query plan
- **Parallelization**
- 依赖用户提供的注解,来判断 UDF 中的哪些部分可以并行执行
- **Inline**
- 将 UDF 转换为声明式的形式,然后 inline it into the calling query.
-------
# 3. Microsoft SQL Server UDF
## 3.1 History
- **2001** - Microsoft 添加了 TSQL Scalar UDFs
- **2008** - 认识到 UDFs are "evil"
- **2010** - Microsoft 承认UDF are evil
- [Soften the RBAR impact with Native Compiled UDFs in SQL Server 2016](https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/sql-server-blog/soften-the-rbar-impact-with-native-compiled-udfs-in-sql-server/ba-p/305260?advanced=false&collapse_discussion=true&search_type=thread)
- **2014** - IIT-B 研究 [UDF decorrelation](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6816679)
- **2015** - MSFT Gray Lab 开始 [Froid project](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/project/froid/)
- **2018** - Froid 添加到 SQL Server 2019
- [Scalar UDF Inlining](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/user-defined-functions/scalar-udf-inlining?view=sql-server-ver16)
## 3.2 Forid
- [Froid: Optimization of Imperative Programs in a Relational Database](https://15721.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2020/papers/24-udfs/p432-ramachandra.pdf)
- 自动将 UDFs 转换成关系代数表达式(以**子查询**的形式内联到查询中)
- 不需要应用开发者改动 UDF 代码
- 在 **rewrite** 阶段执行转换,避免更改 cost-base optimizer
- 商业数据库已经具备使得子查询高效执行的转换规则
## 3.3 Sub-Queries
- DBMS 将 where 条件中 的nested sub-queries 视作函数
- 接收参数、返回一个单值或者一组值
- 两种途径:
- rewrite to de-corelate and / or flatten them
- decompose nested query and store result to temporary table,then the outer joins with the temporary table
### Rewrite
```SQL
-- 获取购买了两次以上的第一个用户:
SELECT user_id FROM orders AS o1
WHERE EXISTS(
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM orders AS o2
WHERE o1.user_id = o2.user_id
GROUP BY o2.user_id HAVING COUNT(*) >= 2
)
ORDER BY user_id ASC LIMIT 1;
```
重写为:
```SQL
SELECT user_id FROM orders
GROUP BY user_id
HAVING COUNT(*) >= 2
ORDER BY user_id ASC LIMIT 1;
```
### Lateral Join
- lateral inner subquery 可以引用其他 table 的列(相同 nest level 可以互相引用)
- 允许在 **FROM** 从句中包含 sub-queries
- DBMS 迭代被引用的 table 的每一个 row,然后在 inner sub-query 中 evalutate 每一个 row。
- inner sub-query 返回的 rows 添加到与 outer query join 的结果中
```SQL
-- 获取购买了至少两次的第一个用户,以及该用户的首次和第二次的购买时间
SELECT user_id, first_order, next_order, id
FROM (SELECT user_id,
MIN(created) AS first_order
FROM orders GROUP BY user_id) AS o1
INNER JOIN LATERAL
(SELECT id, created AS next_order
FROM orders
WHERE user_id = o1.user_id
AND created > o1.first_order
ORDER BY created ASC LIMIT 1) AS o2
ON true
LIMIT 1;
```
第二个 sub-query 引用了第一个 sub-query 的列(`user_id`、`first_order`)
## 3.4 Froid Overview
1. Transform Statments
2. Break UDF into regions
3. Merge Expressions
4. Inline UDF Expression into Query
5. Run Updated Query through Optimizer
### Step #1 - Transform Statements
### Step #2 - Break Into Regions
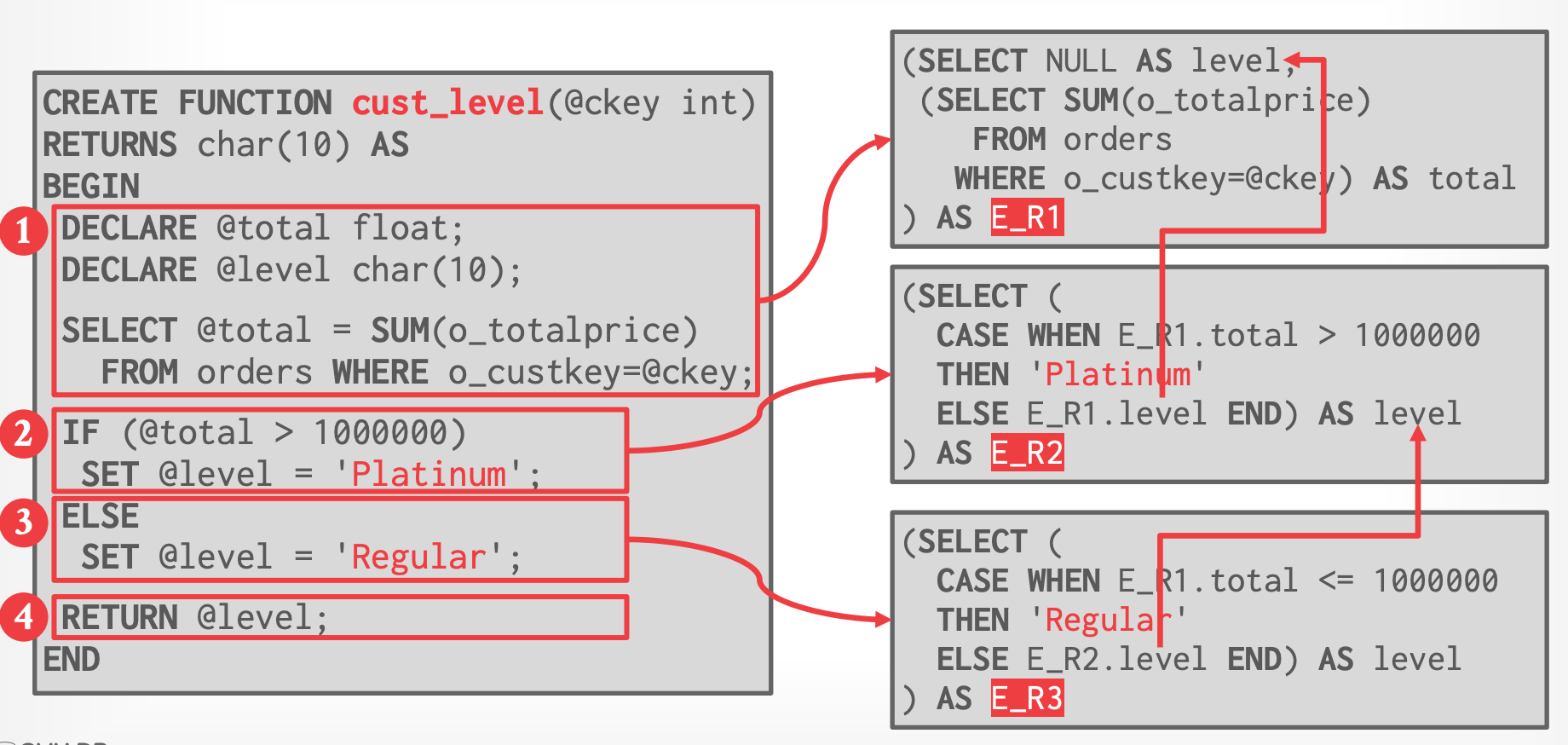
- E_R1等:临时表
- 一个临时表会引用另外一个临时表,因此需要 Lateral Join
### Step #3 - Merge Expressions
- 将 regions 合并成一个巨大的 SQL 语句,它等价于 UDF
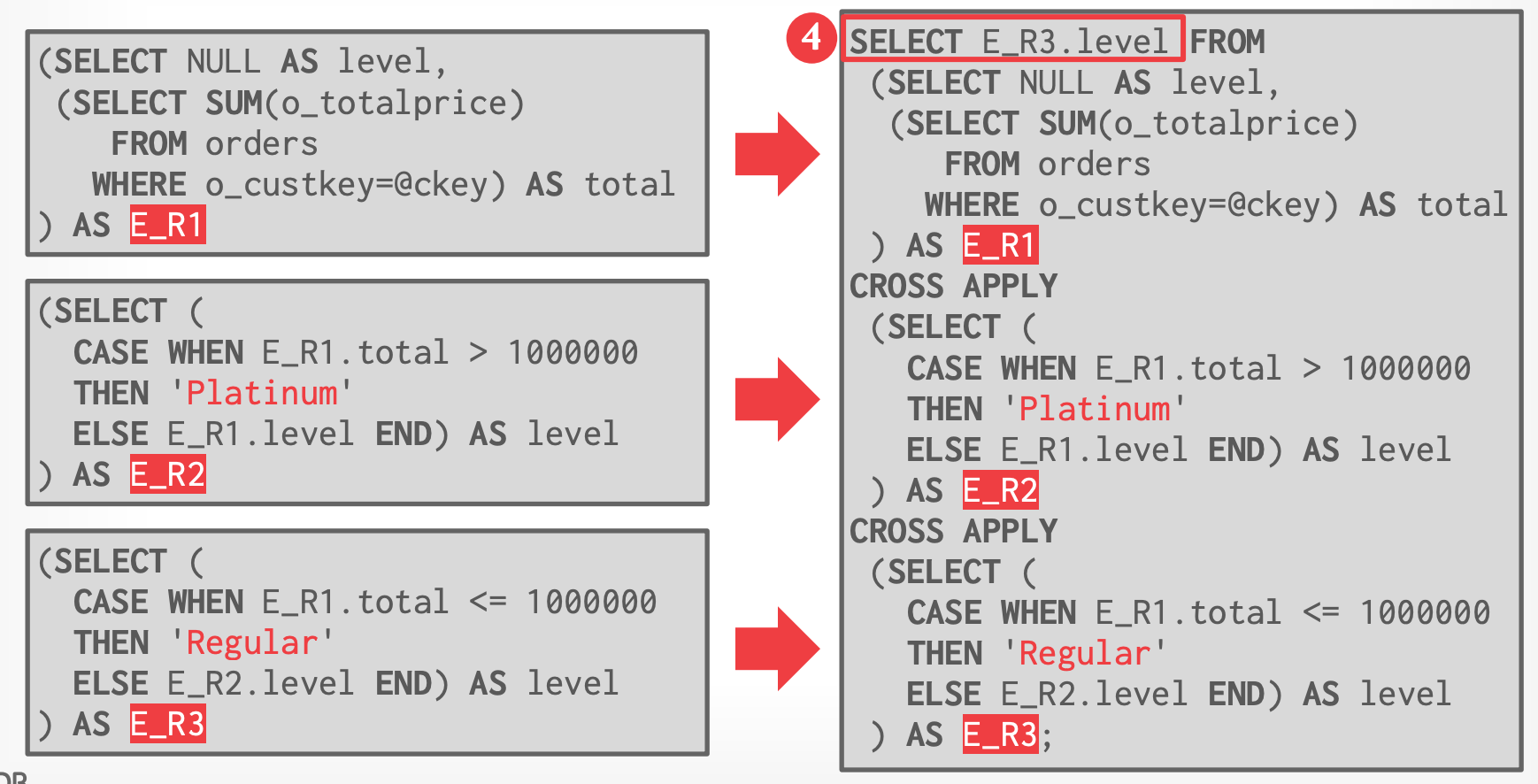
- CROSS APPLY:类似 Lateral Join
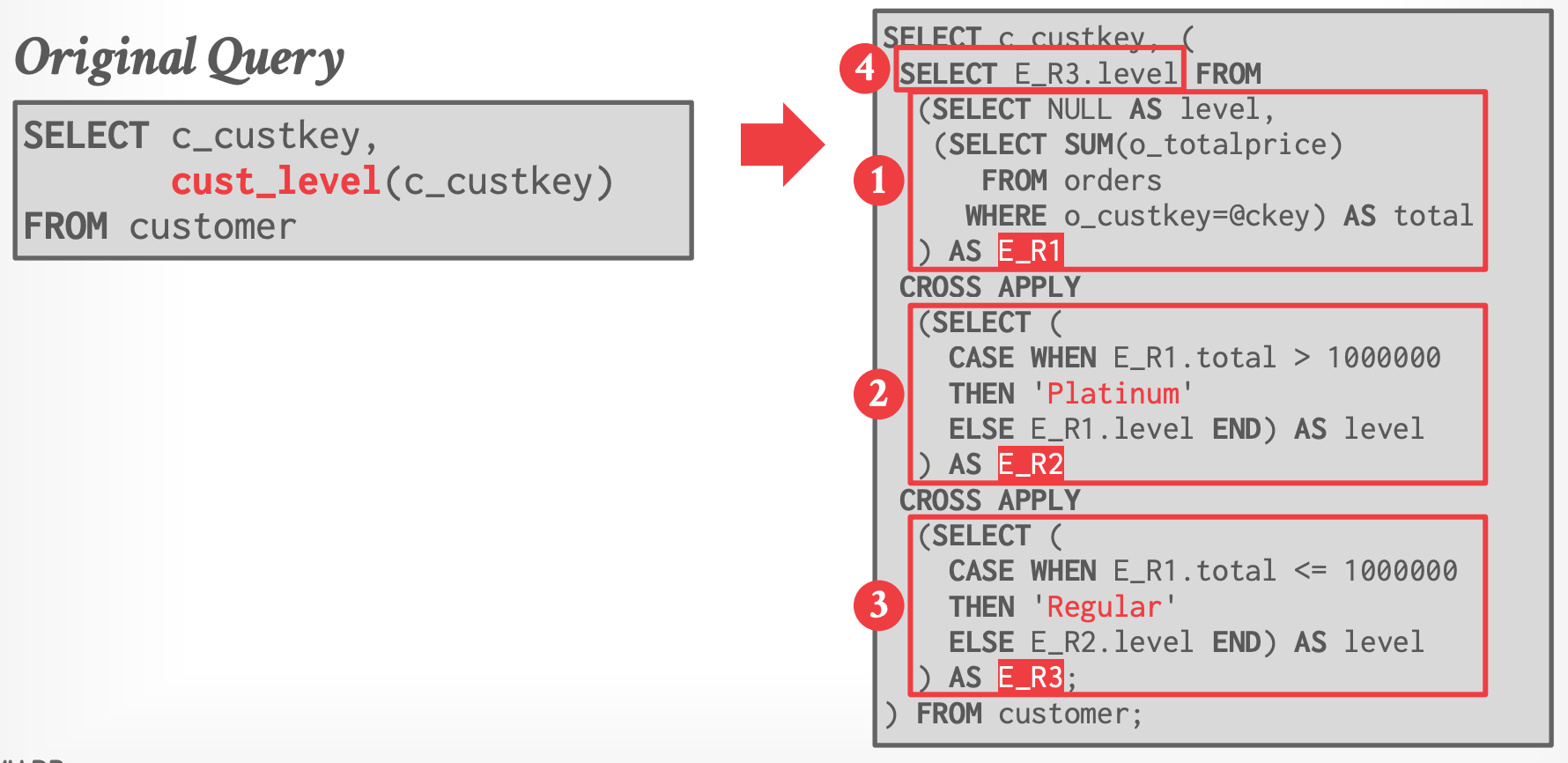
### Step #4 - Inline Expression
- 将 UDF 生成的 SQL 语句嵌入到原始查询语句中
### Step #5 - Optimize
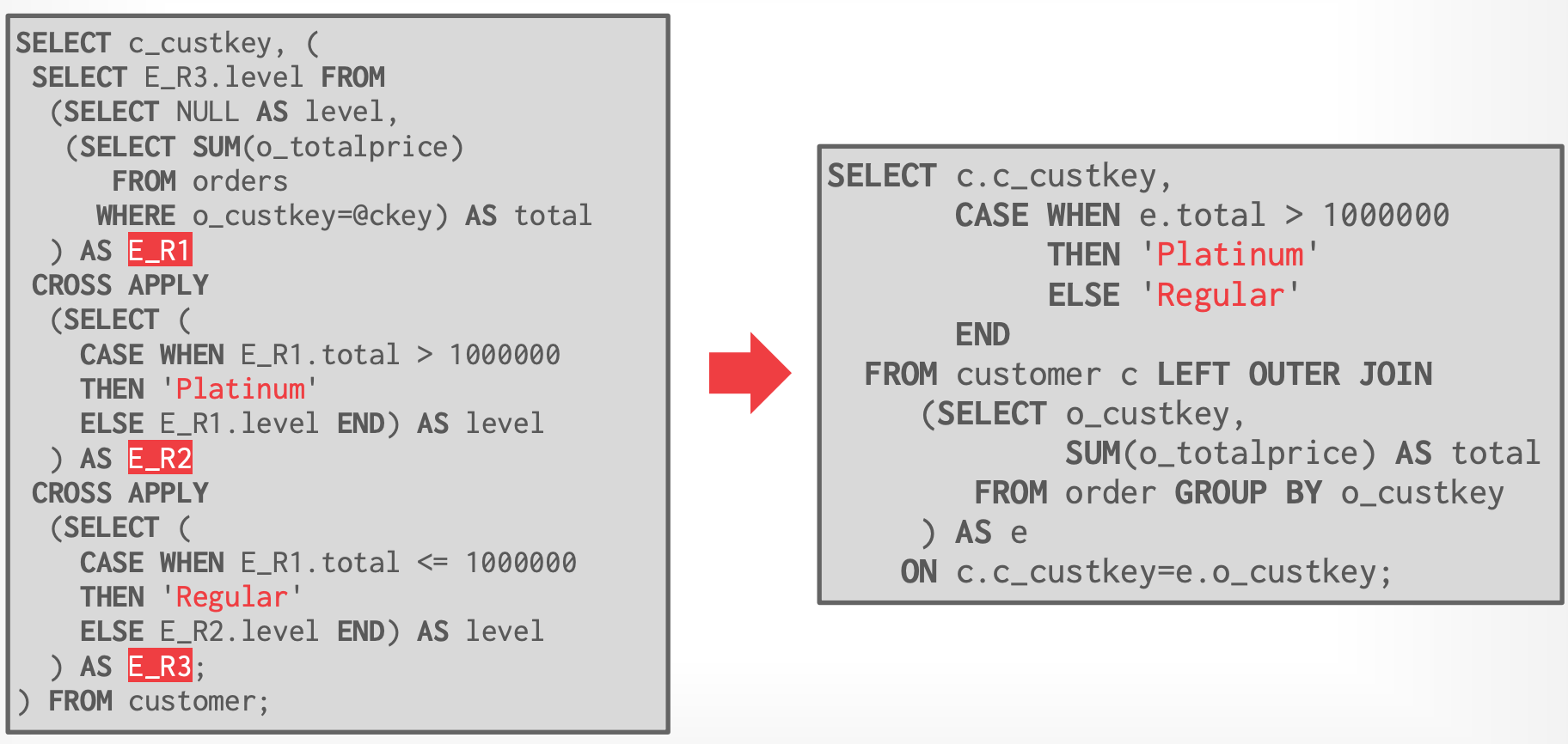
- **Bonus Optimizations**
- 
- 
- 传入的参数是常量
## 3.5 Supported Operations(2019)
- 支持的 T-SQL 语法
- DECLARE,SET(变量声明、赋值)
- SELECT(SQL query、assignment)
- IF / ELSE / ELSE IF(支持任意嵌套)
- RETURN(可以出现多个)
- EXISTS、NOT EXISTS、ISNULL,IN 等其他关系代数操作
- 调用UDF(即在一个 UDF 中调用另外一个 UDF,可以配置需要 inline 的 depth)
- 所有的 SQL datatypes
- inline 可以覆盖的场景
- 
--------
# 4. APFEL: UDFs-To-CTEs
- 将 UDFs 重写为 CTEs
- 使用 recursive CTEs 可以实现 Forid 无法支持的 iterations 和 其他 control flow
- 以 rewrite middleware layer 的形式,可以运行在任何支持 CTEs 的 DBMS 中
- [Compiling PL/SQL Away](https://15721.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2020/papers/24-udfs/p1-duta-cidr20.pdf)
## 4.1 Overview
1. [Static single-assignment form](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Static_single-assignment_form)
2. [Administrative Normal Form](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A-normal_form)
3. Mutual to Direct Recursion
4. Tail Recursion to `WITH RECURSVE`
5. Run Through Query Optimizer
### Step #1 - Static Single Assignment
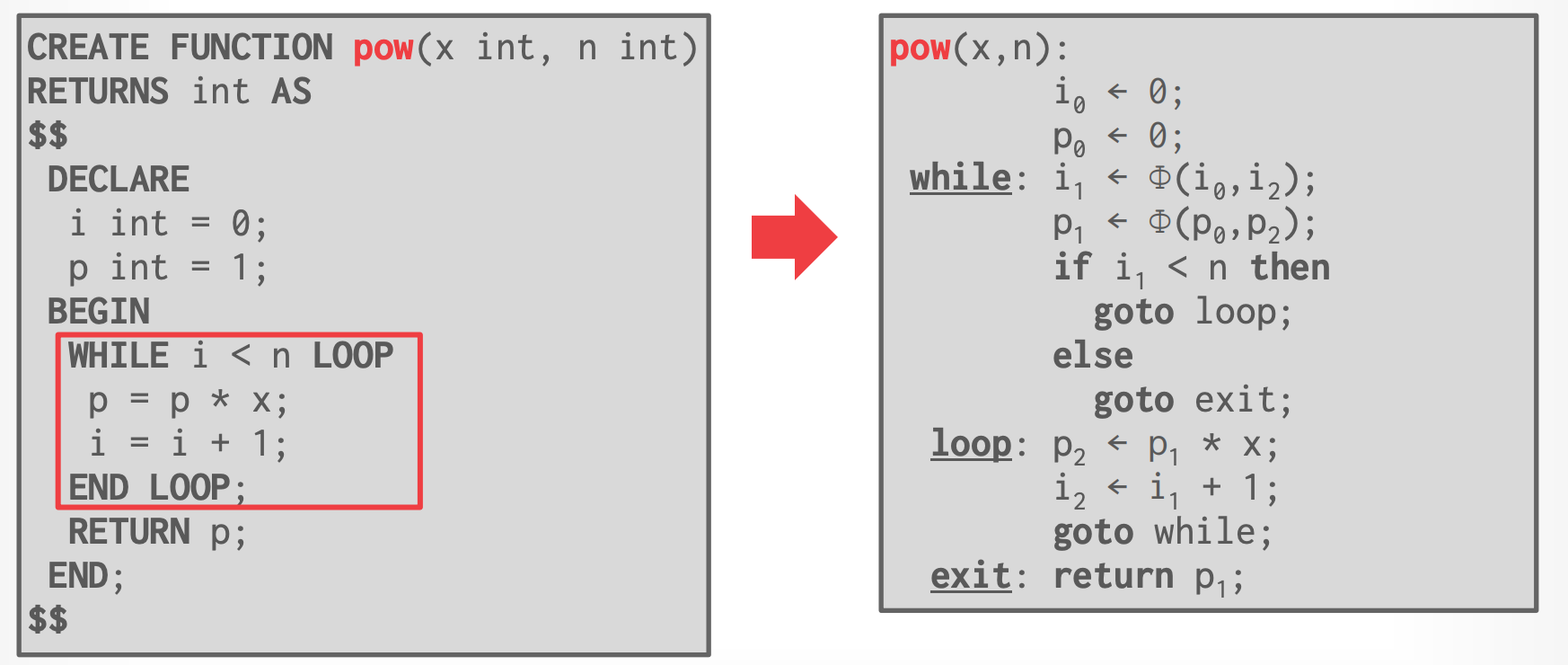
### Step #2 - Administrative Normal Form
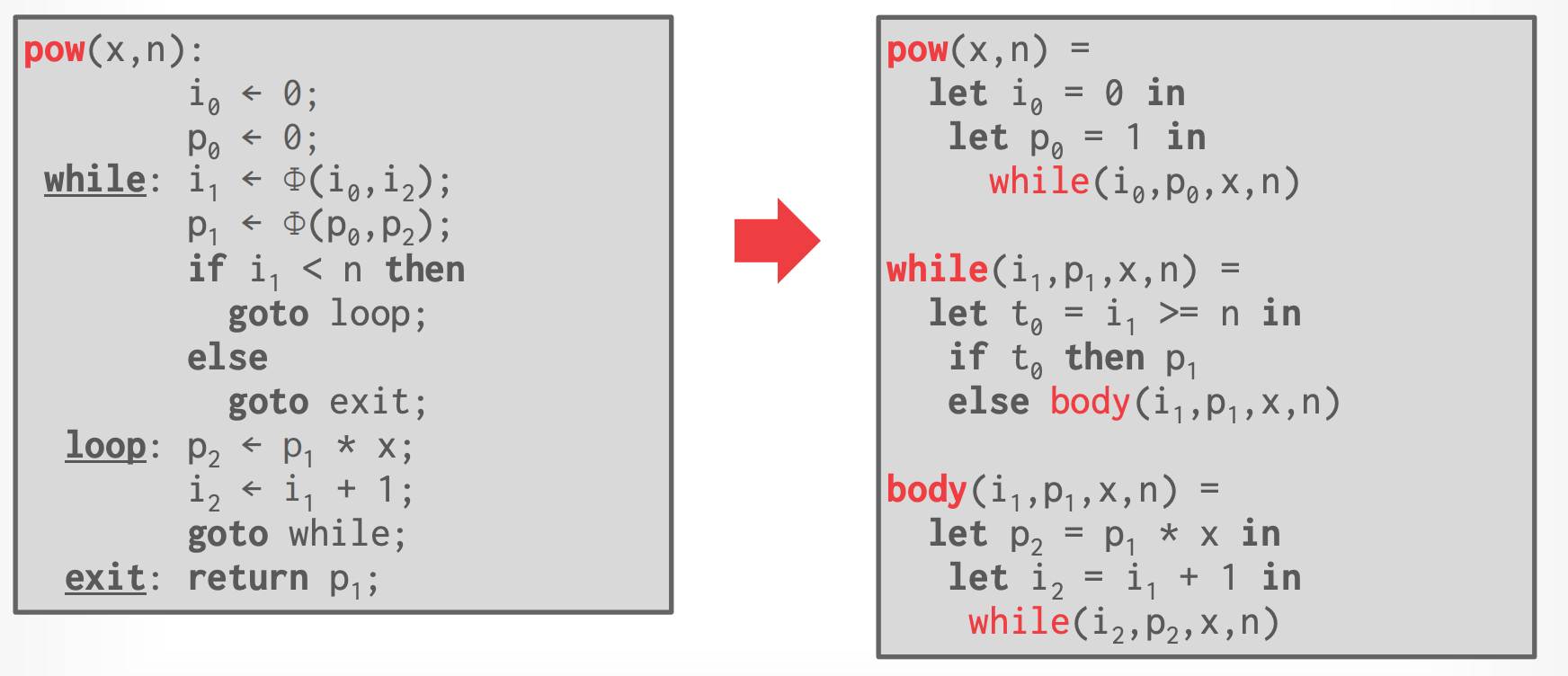
- 多个 blocks
### Step #3 - Mutual To Direct Recursion
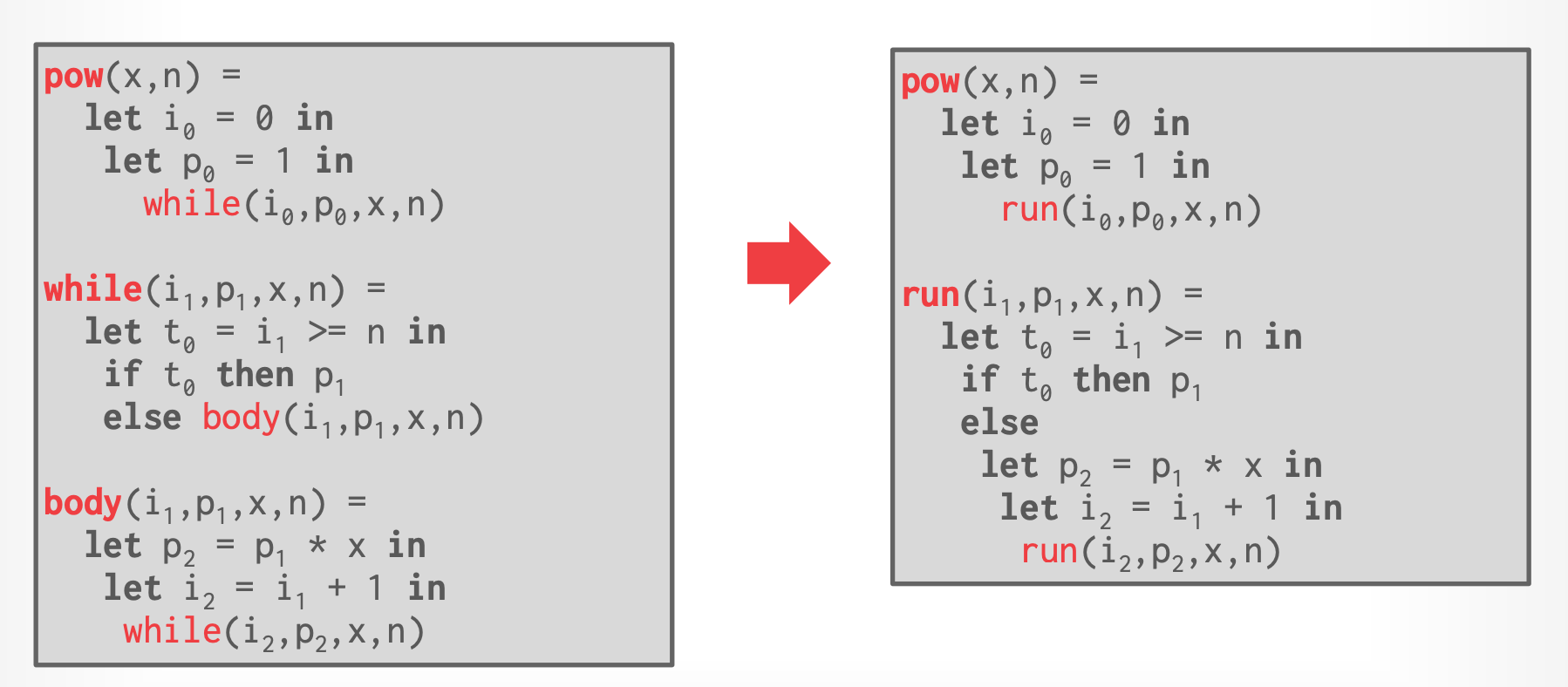
- 只能在函数的结束处调用另外一个函数
### Step #4 - WITH RECURSIVE
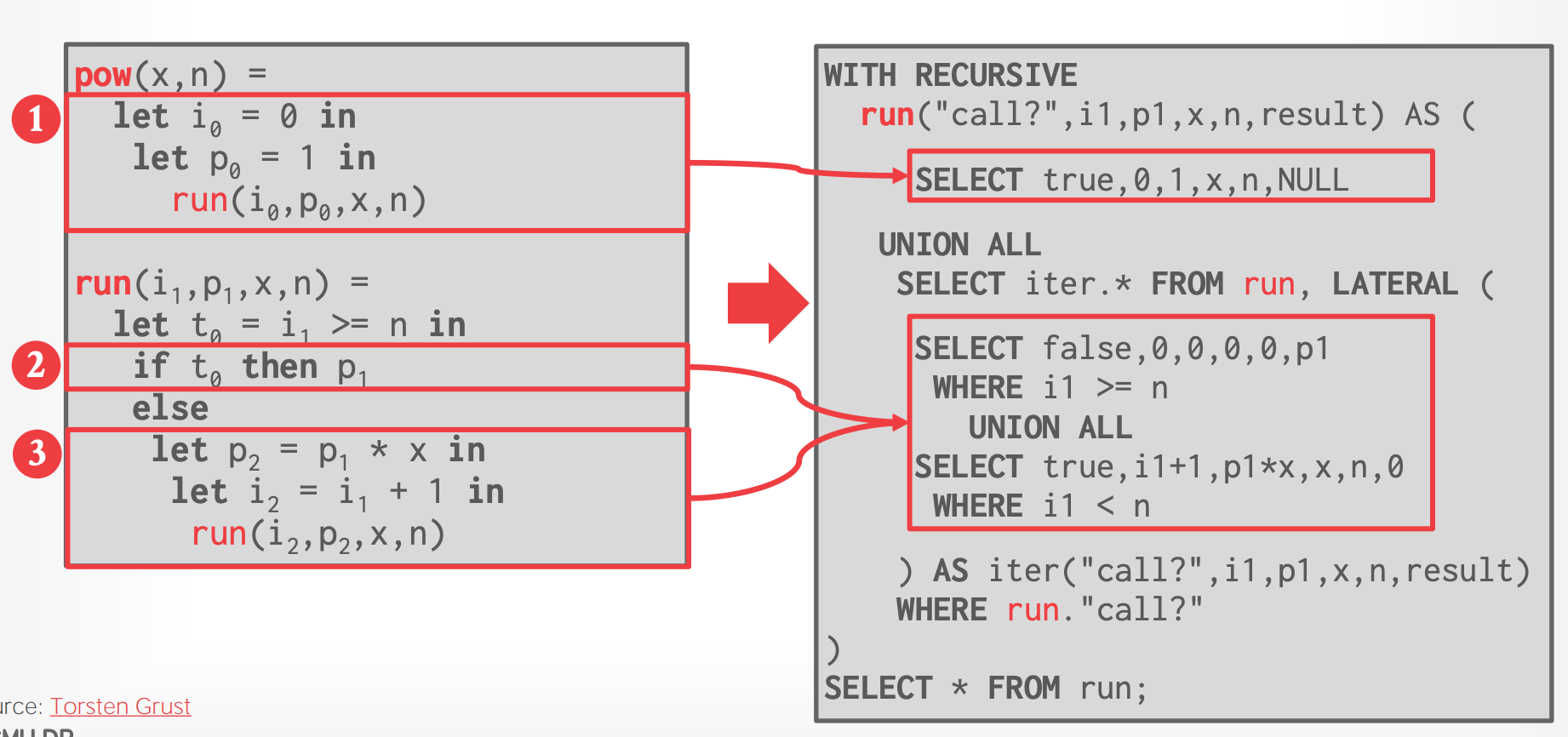
-----------
# 5. Froid: What Happened Next
- **2018** – Froid added to SQL Server 2019.
- **2019** – Huge performance wins in the wild.
- **2020** – High praise from Andy.
- **2021** – ProcBench paper released.
- [Procedural Extensions of SQL: Understanding their usage in the wild](https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol14/p1378-ramachandra.pdf)
- [SQL-ProcBench](https://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol14/p1378-ramachandra.pdf)
- SQL Server 的 optimizer 只能 decorrlate 2 / 13 个带参数的 UDFs
- Umbra optimizer 可以 decorrelate 所有 13 个 UDFs
## 5.1 Decorrelation Of SubQueries
### MSSQL
- [Orthogonal optimization of subqueries and aggregation](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/375663.375748)
- Some rewrites may require duplicating subexpressions in the query plan tree (and are cost-based decisions)
### Germans
- [Unnesting Arbitrary Queries](https://cs.emis.de/LNI/Proceedings/Proceedings241/383.pdf) [[unnesting-arbitrary-queries]]
- 引入一个新的 Dependent Join operator 到 Query Plan DAG 中
- 可以系统地 decorrelates 任意 subquery
- UDF inlining 后为了获取更好的性能,需要一个 German-style query optimizer
- 如 DuckDB
---------
# Parting Thoughts
- 另外一种优化方式:将 UDF 编译成机器码
- 但是无法解决 optimizer 的 cost model 问题