# 1. Systems Discussion
- Google BigQuery / Dremel
- Databricks Spark SQL / Photon
- Snowflake
- DuckDB
- Velox
- Amazon Redshift
## 1.1 Reoccurring Themes
- Resource Disaggregation
- Lack of Statistics
- Columnar & Non-Relational Data
- Vectorized Execution
## 1.2 Data Systems At Google
- **NoSQL**
- MapReduce(2004) -> Hadoop, Spark
- BigTable (2005 ) -> Hbase, Accumulo, Hypertable
- Chubby (2006) -> Zookeepr, etcd
- **SQL**
- Megastore. (2010)
- Vitess (2010) -> Vitess, Planetscale
- Dremel (2011) -> Drill, Impala, Dermio
- Spanner (2011) -> CockroachDB, TiDB
- F1 (2013)
- Mesa (2014)
- Napa (2021)
-----------
# 2. Google Dremel
- Paper: [Dremel: a decade of interactive SQL analysis at web scale](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.14778/3415478.3415568)
- 视频:[Query Processing in Google BigQuery (Hossein Ahmadi + Aleksandras Surna)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zk5_RcRg3nA)
- 最初于2006年开发,作为分析其他工具生成的数据的 side project。
- 目标是 interactive,即支持对 data files 的原地 ad-hoc 查询
- 第一个版本不支持 joins
- 2010 年代后期改写为基于 GFS 的 shared-disk 架构
- 2012 年作为公开商业产品发布(BigQuery)
## 2.1 In-Situ Data Processing
- 以原始格式对存储在 shared storage 上的数据文件进行查询,不需要先 ingest 到 DBMS 中
- 通常也称为 data lake
- data laekhouse 是位于这些所有之上的 DBMS
- 目标是减少开始分析数据前的准备时间
- 用户期望牺牲查询性能来避免 re-encode / load data files
## 2.2 Key Features
- Shared-Disk / Disaggregated Storage
- Vectorized Query Processing
- Shuffle-based Distributed Query Execution
- Columnar Storage
- Zone Maps / Filters
- Dictionary + RLE Compression
- Only Inverted Indexes
- Hash Joins Only
- Heuristic Optimizer + Adaptive Optimizations
- 执行期间可调整 query plan
## 2.3 Query Execution
- DBMS 将一个 logical plan 转换成包含多个 parallel tasks 的 stages(pipelines)
- 每个 task 必须是 dererministic 和 idempotent,来支持 restarts
- Root node(Coordinartor)批量获取目标文件的元数据,然后嵌入到 query plan 中
- 避免几千个 workers 同时访问分布式文件系统上的元数据(如果是 worker 单独请求 coordinator 的话)
- 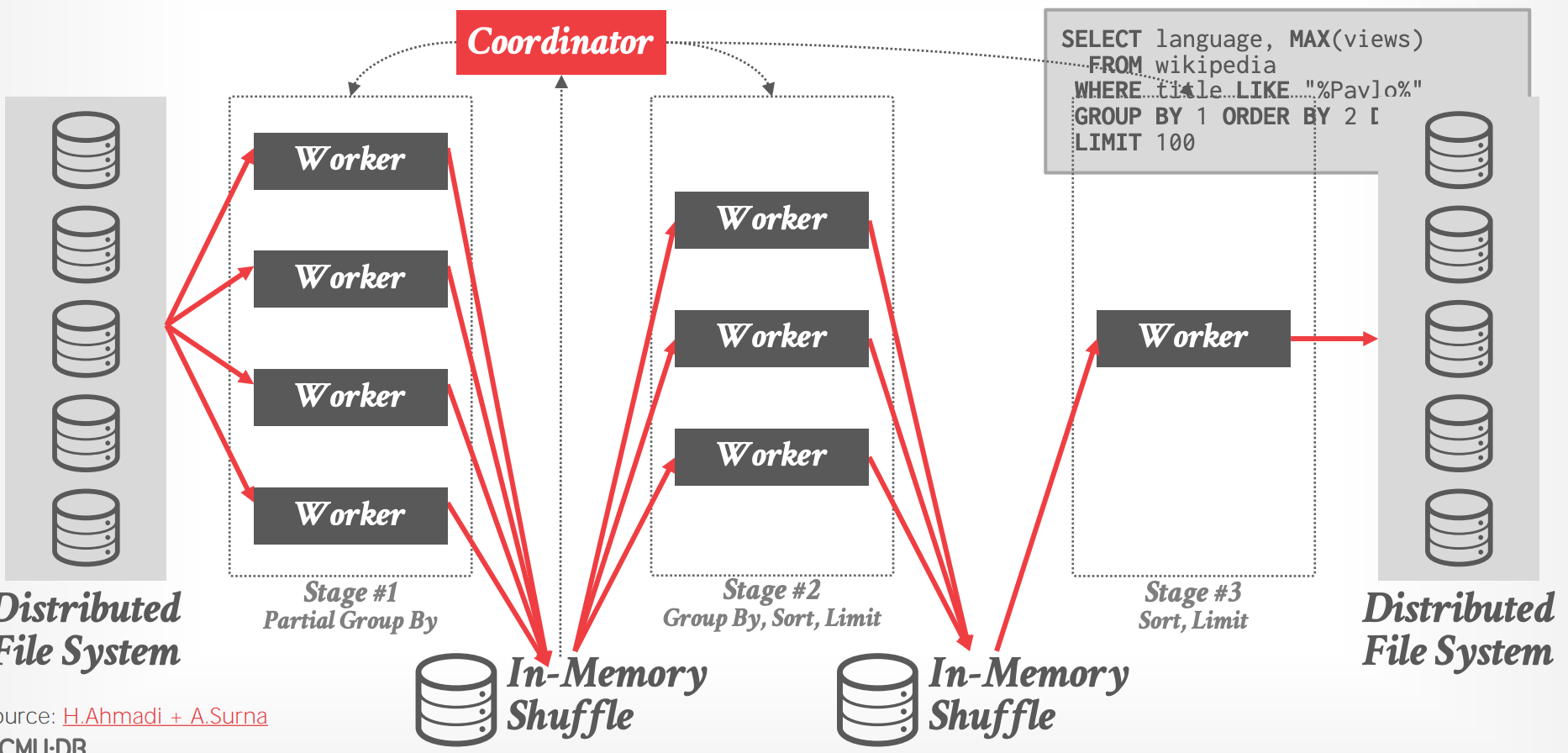
- Stage #2 可以 speculatively executing,即有些场景下不需要等 Stage 1 完成,就可以从它获取数据执行
- dedicated hardware for shuffle nodes,支持内存置换到磁盘
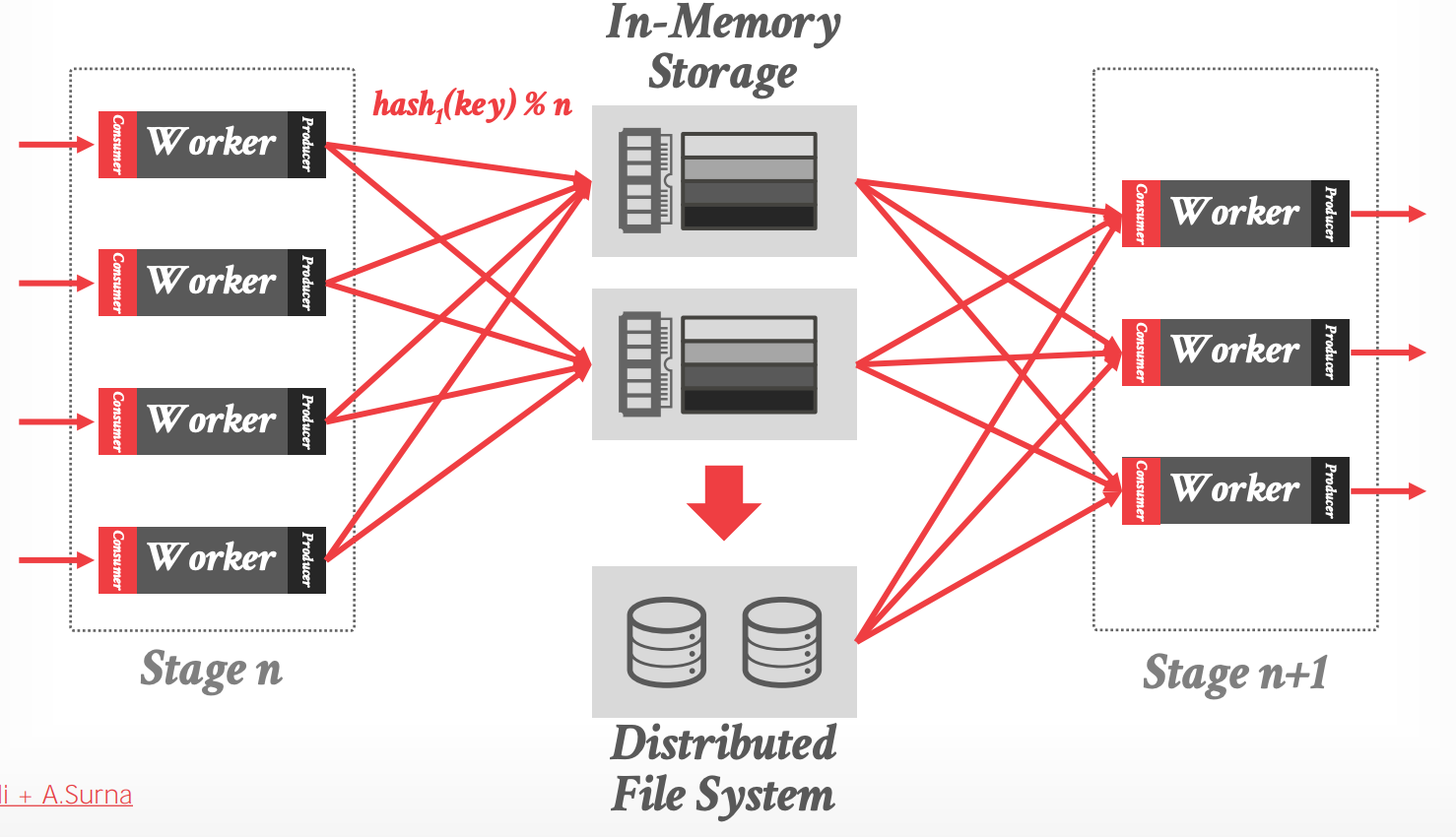
## 2.4 In-Memory Shuffle
- 生产者/消费者 模型,使用专门的节点(shuffle nodes),将一个 stage 的中间结果传输到下一个 stage。
- Workers 发送输出到 shuffle nodes
- Shuffle nodes 使用 hashed 分区在内存中存储数据
- 下一个 stage 的 workers 从 shuffle nodes 上获取它们的输入
- Shuffle nodes 在内存中存储数据,只在必要时才 spill 到 disk 上。
- 
- shuffle 阶段代表了查询生命期中的 checkpoints,coordinator 来保证所有的 tasks 都完成了。
- 当当前 stage 的所有 tasks 完成了且产生了输出后,会释放 worker 资源用于分配其他任务
- **Fault Tolerance / Staggler Avoidance**
- 如果一个 worker 没有在规定时间内产生 task 的结果,coordinator 会 speculatively 执行一个冗余的 task
- **Dynamic Resource Allocation**
- 根据 stage 的输出大小,增加 / 减少下一个 stage 的 workers 数量
## 2.5 Query Optimization
- 如果没有统计信息,DBMS 如何优化一个查询
- DBMS 之前没有见过这些 Data files
- 查询其他 DMBSs(connectors)
- Dremel 的 optimizer 使用了分层的形式(RBO + CBO 两遍)来生成一个初步的 physical plan 去执行
- Rules:predicate pushdown、star schema contriaint propagtion、primary / foreign key hints、join ordering
- CBO 只有当数据有统计信息时才能进行
- 为了避免 cost model 预估不准带来的问题,Dremel 使用 dynamic query optimization
### Dynamic Query Optimization
- 通过对之前 stage 的观测,**在 stage 开始之前**更改 query plan
- 避免数据统计信息不准带来的问题
- Optimization Examples
- 更改 stage 的 workers 数量
- shuffle vs. broadcast join 之前的切换
- 更改 physical operator 的实现
- dynamic repartitioning
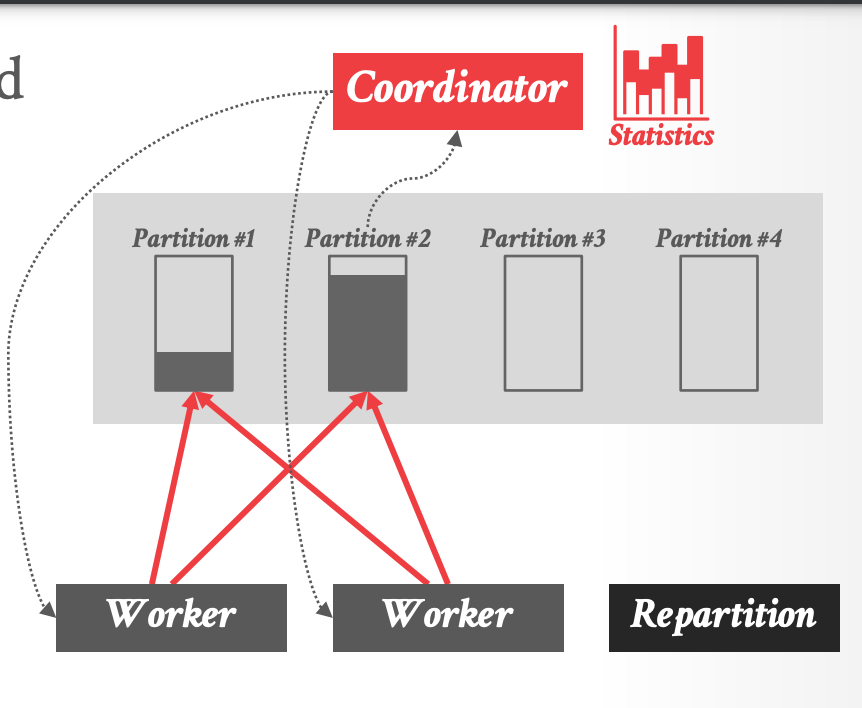
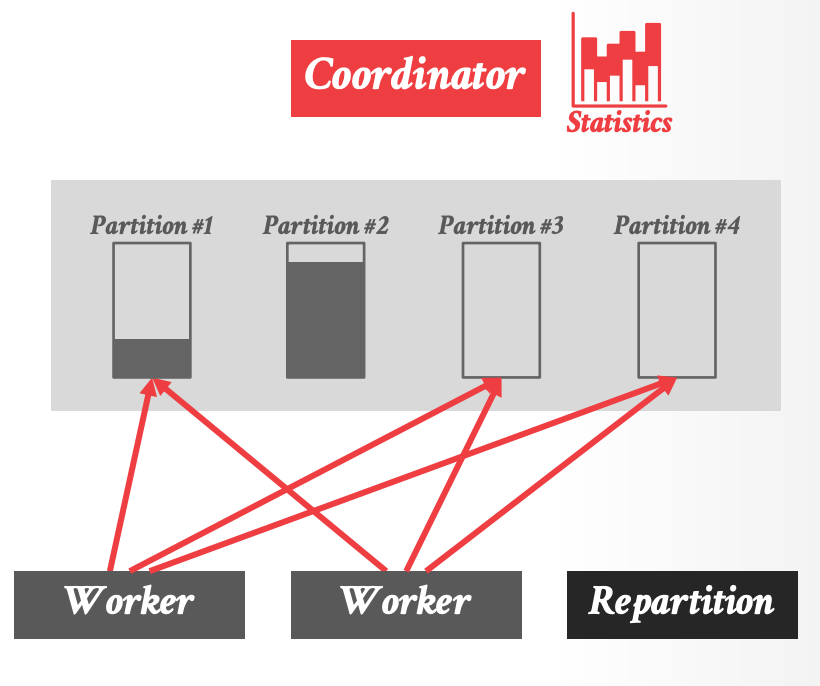
### Dynamic Repartitioning
- Dremel 动态地进行负载均衡,调整中间结果的分区方式,来适应 data skew
- DBMS 检测是否 shuffle partition 太满,然后指示 workers 调整它们的 partitioning schema.
- 示例:Partition 2 overfull
1. 
2. 
3. 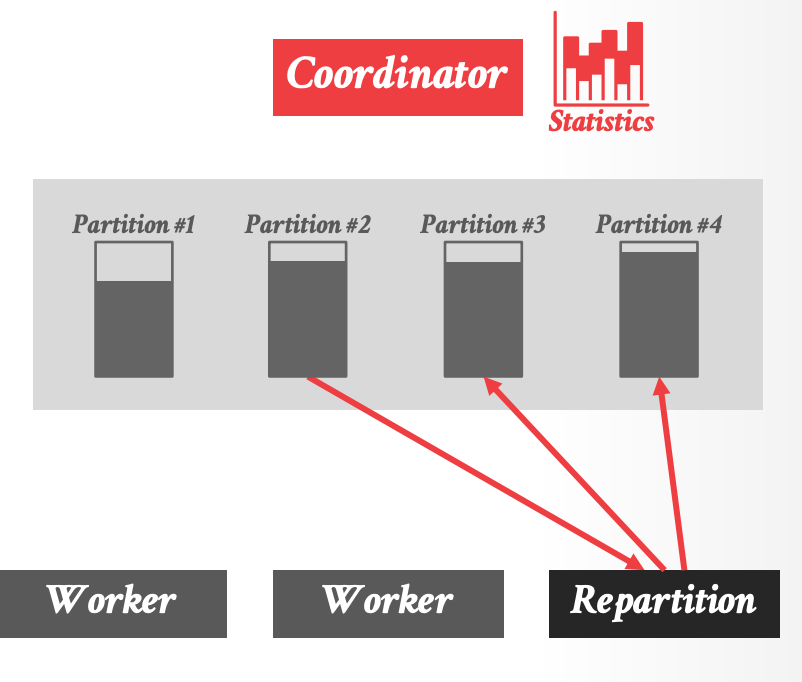
- Repartition 是一类特殊的 worker,负责将数据从旧的分区(2) rehash 到的新的分区(3和4)
## 2.6 Storage
- DMBS 依赖 Google 的分布式文件系统 [Colossus](https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/storage-data-transfer/a-peek-behind-colossus-googles-file-system) 来扩展存储容量
- 依赖 [Capacitor](https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/bigquery/inside-capacitor-bigquerys-next-generation-columnar-storage-format) 的列存编码机制来支持嵌套的关系型和半结构化数据
- Capacitor 还提供了带有 basic filtering 能力的访问库
- 类似 Parquet vs. Orc 格式
- [ ] Repetition and definition fields are embedded in columns to avoid having to retrieve/access ancestor attributes.
## 2.7 Schema Representation
- Dremel 内部的存储格式是自描述的
- DBMS 需要理解的所有东西都在文件内
- 但是 DBMS 读取文件时必须解析内嵌在文件内部的 schema
- 表可能有几千个列,大多数查询只需要一部分列
- DBMS 以列存的格式存储 schemas 来减少获取 metadata 的开销。
## 2.8 SQL
- 2010年代早期,许多 Google 内部的 DBMS 每一个都有自己的 SQL 方言。
- GoogleSQL projection 统一了这些重复的工作,构建了一个 data model、type system、syntax、semantic 和 function library。
- 开源版本:[ZetaSQL](https://github.com/google/zetasql)
- [Spanner: Becoming a SQL System](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3035918.3056103)
--------------
# 3. Observation
- 自从 2011 的 VLDB paper 后,多个 DBMS projects 拷贝 / 参考了 Dremel
- [Apace Drill](https://drill.apache.org/)
- [Dremio](https://www.dremio.com/)
- [Apache Impala](https://impala.apache.org/)
- [Apache Uniffle](https://uniffle.apache.org/)提供了 distributed shuffle as a service。
## 3.1 Apache Drill
- Dremel 的开源实现,但构建在 Hadoop 之上
- 项目于2012年在 MapR 启动
- 利用 [Janino](http://janino-compiler.github.io/janino/)实现了代码生成
- HPE 在 2020 年宣布不再支持 Drill 的开发。
## 3.2 Dremio
- 基于 Apache Arrow,受到 Dremel 启发的 开源 / 商业 DBMS
- 开始于2015年, CMU 校友开发
- 借助 user-defined materialized views([reflections](https://docs.dremio.com/software/reflections/)) 来加速对外部数据文件的查询
- 同样依赖 Java-based codegen 和 向量化。
## 3.3 Apache Impala
- 受到 Dremel 启发的 DBMS,在分布式文件系统上执行查询
- 2012 年开始,Cloudera 公司
- 支持 codegen of filters 和 parsing logic。
- 在每个数据节点上放置 exectuor 组件,以提供解析和谓词下推。
- 
-------
# Parting Thoughts
- Dremel是一种创新的DBMS,早于所有其他主要的云原生OLAP DBMS。
- shuffle 阶段看起来存在浪费,但是简化了工程实现,并且可以提升性能。
- 它也是将 DBMS 的组件分解为单独的服务以抽象 raw resources 的好例子。