# 1. Logical Query Optimization
- 使用 pattern matching rules 将一个 logical plan 转换成另一个等价的 logical plan
- 目标是增加在搜索中枚举出最佳 plan 的可能性。
- 这些 plan 之间无法相互比较,因为没有 cost model。
- 但可以始终直接转换成更好的那个(比如 1=2 -> false)
- [Course:Query Optimization](https://db.in.tum.de/teaching/ws1819/queryopt/?lang=en)
## 1.1 Split Conjunctive Predicate
- 将 predicates 分解成它们最简单的形式,以便 optimizer 更容易移动它们
- 将单个 filter 表达式拆分
## 1.2 Predicate Pushdown
- 将 predicate 移动到 plan 中尽可能低的位置
## 1.3 Replace Cartesian Products with Joins
- 使用 join predicates 将所有 Certesian Products 替换为 inner joins。
## 1.4 Projection Pushdown
- 在 pipeline breaker 之前消除多余的 attributes,来减少 materialization cost。
-------
# 2. Physical Query Optimization
- 将 query plan 的 logical operators 转换成 physical operators
- 添加更多的 execution infomation
- 选择 indexes / access paths
- 挑选 operator 的实现
- 选择何时 materialize(例如 temp tables)
- 该阶段必须支持 cost model estimates
## 2.1 Observation
- 真实世界的查询语句更加复杂
- Outer Joins
- Semi Joins
- Anti Joins
- Lateral Joins
## 2.2 Reordering Limitations
```SQL
SELECT * FROM A
LEFT OUTER JOIN B ON A.id = B.id
FULL OUTER JOIN C ON B.val = C.id;
```
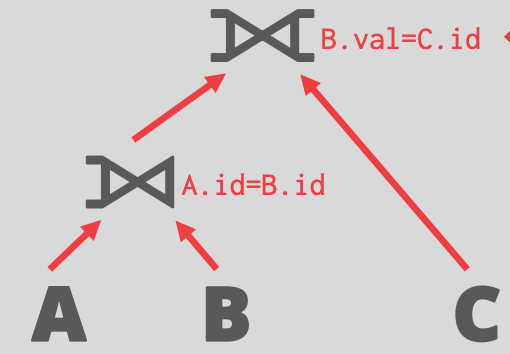
- 不能进行 reordering
- 两个 join operators 不满足交换律
- The DBMS does not know the value of `B.val` until after computing the join with A.
- down-top 方式更容易处理这种情况
## 2.3 Plan Enumeration
- **方式 #1 : Transformation**
- 修改一个已经存在的 query plan 的某些部分,转换成另一个等价的 plan
- Top-Down Search
- **方式 #2 : Generative**
- Iteratively assemble and add building blocks to generate a query plan
- Bottom-Up Search
- [On the correct and complete enumeration of the core search space](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/2463676.2465314)
## 2.4 Dynamic Programming Optimizer
- [Dynamic Programming Strikes Back](https://15721.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2020/papers/20-optimizer2/p539-moerkotte.pdf)
- 将 query 建模为一个 hypergraph,然后逐步扩展来枚举 new plans
- Algorithm Overview:
- Iterate connected sub-graphs and incrementally add new edges to other nodes to complete query plan
- Use rules to determine which nodes the traversal is allowed to visit and expand.
- **Examples**:
- Hyper
- Umbra
- DuckDB
------------
# 3. Cascades
- [The Cascades Framework for Query Optimization](https://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/infolab/Data/Courses/CS632/Papers/Cascades-graefe.pdf)
- [EFFICIENCY IN THE COLUMBIA DATABASE QUERY OPTIMIZER](https://15721.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2020/papers/20-optimizer2/xu-columbia-thesis1998.pdf)
- Vocano query optimizer 的面向对象实现
- Top-down 方式(backward chaining),使用 branch-and-bound search
- [ ] Supports simplistic expression re-writing through a direct mapping function rather than an exhaustive search.
- Key ideas:
- **Optimization tasks as data structure**
- task 结构定义了目标 pattern 和 transformation,交给 search / rules engine
- heuristic:if else 语句
- **Rules to place property enforcers**
- 可以定义 property 约束,engine 确保 subtree 满足 properties
- **Ordering of moves by promise**
- 可以定义优先级,应用 transformations 的顺序
- 根据 cost model 可以即时调整
- **Predicates as logical/physical operators**
- where clauses / join clauses
- microsoft 不支持,cockroach 支持(scalar expressions)
- [ ] [Halloween Problem](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Halloween_Problem)
## 3.1 Expressions
- Cascades 中 的一个表达式代表了查询中的某个操作,它可以有零到多个 input 表达式。
- Hign level operator
- Optimizer 需要能够快速判断两个表达式是否等价
```SQL
SELECT * FROM A
JOIN B ON A.id = B.id
JOIN C ON C.id = A.id;
```
- **Logical Expresssion**: $\large (A \bowtie B) \bowtie C$
- **Physical Expression:** $\large (A_{seq} \bowtie_{HJ} B_{Seq}) \bowtie_{NL} C_{Idx}$
## 3.2 Groups
- 一个 group 是一组逻辑上等价的 logical 和 physical expressions,它们输出的结果相同(unordered)
- 一个表达式的所有逻辑形式
- 为相应的逻辑形式选择**允许的**物理 operators ,而所产生的所有物理表达式
- 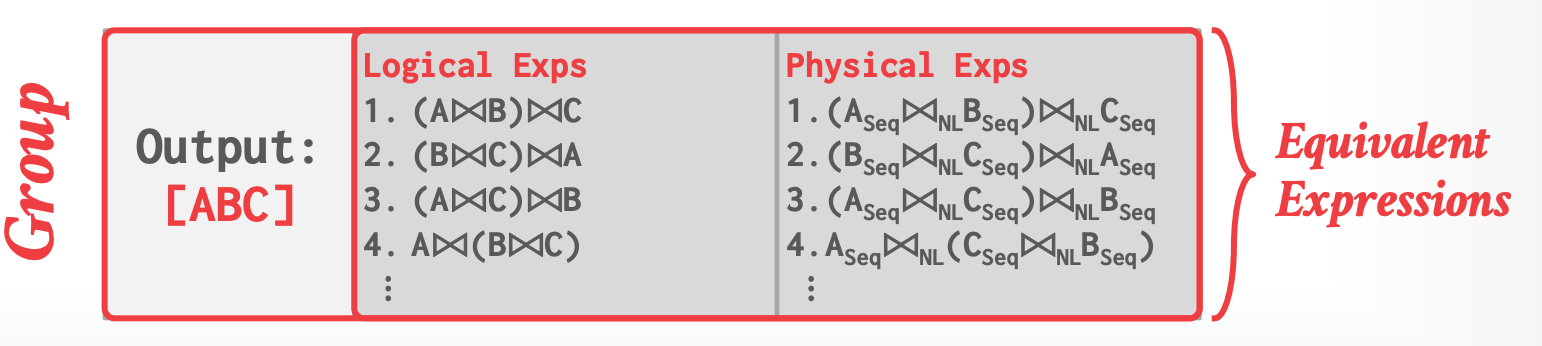
- Vocolno:一次性生成整个 group,然后物化。(例如100个 tables join,物化的结果会非常大)
- Cascades:按需 on-the-fly 生成 group 内的表达式
## 3.3 Multi-Expression
- Optimzer 不显式地实例化 group 内所有可能的表达式,而是将 group 内冗余的表达式隐式地表示为一个 multi-expression
- 可以减少 transformations 的 次数、storage overhead 和重复的 cost estimations
- 
- A、B 是一个 placeholder,可能有多种形式,这里不关心它具体是什么
## 3.4 Rules
- **Rule** 将一个表达式转换成另一个等价的表达式
- **Transformation Rule**:Logical -> Logical
- **Implementation Rule**:Logical -> Physical
- 每条 rule 表现为一对属性:
- **Pattern**:定义了可以应用这条规则的 logical expression 的结构
- **Substitue**:定义应用完规则后结果的结构(the structure of the result)
- 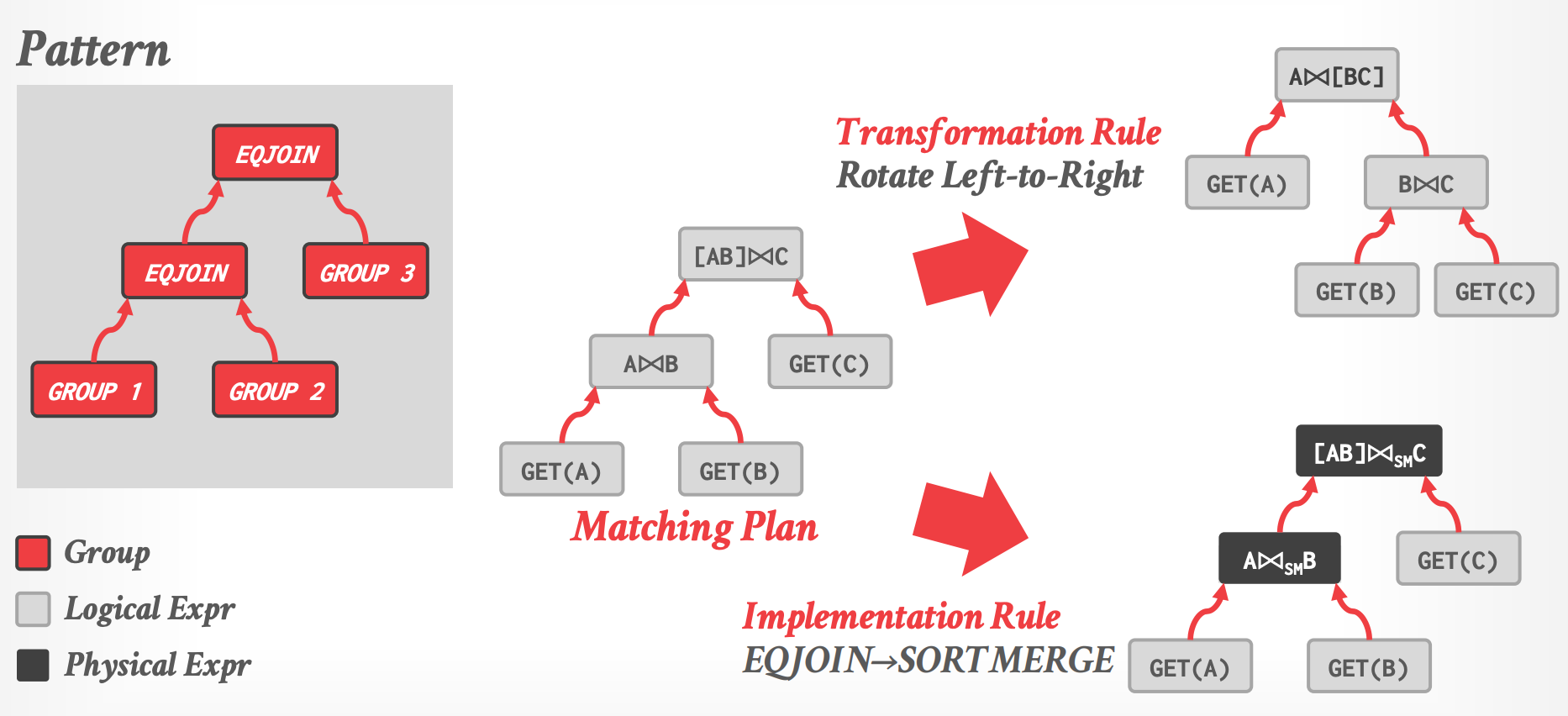
- Group: placeholder
- 潜在问题:两条相反的规则,来回转换,无限循环
## 3.5 Memo Table
- 存储之前所有已经 explored alternatives 到一个紧凑的 graph structure / hash table
- 原始 paper 使用 graph structure,大多数开源实现使用 hash table
- 等价的 operator trees 和 他们对应的 plans 一起存储到 group 中。
- 提供 memoization、duplicate detection 以及 property 和 cost managent
- 如果之前已经 subtree 做过这个 transformation,则可以重用它(包含它的 cost 信息)
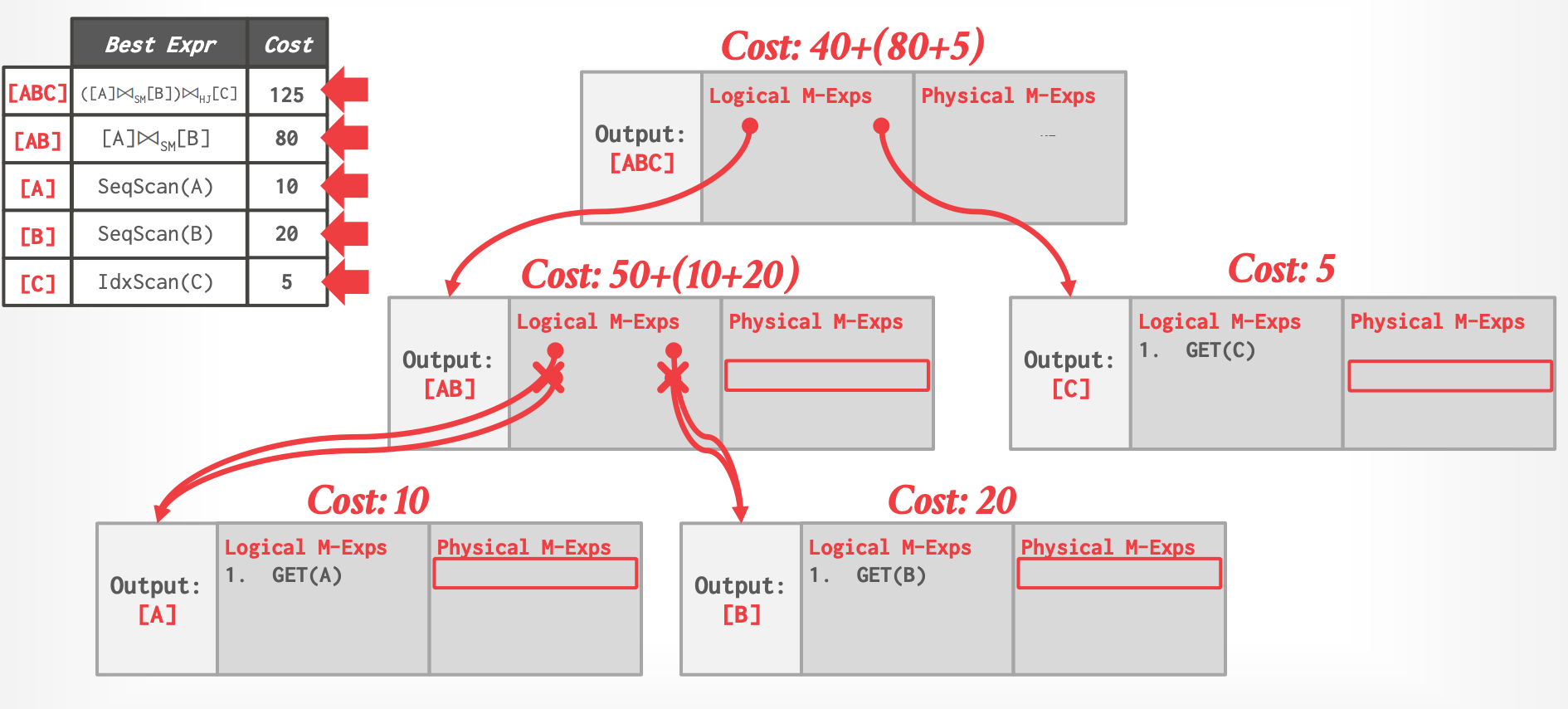
### Principle Of Optimality
- [Exploiting Upper and Lower Bounds In Top-Down Query Optimization](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/646290.686937)
- 一个 Optimal plan 的每个 sub-plan 自身也是 optimal
- cost 是累加的
- 这使得 optimizer 可以限制 search space 到一个组较小的 expressions。
- optimizer 不需要考虑如下 plan:
- 它包含了一个 sub-plan P1,P1 比与它等价且 pyhsical properties 相同的 P2 的 cost 高
- 
## 3.6 Search Termination
- **方式 #1 :Transformation Exhaustion**
- Usually done per group
- **方式 #2 :Wall-clock Time**
- **方式 #3 :Transfomation Count**
- **方式 #4 :Cost Threshold**
- 找到一个 cost 低于某个阈值的 plan 后停止
## 3.7 Implementations
- **Standalone**:
- [Wisconsin OPT++](https://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~navin/research/apg.html) (1990s)
- [Portland State Columbia](http://web.cecs.pdx.edu/~len/Columbia/) (1990s)
- [Greenplum Orca](https://github.com/greenplum-db/gporca) (2010s)
- [Apache Calcite](https://calcite.apache.org/) (2010s)
- **Integrated**:
- Microsoft SQL Server (1990s)
- [Tandem NonStop SQL](https://www.vldb.org/conf/1996/P592.PDF)(1990s)
- [Clustrix](http://docs.clustrix.com/display/CLXDOC/Query+Optimizer)(2000s)
- CockroachDB (2010s)
------------
# 4. Real-World Implementations
## 4.1 Microsoft SQL Server
- 1995年开始,第一个 Cascades 实现
- 衍生产品在许多微软数据库产品中使用
- 所有的 transformations 都使用 C++ 编写,没有 DSL
- Scalar / expression transformations 使用 procedural code 而非 rules
- DBMS 在多个阶段应用 transformation,会增加优化的 scope 和 complexty
- The goal is to leverage domain knowledge to apply transformations that you always want to do first to reduce the search space.
- [video: The Cascades Framework for Query Optimization at Microsoft](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pQe1LQJiXN0)
- 
- Trivial Plan Short-circuit:比如 select * 带主键条件,足够简单,不需要进一步优化
- Statistics Identification / Collection:如果没有统计信息,可能会阻塞现场收集
- **Optimization #1 :** Timeouts 基于 transformations 的个数而非 wallclock time
- 保证 overloaded system 不产生跟常规操作不同的 plans
- **Optimization #2:** Pre-popluate Memo table(针对可能有用的 join orderings,先放进去)
- Heuristics that consider relationships between tables
- Syntactic appearance in query.
## 4.2 Apache Calcite
- [Apache Calcite: A Foundational Framework for Optimized Query Processing Over Heterogeneous Data Sources](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3183713.3190662)
- 单独可扩展的查询优化框架,使用于 data processing systems
- 支持可插拔的 query languages、cost models 和 rules
- 不区分 logical 和 physical operators,physcial operators 以 annotations 的形式提供
- 最初是 [LucidDB](https://dbdb.io/db/luciddb) 的一部分
## 4.3 Greenplum Orca
- [Orca: a modular query optimizer architecture for big data]()
- [https://github.com/greenplum-db/gporca](https://github.com/greenplum-db/gporca)
- 独立的 C++ Cascades 实现
- 最初为 Greenplum 而写
- 扩展支持了 [HAWQ](https://hawq.apache.org/)
- DBMS 集成 Orca 的方式:
- 实现 API 提供 catalog、stats 和 logical plans
- Orca 输出 physcial plans
- 支持多线程 search
### Engineering
- **Remote Debugging**
- 当错误发生时自动 dump optimizer 的 state
- dump 可以让 optimizer 恢复出问题的现场,方便进一步调试
- **Optimizer Accuracy**
- 自动检查两个 plan 的 cost ordering 是否与实际执行的 cost 相匹配。
- 同时运行 best 和 second plan
## 4.4 Cockroachdb
- 2018 年编写的 custom cascades 实现
- 所有的 transfomation rules 使用 DSL([OptGen](https://github.com/cockroachdb/cockroach/blob/master/pkg/sql/opt/optgen/lang/doc.go)) 来编写,然后 codgen 成 golang。
- 可以在 rule 中内嵌 Go 逻辑来执行复杂的分析和修改
- 跟 relational operator 一起考虑了 scalar expression(predicates)的 transformation
- [Video: CockroachDB's Query Optimizer](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wHo-VtzTHx0)
## 4.5 SingleStore
- [Paper: The MemSQL Query Optimizer](http://www.vldb.org/pvldb/vol9/p1401-chen.pdf)
- **Rewriter**
- Logical-to-Logical transformations(with access to the cost model)
- **Enumerator**
- Logical-to-physical transformations
- 大多是 join ordering
- **Planner**
- 将 enumerator 生成的 phyiscal plan 转换回 SQL,将 SQL 发生到 executor nodes
- 再次进行优化,借助 executor local 的 统计信息
- Contains SingleStore-specific commands for moving data
----------
# Parting Thoughts
- 所有这些都依赖一个好的 cost model
- 一个好的 cost model 依赖好的 statistics