# 1. History
## Advent of Spark
- 来自 Berkeley,高性能和更具表达能力的 Hadoop 替代品。
- 存算分离
- 支持 迭代算法(相同的数据多遍处理)
- 使用 Scala 编写,所以 运行在 JVM 上。
- 最初只支持 low-level RDD API。
- 后来添加了更高层次的抽象即 [DataFrame](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pandas_(software)#DataFrames) API。
## Shark(2013)
- [Shark: SQL and rich analytics at scale](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/2463676.2465288)
- Facebook Hive 中间件的修改版,可以将 SQL 转换成 Spark API 程序(jobs)。
- SQL 只支持注册到 Hive Catalog 上的 data files。
- Spark 程序在 API 调用中间无法执行 SQL。
- Shark 依赖 Hive 的 query optimizer,该 optimizer 是为在 Hadoop 上运行 Map-reduce jobs 而设计的
- Spark 拥有功能更丰富的 native API。
## Spark SQL(2015)
- [Spark SQL: Relational Data Processing in Spark](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/2723372.2742797)
- Row-based SQL engine,原生地运行在 Spark 内部,支持 Scala-based query **codgen**。
- 中间结果使用内存中的列存形式(raw byte buffers)
- Dictionary encoding、RLE、bitpacking compressions
- query stages 之间使用 in-memory shuffle
- DBMS 将查询的 WHERE 从句表达式树转换成 Scalar ASTs,然后编译 ASTs 来生成 JVM bytecode。
## Databricks Photon(2022)
### JVM Problems
- Databricks 的负责逐渐变得 CPU bound
- NVMe SSD caching 和 adaptive shuffling,带来了更少的 disk stalls。
- Better filtering to skip reading data
- 他们发现很难进一步优化基于 JVM 的 Spark SQL 执行引擎
- heap 大于 64 GB 时的 GC slowdown
- 对于 large methods, JIT codegen 存在限制
### Photon
^d56cfa
- [Photon: A Fast Query Engine for Lakehouse Systems](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3514221.3526054)
- 单线程的执行引擎(不是一个独立的系统),通过 JNI 嵌入到 Databricks Runtime(DBR)中。
- 在适当的情况下覆盖现有引擎
- 同时支持 Spark 的早期 SQL engine 和 Spark 的 DataFrame API
- 无缝处理 row-oriented DBR 与 column-oriented Photon 之间的阻抗不匹配。
- 加速对 data lake 中 raw / uncurated files 之上 query plans 的执行
### Key Features
- Shared-Disk / Disaggregated Storage
- Pull-based Vectoroized Query Procesing
- Precompiled Primitives + Expression Fusion
- Shuffle-based Distributed Query Execution
- Sort-Merge + Hash Joins
- Unified Query Optimizer + Adaptive Optimizations
------------
# 2. Spark
## Spark: Query Execution
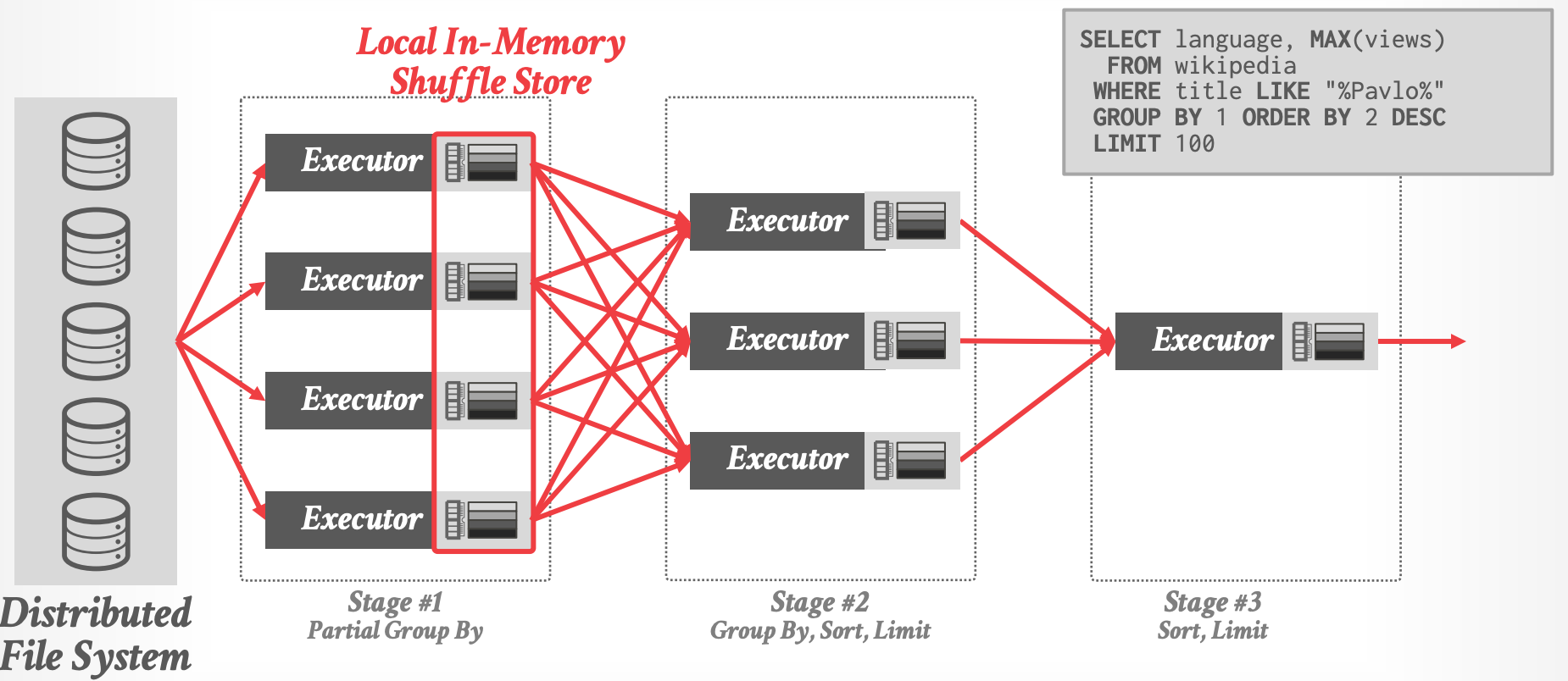
## Photon: Vectorized Query Processing
- Photon 是一个 pull-based vectorized engine,operator kernels 使用了 precompiled primitives。
- 将 physical plan 转换成一系列对 column batches 执行 low-level 操作的函数指针
- Databricks:构建/维护 vectorized engine 比 JIT engine 更容易
- 花费很多时间来创建 specialized codepaths,来接近 JIT 的性能
- 每次调用 Photon operator 的 GetNext,都输出一个 column batch
- 一个或多个 column vectors,一个 postition list vector (表明哪些位置是有效的)
- 每个 column vecor 包含了 null bitmap
- 
- Databricks: Position list vector 性能比 active row bitmap 好
- [Filter Representation in Vectorized Query Execution](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3465998.3466009)
- Photon 不支持 Hyper-style operator fusion,好处是可以收集每个 operator 的 metrics 来帮助用户理解 query behavior。
- Vertical fusion over multiple operators in a pipeline.
- 但 Photon 支持 expresion primitives 融合来减少函数调用
- Horizontal fusion within a single operator.
- 
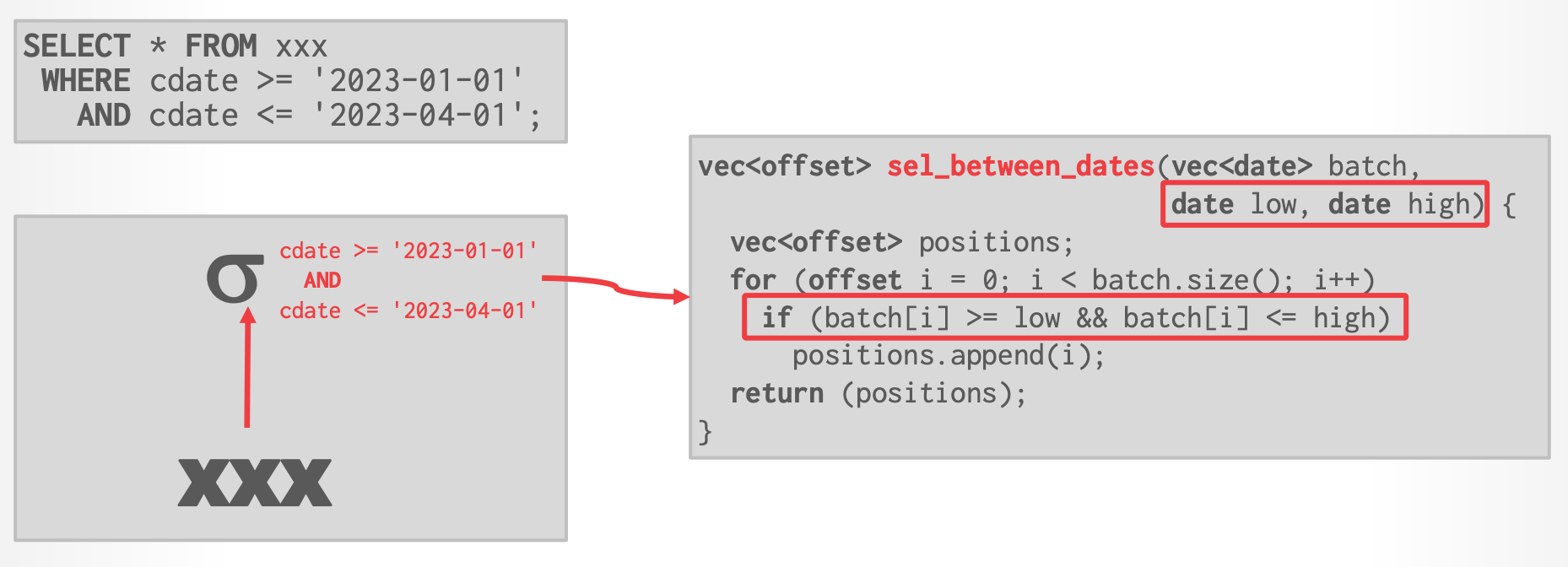
- 
## Memory Management
- 所有的内存分配都使用内存池,内存池由运行在 JVM 中的 DBR 管理。
- 只有一个内存池,容易跟踪运行时的内存使用情况
- 因为没有 data statistics, DBMS 的内存分配必须更加 dynamic:
- 当 operator 内存不足时不会置换到磁盘,而是向 manager 申请更多内存,由 manager 决定回收哪些 operators 的内存
- 简单的启发式:从分配最少但能满足请求的 operator 上回收内存
## Catalyst Query Optimizer
- 用 Scala 编写用于 Spark SQL 的 Cascades-style query optimizer
- 在 pre-defined stages 中执行 transformations,类似 Microsoft SQL Server
- 三种类型的 transformations:
- **Logical -> Logical** ( Analysis & Optimization Rules )
- **Logical -> Physical** ( Strategies)
- **Physical -> Pyhsical** (Preparation Rules)
- [Video: A Deep Dive into Spark SQL's Catalyst Optimizer (Cheng Lian + Maryann Xue, DataBricks)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xb2zm4-F1HI)
### Photon: Physical Plan Transformation
- 从下到上遍历 original query plan,将它转换成 Photon-specific physical plan。
- 新的目标:Limit the number of runtime switches between old engine and new engine.
- 避免 Java 与 C 之间的来回转换
- 
## Runtime Adaptivity
- **Query-Level Adaptivity(Macro)**
- 每个 shuffle stage 的结尾处,重新评估查询计划决策。
- 类似于 Dremel
- 由 DBR wrapper 提供该能力
- **Batch-Level Adaptivity(Micro)**
- Specialized code paths inside of an operator to handle the contents of a single tuple batch.
- 由 Photon 在查询执行期间完成
### Spark:Dynamic Query Optimization
- 在一个 stage 开始之前根据上一个 stage 的结果更改 query plan
- 避免了优化器根据不准确(或不存在)的数据统计进行决策的问题。
- Optimization Examples:
- 动态地在 shuffle 与 broadcast join 之间转变
- 动态地 coalesce partitions
- 动态地优化 skewed joins
### Spark:Partition Coalescing
- Spark 为每个 stage 过量分离了大量 sufflle partitions
- 分区足够大来分摊数据量
- 当 shuffle 完成后,DBMS 使用启发式算法来合并未充分利用的 partitions。
- 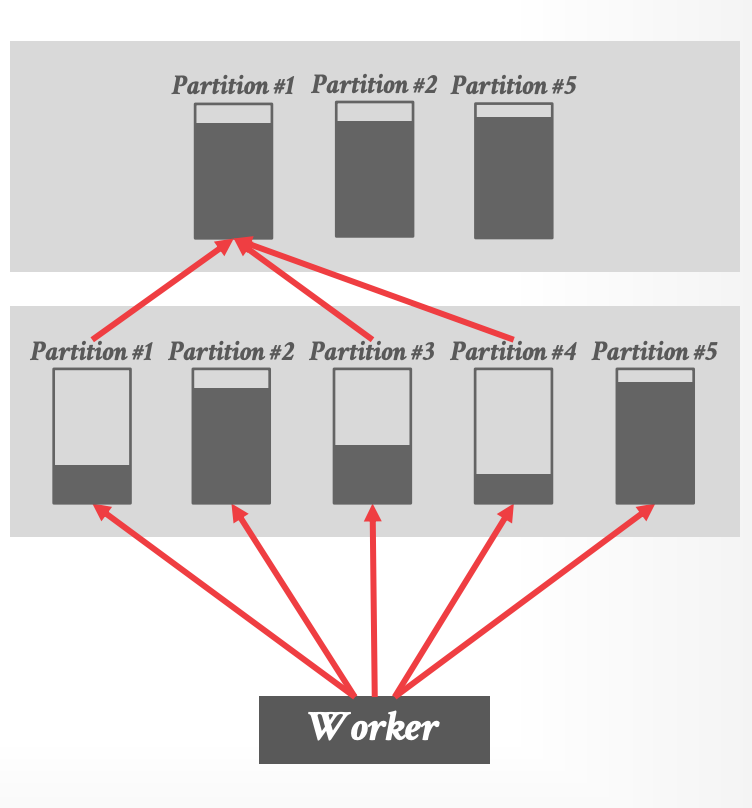
- 在缺乏统计信息的前提下,该手段是有必要的
### Photon: Batch-Level Adaptivity
- ASCII 与 UTF-8 data 分别使用不同的 primitives
- column vector 中的 values 都是 NOT NULL 的
- 省略检查 NULL 的分支
- No inactive rows in column batch(都是有效的)
- 消除 position lists 中的 indirect lookups
### Observation
- data lakes 缺少统计信息,使得查询优化变得很难
- Adaptivity 能有所改善,但是如果知道数据的相关信息会更好
- 思路:订阅 CDC 增量变更,DBMS 来计算统计信息
- Delta lake:后台将 log 转换成 Parquet files(带有计算好的统计信息)
- [Kudu](https://kudu.apache.org/kudu.pdf)
-------------
# Parting Thoughts
- Photon 有趣的部分:
- 使用 precompiled primitives
- 并且集成到了 JVM runtime 中